Abstract
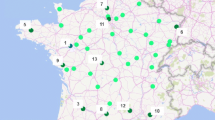
An Iranian National Quince collection containing 40 quince genotypes, originating from six distinct geographic areas, was screened using 15 SSR markers developed originally for apple and pear genomes. Overall, 13 markers exhibited polymorphism, with an average of 5.36 putative alleles per locus and a mean PIC value of 0.76. An UPGMA analysis divided the quince genotypes into five major clusters. The same results were obtained when the principal coordinates were plotted. The assignment test successfully allocated 83% of individuals into their place of origin. These results agree somewhat with the geographic origin of the quince accessions, and we conclude that geographic isolation leads to considerable genetic differentiation among Iranian quince collections. A significant ratio of transferability with a mean of 87.86% was measured, and we deduced that STMS markers derived from pear and apple have enough potential to detect polymorphism and differentiation in quince.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek HJ, Beharav A, Nevo E (2003) Ecological-genomic diversity of microsatellites in wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum, populations in Jordan. Theor Appl Genet 106:397–410
Bayazit S, Imrak B, Küden A, Kemal GM (2011) RAPD analysis of genetic relatedness among selected quince (Cydonia oblonga Mill.) accessions from different parts of Turkey. Hort Sci 38:134–141
Bell LR, Leitao MJ (2011) Cydonia. In: Chittaranjan K (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–16
Bhat ZA, Dhillon WS, Rashid R, Bhat JA, Dar WA, Ganaie MY (2010) The role of molecular markers in improvement of fruit crops. Nat Sci Biol 2:22–30
Burstin J, Deniot G, Potier J, Weinachter C, Aubert G, Baranger A (2001) Microsatellite polymorphism in Pisum sativum. Plant Breed 120:311–317
Davies N, Villablanco FX, Roderick GK (1999) Determining the source of individuals: multilocus genotyping in nonequilibrium population genetics. Tree 14:17–21
Decroocq V, Fave MG, Bordenave H, Decroocq S (2003) Development and transferability of apricot and grape EeST microsatellite markers across taxa. Theor Appl Genet 106:912–922
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA miniprepration: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Downey SL, Lezzoni AF (2000) Polymorphic DNA markers in black cherry (Prunus serotina) are identified using sequences from sweet cherry, peach, and sour cherry. J Am Soci Hort Sci 125:76–80
Dumanoglu H, Gunes TN, Aygun A, San B, Akpinar EA, Bakir M (2009) Analysis of clonal variations in cultivated quince (Cydonia oblonga ‘Kalecik’) based on fruit characteristics and SSR markers. N Z J Crop Hort Sci 37:113–120
FAO (2007) Agricultural Statistics, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http:\\www.faostat.fao.org. Accessed 23 Mar 2009
Ganopoulos I, Merkouropoulos G, Pantazis S, Tsipouridis C, Tsaftaris A (2011) Assessing molecular and morpho-agronomical diversity and identification of ISSR markers associated with fruit traits in quince (Cydonia oblonga). Genet Mol Res 10:2729–2746
Gianfranceschi L, Seglias N, Tarchini R, Komjanc M, Gessler C (1998) Simple sequence repeats for the genetic analysis of apple. Theor Appl Genet 96:1069–1076
Guilford P, Prakash S, Zhu JM, Rikkerink E, Gardiner S, Bassett H, Forster R (1997) Microsatellites in Malus domestica (apple) abundance, polymorphism and cultivar identification. Theor Appl Genet 94:249–254
Haghnazari A, Samimifard R, Najafi J, Mardi M (2005) Genetic diversity in pea (Pisum sativum L.) accessions detected by sequence tagged microsatellite markers. Genet Breed 59:145–152
Halász J, Hoffmann V, Szabó Z, Nyéki J, Szabó T, Hegedûs A (2009) Characterization of quince (Cydonia oblonga Mill.) cultivars using SSR markers developed for apple. Int J Hort Sci 15(4):7–10
Hamza S, Hamida WB, Rebai A, Harrabi M (2004) SSR-based genetic diversity assessment among Tunisian winter barley and relationship with morphological traits. Euphytica 135:107–118
Hokanson SC, Szewc-McFadden AK, Lamboy WP, Mcferson JR (1998) Microsatellite (SSR) markers reveal genetic identities, genetic diversity and relationship in a Malus×domestica Borkh. core subset collection. Theor Appl Genet 97:671–683
Hokanson SC, Lamboy WF, Szewc-McFadden AK, McFerson JR (2001) Microsatellite (SSR) variation in a collection of Malus (apple) species and hybrids. Euphytica 118:281–294
Kaneko Y, Nagaho I, Bang SW, Matsuzawa Y (2000) Classification of flowering quince cultivars (genus Chaenomeles) using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Breed Sci 50:139–142
Lewis PO, Zaykin D (1996) Statistical genetics program. In: Weir BS (ed) Genetic data analysis: methods for discrete population genetic data. Statistical genetics. North Carolina State University, II
Liebhard R, Ganfranceschi L, Koller B (2002) Development and characterization of 140 new microsatellites in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Mol Breed 10:217–241
Mnejja M, Garcia-Mas J, Audergon J-M, Arus P (2010) Prunus microsatellite marker transferability across rosaceous crops. Tree Genet Genomes 6:689–700
Nasiri J, Haghnazari A, Saba J (2009) Genetic diversity among varieties and wild species accessions of pea (Pisum sativum L.) based on SSR markers. Afr J Biotech 8:3405–3417
Paetkau D, Strobeck C (1995) The molecular basis and evolutionary history of a microsatellite null allele in bears. Mol Ecol 4:519–520
