Abstract
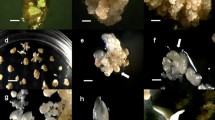
Direct somatic embryogenesis from ray floret explants of five chrysanthemum cultivars has been obtained within 12 – 15 d on Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and 6-benzyladenine (BA). Scanning electron microscopic observation also confirmed the direct origin of somatic embryos from explants. Somatic embryos developed asynchronously on the adaxial surface of explants. Among the five cultivars tested, Birbal Sahani was best responding (40 % explants responded on 4 mg dm−3 2,4-D and 2 mg dm−3 BA supplemented medium). Precocious germination of somatic embryos was noticed on the same medium. The best sucrose concentration in the medium was found to be 60 g dm−3 where 70 % explants responded while 55 % embryogenic response was obtained on medium supplemented with 400 mg dm−3 inositol. Plants developed from somatic embryos were transferred to soil and produced true-to-type flowers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
6-benzyladenine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NAA:
-
naphthaleneacetic acid
References
Chakrabarty, D., Mandal, A.K.A., Datta, S.K.: Management of chimera through direct shoot regeneration from florets of chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.).-J. hort. Sci. Biotechnol. 74: 293–296, 1999.
Chakrabarty, D., Mandal, A.K.A. Datta, S.K.: Retrival of new coloured chrysanthemum through organogenesis from sectorial chimera.-Curr. Sci. 78: 1060–1061, 2000.
Chen, T.H.H., Marowitch, J., Thompson, B.G.: Genotyping effects on somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from callus cultures of alfalfa.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 8: 73–81, 1987.
Datta, S.K., Chakrabarty, D., Mandal, A.K.A.: Gamma ray induced genetic manipulation in flower colour and shape in Dendranthema grandiflorum and their management through tissue culture.-Plant Breed. 120: 91–92, 2001.
Fambrini, M., Coinini, G., Pugliesi, C.: Development of somatic embryos from morphogenetic cells of the interspecific hybrid Helianthus annuus × Helianthus tuberosus.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 114: 205–214, 1996.
Finer, J.J.: Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature embryos of hybrid sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) on a high sucrose containing medium.-Plant Cell Rep. 6: 372–376, 1987.
Haccius, B.: Question of unicellular origin of non-zygotic embryos in callus cultures.-Phytomorphology 28: 74–81, 1978.
Lazzeri, P.A., Hildebrand, D.F., Collins, G.B.: Soybean somatic embryogenesis. Effects of nutritional, physical and chemical factors.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 10: 209–220, 1987.
Maheswaran, G., Williams, E.G.: Direct somatic embryoid formation on immature embryos of Trifolium repens, T. pratense and Medicago sativa and rapid clonal propagation of Trifolium repens.-Ann. Bot. 54: 201–211, 1984.
Maheswaran, G., Williams, E.G. Origin and development of somatic embryos formed directly on immature embryos of Trifolium repens in vitro.-Ann. Bot. 56: 619–630, 1985.
Mandal, A.K.A., Chakrabarty, D., Datta, S.K.: In vitro isolation of solid novel flower colour mutants from induced chimeric ray florets of chrysanthemum.-Euphytica 114: 9–12, 2000a.
Mandal, A.K.A., Chakrabarty, D., Datta, S.K.: Use of in vitro techniques in mutation breeding of chrysanthemum.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 60: 33–38, 2000b.
Mandal, A.K.A., Dutta Gupta, S., Chatterji, A.K.: Factors affecting somatic embryogenesis in safflower.-Biol. Plant. 44: 503–507, 2001.
Mandal, A.K.A., Dutta Gupta, S.: Somatic embryogenesis of safflower: influence of auxin and ontogeny of somatic embryos.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 72: 27–31, 2003.
May, R.A., Trigiano, R.N.: Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaves of Dendranthema grandiflora.-J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci. 116: 366–371, 1991.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F.: A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue culture.-Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–491, 1962.
Ozias-Akins, P., Anderson, W.F., Holbrook, C.C.: Somatic embryogenesis in Arachis hypogea L.: genotype comparison.-Plant Sci. 3: 103–111, 1992.
Sellars, R.M., Southard, G.M., Phillips, G.C.: Adventitious somatic embryogenesis from cultured immature zygotic embryos of peanut and soybean.-Crop Sci. 30: 408–414, 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, A.K.A., Datta, S.K. Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from ray florets of chrysanthemum. Biol Plant 49, 29–33 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-0033-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-0033-6