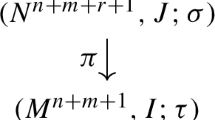Abstract
A basic and substantial theorem of one-dimensional systems theory, due to R. Kalman, says that an arbitrary input/output behavior with proper transfer matrix admits an observable state representation which, in particular, is a realization of the transfer matrix. The state equations have the characteristic property that any local, better temporal, state at time zero and any input give rise to a unique global state or trajectory of the system or, in other terms, that the global state is the unique solution of a suitable Cauchy problem. With an adaption of this state property to the multidimensional situation or rather its algebraic counter-part we prove that any behavior governed by a linear system of partial differential or difference equations with constant coefficients is isomorphic to a canonical state behavior which is constructed by means of Gröbner bases. In contrast to the one-dimensional situation, to J.C. Willems’ multidimensional state space models and and to J.F. Pommaret’s modified Spencer form the canonical state behavior is not necessarily a first order system. Further first order models are due E. Zerz. As a by-product of the state space construction we derive a new variant of the algorithms for the computation of the Hilbert function of finitely generated polynomial modules or behaviors. J.F. Pommaret, J. Wood and P. Rocha discussed the Hilbert polynomial in the systems theoretic context. The theorems of this paper are constructive and have been implemented in MAPLE in the two-dimensional case and demonstrated in a simple, but instructive example. A two-page example also gives the complete proof of Kalman’s one-dimensional theorem mentioned above. We believe that for this standard case the algorithms of the present paper compare well with their various competitors from the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apel, J.: The theory of involutive divisions and an application to Hilbert function computations. J. Symbolic Comput. 25, 683–704 (1998)
Apel, J.: On a conjecture of R.P. Stanley II: quotients modulo monomoial ideals. J. Algebraic Combin. 17, 57–74 (2003)
Blondel, V.D., Megretski, A. (eds.): Unsolved Problems in Mathematical Systems and Control Theory. Princeton University Press, New Jersey (2004)
Egorov, Y.V., Shubin, M.A. (eds.): Partial Differential Equations I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1992)
Egorov, Y.V., Shubin, M.A. (eds.): Partial Differential Equations III. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1991)
Fröhler, S., Oberst, U.: Continuous time-varying linear systems. Systems Control Lett. 35, 97–110 (1998)
Ganzha, V.G., Mayr, E.W., Vorozhtsov, E.V. (eds.): Computer Algebra in Scientific Computing. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1999)
Gelfand, I.M., Shilov, G.E.: Generalized Functions III Theory of Differential Equations Academic Press, New York (1967)
Gerdt, V.P.: Completion of linear differential systems to involution. In: Ganzha, V.G., Mayr, E.W., Vorozhtsov, E.V. (eds.) Computer Algebra in Scientific Computing, pp. 115–137. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1999)
Gluesing-Luerssen, H.: Linear Delay-Differential Systems with Commensurate Delays: An Algebraic Approach. Lecture Notes in Mathematics 1770, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (2002)
Hörmander, L.: The Analysis of Linear Partial Differential Operators I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1983)
Hörmander, L.: The Analysis of Linear Partial Differential Operators II. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1983)
Janet, M.: Sur les systèmes d’équations aux dérivées partielles. J. Math. Pures Appl. 8, 65–151 (1920)
Kailath, T.: Linear Systems. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey (1980)
Kalman, R.E.: Mathematical description of linear dynamical systems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 1, 152–192 (1963)
Kreuzer, M., Robbiano, L.: Computational Commutative Algebra 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (2000)
Lu, P., Liu, M., Oberst, U.: Linear recurring arrays, linear systems and multidimensional cyclic codes over Quasi–Frobenius rings. Acta Appl. Math. 80, 175–198 (2004)
Macaulay, F.S.: The Algebraic Theory of Modular Systems. Cambridge University Press, UK (1916)
Malgrange, B.: Systèmes Différentiels Involutifs. Prépublication 636, Institut Fourier Grenoble, France (2004)
Oberst, U.: Multidimensional constant linear systems. Acta Appl. Math. 20, 1–175 (1990)
Oberst, U.: Variations on the fundamental principle for linear systems of partial differential and difference equations with constant coefficients. AAECC 6, 211–243 (1995)
Oberst, U.: Canonical State Representations and Hilbert Functions of Multidimensional Systems (with historical comments and a discussion of Professor Pommaret’s remarks). Talk at the conference D3, Linz, Austria (May 2006)(homepage of the Gröbner-Semester)
Oberst, U., Pauer, F.: The constructive solution of linear systems of partial difference and differential equations with constant coefficients. Multidimens. Systems Signal Process. 12, 253–308 (2001)
Palamodov, V.P.: Linear Differential Operators. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1970)
Polderman, J.W., Willems, J.C.: Introduction to Mathematical Systems Theory. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1998)
Pommaret, J.-F.: Systems of Partial Differential Equations and Lie Pseudogroups. Gordon and Breach, New York (1978)
Pommaret, J.-F.: New perspectives in control theory for partial differential equations. IMA J. Math. Control Inform. 9, 305–330 (1992)
Pommaret, J.-F.: Partial Differential Control Theory, Volume I: Mathematical Tools, Volume II: Control Systems Kluwer, Dordrecht (2001)
Pommaret, J.-F.: Localization and transfer matrix computation for linear multidimensional control systems. Proceedings MTNSLeuven, Belgium (2004)
Pommaret, J.-F.: Lecture Notes of the mini-course on algebraic analysis of control systems defined by partial differential equations, pp. 1–45. Gröbner Semester Linz, Sections D2 and D3, RISC, Hagenberg, and RICAM, Linz, Austria (May 2006)
Rapisarda, P., Willems, J.C.: State maps for linear systems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 35, 1053–1091 (1997)
Riquier, C.: Les Systèmes d’Équations aux Dérivées Partielles. Gauthiers-Villars, Paris, France (1910)
Rocha, P., Willems, J.C.: Markov properties for systems described by PDEs and first-order representations. Systems Control Lett. 55, 538–542 (2006)
Stanley, R.P.: Combinatorics and Commutative Algebra, 2nd edn., Birkhäuser, Boston (1996)
Sturmfels, B.: Solving Systems of Polynomial Equations. American Mathematical Society, Providence, Rhode Island (2002)
Treves, F.: Basic Linear Partial Differential Equations. Academic Press, New York (1975)
Vardulakis, A.I.G.: Linear Multivariable Control. Wiley, Chichester, West Sussex, England (1991)
Vasconcelos, W.V.: Computational Methods in Commutative Algebra and Algebraic Geometry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1998)
Willems, J.C.: Paradigms and puzzles in the theory of dynamical systems. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 36, 259–294 (1991)
Willems, J.C.: State and first order representations. In: Blondel, V.D. and Megretski, A. (eds.) Unsolved Problems in Mathematical Systems and Control Theory, pp. 54–57. Princeton University Press, New Jersey (2004)
Wolovich, W.A.: Linear Multivariable Systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1974)
Wood, J., Rocha, P., Rogers, E., Owens, D.H.: Structure indices for multidimensional systems. IMA J. Math. Control Inform. 17, 227–256 (2000)
Zerz, E.: Topics in Multidimensional Linear Systems Theory. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences 256, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oberst, U. Canonical State Representations and Hilbert Functions of Multidimensional Systems. Acta Appl Math 94, 83–135 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-006-9068-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-006-9068-8
Key words
- state
- Hilbert function
- behavior
- multidimensional system
- partial differential equation
- partial difference equation
- polynomial module