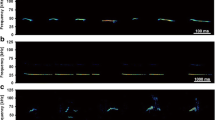
We studied the specific features of ultrasonic vocalization of Wistar rats in various motivational and emotional states. No significant changes were found in ultrasonic vocalization of rats during experimental food motivation and after the satisfaction of food requirements. The state of thirst and satisfaction of water requirements in animals were associated with an increase in the mean frequency of ultrasound and dominance of ultrasonic waves of a higher frequency. The formation of a negative emotional state in rats after immobilization with simultaneous electrocutaneous stimulation was accompanied by a decrease in the total duration of ultrasonic vocalization and shift in the power spectrum of ultrasound towards the dominant frequencies of 20-30, 40-50, and 80-90 kHz. During the post-stress period, the maximum power of ultrasonic waves approached the baseline (30-40 kHz). Our results indicate that the formation of various motivational and emotional states in rats is characterized by specific patterns of ultrasonic vocalization. Therefore, the parameters of ultrasonic vocalization can serve as an objective criteria for the subjective state of a living organism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. N. Karkishchenko, Yu. V. Fokin, D. S. Sakharov, et al., Biomeditsina, No. 1, 4–23 (2011).
S. S. Pertsov, E. V. Koplik, V. L. Stepanyuk, and A. S. Simbirtsev, Byull. Eksp. Biol., 148, No. 8, 161–165 (2009).
R. J. Blanchard, D. C. Blanchard, R. Agullana, and S. M. Weiss, Physiol Behav., 50, No. 5, 967–972 (1991).
I. Branchi, D. Santucci, and E. Alleva, Behav. Brain Res., 125, Nos. 1–2, 49–56 (2001).
H. K. Dinh, A. Larkin, L. Gatlin, and E. Jr. Piepmeier, J. Pharm. Sci. Technol., 53, No. 1, 40–43 (1999).
D. Jourdan, D. Ardid, E. Chapuy, et al., Pain, 63, No. 2, 237–249 (1995).
D. Jourdan, D. Ardid, and A. Eschalier, Ibid., 95, Nos. 1–2, 165–173 (2002).
M. T. Kaltwasser, Physiol Behav., 48, No. 1, 13–17 (1990).
E. J. Kim, E. S. Kim, E. Covey, and J. J. Kim, PLoS One, 5, No 12, e15077 (2010).
G. W. Pierce and D. R. Griffin, J. Mamm., 19, 454–455 (1938).
C. V. Portfors, J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci., 46, No. 1, 28–34 (2007).
C. Sanchez, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 463, Nos. 1–3, 133–143 (2003).
H. Sugimoto, S. Okabe, M. Kato, et al., PLoS One, 6, No. 7, e22093 (2011).
V. C. Wallace, T. A. Norbury, and A. S. Rice, Eur. J. Pain., 9, No. 4, 445–452 (2005).
M. Wohr, F. I. Roullet, A. Y. Hung, et al., PLoS One, 6, No. 6, e20631 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 153, No. 6, pp. 772–776, June, 2012
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pertsov, S.S., Koplik, E.V., Karkishchenko, N.N. et al. Ultrasonic Vocalization of Rats in Various Motivational and Emotional States. Bull Exp Biol Med 153, 805–808 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1831-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1831-4