Abstract
Background
Insulin resistance is associated with the progression of atherosclerosis and is reported to predict cardiovascular mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Although statins exert pleiotropic effects, it is uncertain whether statin therapy improves insulin resistance in these patients. In this prospective randomized controlled trial, we aimed to evaluate the effects of statin on insulin resistance among 70 patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD).
Methods
Patients were randomized into a statin group (n = 35) or a control group (n = 35). The statin group received 10 mg per day of rosuvastatin for 6 months. We determined insulin resistance by homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index. Serum concentrations of adipokines such as adiponectin, leptin, and resistin were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) assay. As inflammatory markers, high sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and interleukin-6 were also measured.
Results
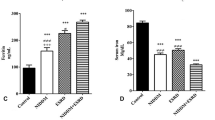
There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between the two groups. Compared to baseline value, statin treatment significantly decreased HOMA-IR index from 2.37 ± 1.08 to 2.05 ± 0.82 (P = 0.014). There was a concordant decrease in hsCRP levels in the statin group (2.05 ± 1.57 to 1.21 ± 0.84 mg/L, P < 0.001), but such improvements were not observed in the control group. When between-group differences in these parameters were compared, hsCRP levels were more decreased in the statin group than in the control group (P = 0.021 for between-group difference), whereas HOMA-IR index was not (P = 0.189 for between-group difference). During this period, statin treatment did not result in the improved adipokine profiles.
Conclusion
This study showed that statin therapy failed to improve insulin resistance in PD patients despite a significant decline in hsCRP levels after statin treatment. Our finding suggests that reducing inflammation by statin is of limited help to fully attenuate insulin resistance in these patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- ELSIA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostasis model assessment insulin resistance
- hsCRP:
-
High sensitive C-reactive protein
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- PD:
-
Peritoneal dialysis
- PTH:
-
Parathyroid hormone
- RAS:
-
Renin angiotensin system
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- RRF:
-
Residual renal function
References
Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988;37:1595–607.
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith Jr SC, Spertus JA, Costa F. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2005;112:2735–52.
Becker B, Kronenberg F, Kielstein JT, Haller H, Morath C, Ritz E, Fliser D. Renal insulin resistance syndrome, adiponectin and cardiovascular events in patients with kidney disease: the mild and moderate kidney disease study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1091–8.
Shinohara K, Shoji T, Emoto M, Tahara H, Koyama H, Ishimura E, Miki T, Tabata T, Nishizawa Y. Insulin resistance as an independent predictor of cardiovascular mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:1894–900.
DeFronzo RA. Pathogenesis of glucose intolerance in uremia. Metabolism. 1978;27:1866–80.
Guarnieri G, Zanetti M, Vinci P, Cattin MR, Barazzoni R. Insulin resistance in chronic uremia. J Ren Nutr. 2009;19:20–4.
Hung AM, Ikizler TA. Factors determining insulin resistance in chronic hemodialysis patients. Contrib Nephrol. 2011;171:127–34.
Manolescu B, Stoian I, Atanasiu V, Busu C, Lupescu O. Review article: the role of adipose tissue in uraemia-related insulin resistance. Nephrology (Carlton). 2008;13:622–8.
Fortes PC, de Moraes TP, Mendes JG, Stinghen AE, Ribeiro SC, Pecoits-Filho R. Insulin resistance and glucose homeostasis in peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2009;29:S145–8.
Zimmermann J, Herrlinger S, Pruy A, Metzger T, Wanner C. Inflammation enhances cardiovascular risk and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1999;55:648–58.
Yeun JY, Levine RA, Mantadilok V, Kaysen GA. C-Reactive protein predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35:469–76.
Jorsal A, Tarnow L, Frystyk J, Lajer M, Flyvbjerg A, Parving HH, Vionnet N, Rossing P. Serum adiponectin predicts all-cause mortality and end stage renal disease in patients with type I diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2008;74:649–54.
Rao M, Li L, Tighiouart H, Jaber BL, Pereira BJ, Balakrishnan VS. Plasma adiponectin levels and clinical outcomes among haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:2619–28.
Shaw SM, Fildes JE, Yonan N, Williams SG. Pleiotropic effects and cholesterol-lowering therapy. Cardiology. 2009;112:4–12.
Baker WL, Talati R, White CM, Coleman CI. Differing effect of statins on insulin sensitivity in non-diabetics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:98–107.
Teixeira AA, Buffani A, Tavares A, Ribeiro AB, Zanella MT, Kohlmann Jr O, Batista MC. Effects of fluvastatin on insulin resistance and cardiac morphology in hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens. 2011;25:492–9.
Sugiyama S, Fukushima H, Kugiyama K, Maruyoshi H, Kojima S, Funahashi T, Sakamoto T, Horibata Y, Watanabe K, Koga H, Sugamura K, Otsuka F, Shimomura I, Ogawa H. Pravastatin improved glucose metabolism associated with increasing plasma adiponectin in patients with impaired glucose tolerance and coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2007;194:e43–51.
von Eynatten M, Schneider JG, Hadziselimovic S, Hamann A, Bierhaus A, Nawroth PP, Dugi KA. Adipocytokines as a novel target for the anti-inflammatory effect of atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:754–5.