Paetkau D, Calvert W, Stirling I, Strobek C (1995) Variation in genetic diversity across the range of North American brown bears. Cons Biol 12:418–429
Paetkau D, Slade R, Burden M, Estoup A (2004) Genetic assignment methods for the direct, real-time estimation of migration rate: a simulation-based exploration of accuracy and power. Mol Ecol 13:55–65
Page RD (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pandian A, Ford R, Taylor PWJ (2000) Transferability of sequence tagged microsatellite site (STMS) primers across four major pulses. Plant Mol Biol Rep 18:1–8
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GenAlex 6: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Pejic IP, Ajmone-Marsan M, Morgante V, Kozumplick P, Castiglioni G, Taramino Motto M (1998) Comparative analysis of genetic similarity among maize inbred lines detected by RFLPs, RAPDs, SSRs and AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 97:1248–1255
Pemberton JM, Slate J, Bancroft DR, Barrett JA (1995) Nonamplifying alleles at microsatellite loci: a caution for parentage and population studies. Mol Ecol 4:249–252
Piry S, Alapettte A, Cornuet JM, Paetkau D, Baudouin L, Estoup A (2004) GeneClass2: a software for genetic assignment and first-generation migrant detection. J Hered 95:536–539
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Rafalski STA (1996) The utility of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238
Primmer CR, Koskinen MT, Piironen J (2000) The one that did not get away: individual assignment using microsatellite data detects a case of fishing competition fraud. Proc Biol Sci 267:1699–1701
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Ray Choudhury P, Tanveer H, Dixit GP (2006) Identification and detection of genetic relatedness among important varieties of pea (Pisum sativum L.) grown in India. Genetica 130:183–191
Röder MS, Plaschke J, Konig SU, Borner A, Sorrells ME (1995) Abundance, variability and chromosomal location of microsatellite in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 246:327–333
Rodriguez-Guisado I, Hernandez F, Melgarejo P, Legua P, Martínez R, Martínez JJ (2009) Chemical, morphological and organoleptical characterisation of five Spanish quince tree clones (Cydonia oblonga Miller). Sci Hort 122:491–496
Rohlf F (2006) NTsys-PC: numerical taxonomy system (ver. 2.2). Exeter Publishing, Setauket
Salamini F, Ozkan H, Brandolini A, Schafer-Pregl R, Martin W (2002) Genetics and geography of wild cereal domestication in the near east. Nat Rev Genet 3:42
Sanchez EE, Menendez RA, Daley LS, Boone RB, John OL, Lombard PB (1988) Characterization of quince (Cydonia) cultivars using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Environ Hort 6:53–59
Schuch MW, Cellini A, Masia A, Marino G (2010) Aluminium-induced effects on growth, morphogenesis and oxidative stress reactions in in vitro cultures of quince. Sci Hort 125:151–158
Stachel M, Lelly T, Grausgruber H, Vollmann J (2000) Application of microsatellites in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) for studying genetic differentiation caused by selection for adaptation and use. Theor Appl Genet 100:242–248
Wagner HW, Sefc KM (1999) Identity 1.0. Centre for Applied Genetics, University of Agricultural Science, Vienna, 1999
Webster AD (2008) Cydonia oblonga, quince. In: Janick J, Paull RE (eds) Encyclopedia of fruit and nuts. CABI, Wallingford, pp 634–642
Weising K, Fung RWM, Keeling DJ, Atkinson RG, Gardner RC (1996) Characterization of microsatellites from Actinidia chinensis. Mol Breed 2:117–131
Weising K, Nybom H, Wolff K, Kahl G (2005) DNA fingerprinting in plants principles, methods, and applications, 2nd edn. CRC, Taylor and Francis Group, New Delhi
Wright S (1978) Evolution and the genetics of populations. Chicago University Press, Chicago
Wünsch A, Hormaza JI (2007) Characterization of variability and genetic similarity of European pear using microsatellite loci developed in apple. Sci Hort 113:37–43
Yamomoto T, Kimura T, Sawamura Y, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T, Ban Y, Matsuta N (2001) SSRs isolated from apple can identify polymorphism and genetic diversity in pear. Theor Appl Genet 102:865–870
Yamomoto T, Kimura T, Sawamura Y, Manabe T, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T, Ban Y, Matsuta N (2002a) Simple sequence repeats for genetic analysis of pear. Euphytica 124:129–137
Yamomoto T, Kimura T, Shoda M, Ban Y, Hayashi T, Matsuta N (2002b) Development of microsatellite markers in Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia). Mol Ecol Notes 2:4–16
Yamomoto T, Kimura T, Shoda M, Imai T, Saito T, Sawamura Y, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T, Matsuta N (2002c) Genetic linkage maps constructed by using an interspecific cross between Japanese and European pears. Theor Appl Genet 106:9–18
Yamomoto T, Kimura T, Soejima J, Sanada T, Hayashi T, Ban Y (2004) Identification of quince varieties using SSR markers developed from pear and apple. Breed Sci 54:239–244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Khoramdel Azad and J. Nasiri contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoramdel Azad, M., Nasiri, J. & Abdollahi, H. Genetic Diversity of Selected Iranian Quinces Using SSRs from Apples and Pears. Biochem Genet 51, 426–442 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9575-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9575-z