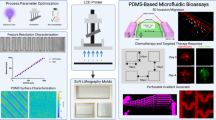
Abstract
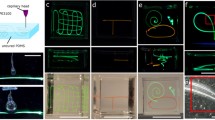
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is advantageous over conventional technologies for the fabrication of sophisticated structures such as 3D micro-channels for future applications in tissue engineering and drug screening. We aimed to apply this technology to cell-based assays using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), the most commonly used material for fabrication of micro-channels used for cell culture experiments. Useful properties of PDMS include biocompatibility, gas permeability and transparency. We developed a simple and robust protocol to generate PDMS-based devices using a soft lithography mold produced by 3D printing. 3D chemical gradients were then generated to stimulate cells confined to a micro-channel. We demonstrate that concentration gradients of growth factors, important regulators of cell/tissue functions in vivo, influence the survival and growth of human embryonic stem cells. Thus, this approach for generation of 3D concentration gradients could have strong implications for tissue engineering and drug screening.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Berthier, D.J. Beebe, Lab Chip 14, 3241 (2014)
P. Carmeliet, R.K. Jain, Nature 407, 6801 (2000)
J. Condeelis, R.H. Singer, J.E. Segall, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 695 (2005)
E. Cukierman, K.E. Sung, X. Su, E. Berthier, C. Pehlke, A. Friedl, D.J. Beebe, PLoS One 10, e76373 (2013)
J. El-Ali, P.K. Sorger, K.F. Jensen, Nature 442, 7101 (2006)
D.S. Eom, S. Amarnath, J.L. Fogel, S. Agarwala, Development 138, 15 (2011)
J.L. Erkal, A. Selimovic, B.C. Gross, S.Y. Lockwood, E.L. Walton, S. McNamara, R.S. Martin, D.M. Spence, Lab Chip 14, 12 (2014)
K.M. Fosen, S.R. Thom, Antioxid Redox Signaling 21, 1634 (2014)
U. Haessler, Y. Kalinin, M.A. Swartz, M. Wu, Biomed. Microdevices 11, 4 (2009)
D. Irimia, Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 12, 259 (2010)
K. Kamei, J. Lab. Autom. 18, 6 (2013)
K. Kamei, S. Guo, Z.T. Yu, H. Takahashi, E. Gschweng, C. Suh, X. Wang, J. Tang, J. McLaughlin, O.N. Witte, K.B. Lee, H.R. Tseng, Lab Chip 9, 4 (2009)
T.M. Keenan, A. Folch, Lab Chip 8, 1 (2008)
T. Kihara, J. Ito, J. Miyake, PLoS One 8, e82382 (2013)
B.J. Kim, M. Wu, Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40, 6 (2012)
D.B. Kolesky, R.L. Truby, A.S. Gladman, T.A. Busbee, K.A. Homan, J.A. Lewis, Adv. Mater. 26, 19 (2014)
Kshitiz, D.H. Kim, D.J. Beebe, A. Levchenko, Trends Biotechnol 29, 8 (2011)
W.E. Lowry, L. Richter, R. Yachechko, A.D. Pyle, J. Tchieu, R. Sridharan, A.T. Clark, K. Plath, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 8 (2008)
T. Ludwig, V. Bergendahl, M. Levenstein, J. Yu, M.D. Probasco, J. Thomson, Nat. Meth. 3, 8 (2006a)
T. Ludwig, M.E. Levenstein, J.M. Jones, W.T. Berggren, E.R. Mitchen, J.L. Frane, L.J. Crandall, C.A. Daigh, K.R. Conard, M.S. Piekarczyk, R.A. Llanas, J.A. Thomson, Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 2 (2006b)
A. Muller, B. Homey, H. Soto, N. Ge, D. Catron, M.E. Buchanan, T. McClanahan, E. Murphy, W. Yuan, S.N. Wagner, J.L. Barrera, A. Mohar, E. Verastegui, A. Zlotnik, Nature 410, 6824 (2001)
J.V. Nauman, P.G. Campbell, F. Lanni, J.L. Anderson, Biophys. J. 92, 4444 (2007)
A. Pluen, P.A. Netti, R.K. Jain, D.A. Berk, Biophys. J. 77, 542 (1999)
L. Przybyla, L. Voldman, Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 5, 293 (2012)
E.K. Sackmann, A.L. Fulton, D.J. Beebe, Nature 507, 181 (2014)
M.D. Symes, P.J. Kitson, J. Yan, C.J. Richmond, G.J. Cooper, R.W. Bowman, T. Vilbrandt, L. Cronin, Nat. Chem. 4, 5 (2012)
K. Takahashi, K. Tanabe, M. Ohnuki, M. Narita, T. Ichisaka, K. Tomoda, S. Yamanaka, Cell 131, 5 (2007)
J.A. Thomson, J. Itskovitz-Eldor, S.S. Shapiro, M.A. Waknitz, J.J. Swiergiel, V.S. Marshall, J.M. Jones, Science 282, 5391 (1998)
H. Yoshioka, M. Mikami, Y. Mori, E. Tsuchida, J. Macromol. Sci. Pure A31, 113 (1994a)
H. Yoshioka, M. Mikami, Y. Mori, E. Tsuchida, J. Macromol. Sci. Pure A31, 121 (1994b)
J. Yu, M.A. Vodyanik, K. Smuga-Otto, J. Antosiewicz-Bourget, J.L. Frane, S. Tian, J. Nie, G.A. Jonsdottir, V. Ruotti, R. Stewart, I.I. Slukvin, J.A. Thomson, Science 318, 5858 (2007)
Acknowledgments
Funding was generously provided by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS): Young Scientists (A) (to K.K.; 23681028) and Challenging Exploratory Research (to K.K.; 26560209); funding was also provided by Terumo Life Science Foundation. The WPI-iCeMS is supported by the World Premier International Research Centre Initiative (WPI), the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Competing financial interests
K. K. and Y. C. are listed as co-inventors on the Japanese provisional patent application based on this research. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 17564 kb)
(MOV 676 kb)
(MOV 614 kb)
(MOV 1563 kb)
(MOV 1304 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamei, Ki., Mashimo, Y., Koyama, Y. et al. 3D printing of soft lithography mold for rapid production of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic devices for cell stimulation with concentration gradients. Biomed Microdevices 17, 36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-9928-y
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-9928-y