Abstract
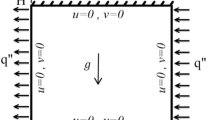
The lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) is used to examine free convection of nanofluids. The space between the cold outer square and heated inner circular cylinders is filled with water including various kinds of nanoparticles: TiO2, Ag, Cu, and Al2O3. The Brinkman and Maxwell-Garnetts models are used to simulate the viscosity and the effective thermal conductivity of nanofluids, respectively. Results from the performed numerical analysis show good agreement with those obtained from other numerical methods. A variety of the Rayleigh number, the nanoparticle volume fraction, and the aspect ratio are examined. According to the results, choosing copper as the nanoparticle leads to obtaining the highest enhancement for this problem. The results also indicate that the maximum value of enhancement occurs at λ = 2.5 when Ra = 106 while at λ = 1.5 for other Rayleigh numbers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c p :
-
specific heat
- c i :
-
discrete particle speeds
- f :
-
density distribution function
- f eq :
-
density equilibrium distribution function
- g :
-
distribution functions for energy
- g eq :
-
equilibrium distribution functions for energy
- g neq :
-
non-equilibrium distribution functions for energy
- g y :
-
gravitational acceleration (m·s−2)
- k :
-
conductivity
- \(\overline {Nu}\) :
-
average Nusselt number
- Nu :
-
local Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number (= ν/α)
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number (= gβΔTH 3/(αν))
- r :
-
radius of circle
- T :
-
temperature
- (u, v):
-
velocity in x- and y-directions
- α :
-
thermal diffusivity (m2·s−1)
- Θ :
-
dimensionless temperature
- ϕ :
-
volume fraction
- µ:
-
dynamic viscosity (Pa·s−1)
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity (m2·s−1)
- λ :
-
aspectratio(=L/(2r))
- ρ :
-
density(kg·m−3)
- τ c :
-
temperature relaxation time
- τ v :
-
flow relaxation time
- β :
-
coefficient of thermal expansion (K−1)
- δ T :
-
thermal boundary layer thickness
- c:
-
cold
- h:
-
hot
- nf:
-
nanofluid
- f:
-
base fluid
- s:
-
solid particles
References
Kuehn, T. H. and Goldstein, R. J. An experimental and theoretical study of natural convection in the annulus between horizontal concentric cylinders. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 74, 695–719 (1976)
Mohammed, H. A., Campo, A., and Saidur, R. Experimental study of forced and free convective heat transfer in the thermal entry region of horizontal concentric annuli. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 37, 739–747 (2010)
Ekundayo, C. O., Probert, S. D., and Newborough, M. Heat transfer from a horizontal cylinder in a rectangular enclosure. Applied Energy, 61, 57–78 (1998)
Onyegegbu, S. O. Heat transfer inside a horizontal cylindrical annulus in the presence of thermal radiation and buoyancy. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 29, 659–671 (1986)
Moukalled, F. and Acharya, S. Natural convection in the annulus between concentric horizontal circular and square cylinders. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 10(3), 524–531 (1996)
Soleimani, S., Sheikholeslami, M., Ganji, D. D., and Gorji-Bandpay, M. Natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid filled semi-annulus enclosure. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 39, 565–574 (2012)
Khanafer, K., Vafai, K., and Lightstone, M. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 46, 3639–3653 (2003)
Sheikholeslami, M., Ganji, D. D., Ashorynejad, H. R., and Rokni, H. B. Analytical investigation of Jeffery-Hamel flow with high magnetic field and nanoparticle by Adomian decomposition method. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 33(1), 25–36 (2012) DOI 10.1007/s10483-012-1531-7
Sheikholeslami, M. and Ganji, D. D. Heat transfer of Cu-water nanofluid flow between parallel plates. Powder Technology, 235, 873–879 (2013)
Sheikholeslami, M., Gorji-Bandpy, M., Ganji, D. D., and Soleimani, S. MHD natural convection in a nanofluid filled inclined enclosure with sinusoidal wall using CVFEM. Neural Computing and Applications (2012) DOI 10.1007/s00521-012-1316-4
Ashorynejad, H. R., Sheikholeslami, M., Pop, I., and Ganji, D. D. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer due to a stretching cylinder in the presence of magnetic field. Heat and Mass Transfer, 49, 427–436 (2013)