NKF-K/DOQI Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy Work Group. Clinical practice guidelines for peritoneal dialysis adequacy: update 2000. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001; 37:S65–S136.
Bodnar DM, Busch S, Fuchs J, Piedmonte M, Schreiber M. Estimating glucose absorption in peritoneal dialysis using peritoneal equilibration tests. Adv Perit Dial. 1993;9:114–8.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9.
Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:1253–62.
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante Jr AW. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:1796–808.
Guarnieri G, Faccini L, Lipartiti T, Ranieri F, Spangaro F, Giuntini D, Toigo G, Dardi F, Berquier-Vidali F, Raimondi A. Simple methods for nutritional assessment in hemodialyzed patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980;33:1598–607.
Kopple JD. McCollum award lecture, 1996: protein-energy malnutrition in maintenance dialysis patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65:1544–57.
Hung AM, Sundell MB, Egbert P, Siew ED, Shintani A, Ellis CD, Bian A, Ikizler TA. A comparison of novel and commonly-used indices of insulin sensitivity in African American chronic hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6:767–74.
Trirogoff ML, Shintani A, Himmelfarb J, Ikizler TA. Body mass index and fat mass are the primary correlates of insulin resistance in nondiabetic stage 3-4 chronic kidney disease patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:1642–8.
Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, Lee Y, Ahn JY, Kim SJ, Koh Y, Shin EK. Simvastatin improves flow-mediated dilation but reduces adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity in hypercholesterolemic patients. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:776–82.
Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, Lee Y, Kim SJ, Park JB, Shin EK. Differential metabolic effects of pravastatin and simvastatin in hypercholesterolemic patients. Atherosclerosis. 2009;204:483–90.
Anagnostis P, Selalmatzidou D, Polyzos SA, Panagiotou A, Slavakis A, Panagiotidou A, Athyros VG, Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP, Kita M. Comparative effects of rosuvastatin and atorvastatin on glucose metabolism and adipokine levels in non-diabetic patients with dyslipidaemia: a prospective randomised open-label study. Int J Clin Pract. 2011;65:679–83.
Chamberlain LH. Inhibition of isoprenoid biosynthesis causes insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 2001;507:357–61.
Yada T, Nakata M, Shiraishi T, Kakei M. Inhibition by simvastatin, but not pravastatin, of glucose-induced cytosolic Ca2+ signalling and insulin secretion due to blockade of L-type Ca2+ channels in rat islet beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;126:1205–13.
Takahashi Y, Satoh M, Tabuchi T, Nakamura M. Prospective, randomized, single-blind comparison of effects of 6 months’ treatment with atorvastatin versus pravastatin on leptin and angiogenic factors in patients with coronary artery disease. Heart Vessels. 2012;27:337–43.
Thongtang N, Ai M, Otokozawa S, Himbergen TV, Asztalos BF, Nakajima K, Stein E, Jones PH, Schaefer EJ. Effects of maximal atorvastatin and rosuvastatin treatment on markers of glucose homeostasis and inflammation. Am J Cardiol. 2011;107:387–92.
Gupta M, Szmitko PE, Tsigoulis M, Braga MF, Kajil M, Herjikaka S, Quan A, Teoh H, Verma S. Effects of ezetimibe add-on to statin therapy on adipokine production in patients with metabolic syndrome and stable vascular disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;56:241–5.
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1487–95.
Shoji T, Emoto M, Nishizawa Y. HOMA index to assess insulin resistance in renal failure patients. Nephron. 2001;89:348–9.
Yoo DE, Lee MJ, Oh HJ, Kim SJ, Shin DH, Yoo TH, et al. Low circulating adiponectin levels are associated with insulin resistance in non-obese peritoneal dialysis patients. Endocr J. 2012;8:685–95.
Ichihara A, Hayashi M, Ryuzaki M, Handa M, Furukawa T, Saruta T. Fluvastatin prevents development of arterial stiffness in haemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17:1513–7.
Vernaglione L, Cristofano C, Muscogiuri P, Chimienti S. Does atorvastatin influence serum C-reactive protein levels in patients on long-term hemodialysis? Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:471–8.
Brunetti ND, Maulucci G, Casavecchia GP, Distaso C, De Gennaro L, Pellegrino PL, Di Biase M. Improvement in endothelium dysfunction in diabetics treated with statins: a randomized comparison of atorvastatin 20 mg versus rosuvastatin 10 mg. J Interv Cardiol. 2007;20:481–7.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Yonsei University (Brain Korea 21) Project for Medical Sciences, a grant from the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation funded by the Korean government (MOST) (R13-2002-054-04001-0), and a grant of the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project of the Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A084001).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doh, F.M., Chang, TI., Koo, H.M. et al. The Effect of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor on Insulin Resistance in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 26, 501–509 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-012-6412-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-012-6412-2