Abu-Nada, E., Masoud, Z., and Hijazi, A. Natural convection heat transfer enhancement in horizontal concentric annuli using nanofluids. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 35, 657–665 (2008)
Alinia, M., Ganji, D. D., and Gorji-Bandpy, M. Numerical study of mixed convection in an inclined two sided lid driven cavity filled with nanofluid using two-phase mixture model. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 38, 1428–1435 (2011)
Sheikholeslami, M., Soleimani, S., Gorji-Bandpy, M., Ganji, D. D., and Seyyedi, S. M. Natural convection of nanofluids in an enclosure between a circular and a sinusoidal cylinder in the presence of magnetic field. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 39, 1435–1443 (2012)
Sheikholeslami, M., Ashorynejad, H. R., Domairry, G., and Hashim, I. Flow and heat transfer of Cu-water nanofluid between a stretching sheet and a porous surface in a rotating system. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Applied Mathematics, 421320 (2012) DOI 10.1155/2012/421320
Yu, D., Mei, R., Luo, L. S., and Shyy, W. Viscous flow computations with the method of lattice Boltzmann equation. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 39, 329–367 (2003)
Succi, S. The Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond, Clarendon Press, Oxford (2001)
Kao, P. H. and Yang, R. J. Simulating oscillatory flows in Rayleigh-Benard convection using the lattice Boltzmann method. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 50, 3315–3328 (2007)
Dixit, H. N. and Babu, V. Simulations of high Rayleigh number natural convection in a square cavity using the lattice Boltzmann method. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 49, 727–739 (2006)
Kefayati, G. H. R., Hosseinizadeh, S. F., Gorji, M., and Sajjadi, H. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in tall enclosures using water-SiO2 nanofluid. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 38(6), 798–805 (2011)
Bararnia, H., Hooman, K., and Ganji, D. D. Natural convection in a nanofluid filled portioned cavity: the lattice-Boltzmann method. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A, 59, 487–502 (2011)
Kefayati, G. H. R., Hosseinizadeh, S. F., Gorji, M., and Sajjadi, H. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of natural convection in an open enclosure subjugated to water/copper nanofluid. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 52, 91–101 (2012)
Ashorynejad, H. R., Mohamad, A. A., and Sheikholeslami, M. Magnetic field effects on natural convection flow of a nanofluid in a horizontal cylindrical annulus using lattice Boltzmann method. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 64, 240–250 (2013)
Sheikholeslami, M., Gorji-Bandpay, M., and Ganji, D. D. Magnetic field effects on natural convection around a horizontal circular cylinder inside a square enclosure filled with nanofluid. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 39, 978–986 (2012)
Seyyedi, S. M., Bararnia, H., Ganji, D. D., Gorji-Bandpy, M., and Soleimani, S. Numerical investigation of the effect of a splitter plate on forced convection in a two dimensional channel with an inclined square cylinder. International Journal of Thermal Scieces, 61, 1–14 (2012)
Bararnia, H., Seyyedi, S. M., Ganji, D. D., and Khorshidi, B. Numerical investigation of the coalescence and breakup of falling multi-droplets. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 424, 40–51 (2013)
Yan, Y. Y. and Zu, Y. Q. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and fluid flow past a rotating isothermal cylinder-an LBM approach. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 51, 2519–2536 (2008)
Xuan, Y. and Roetzel, W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 43(19), 3701–3707 (2000)
Wang, X. Q. and Mujumdar, A. S. Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: a review. International Journal of Thermal Science, 46(1), 1–19 (2007)
Moukalled, F. and Acharya, S. Natural convection in the annulus between concentric horizontal circular and square cylinders. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 10(3), 524–531 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikholeslami, M., Gorji-Bandpy, M. & Domairry, G. Free convection of nanofluid filled enclosure using lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 34, 833–846 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-013-1711-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-013-1711-9