Abstract
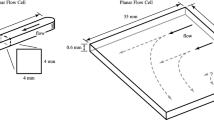
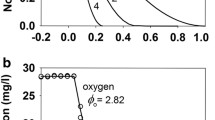
We develop a mathematical model of nanoparticles depositing onto and penetrating into a biofilm grown in a parallel-plate flow cell. We carry out deposition experiments in a flow cell to support the modeling. The modeling and the experiments are motivated by the potential use of polymer nanoparticles as part of a treatment strategy for killing biofilms infecting the deep passages in the lungs. In the experiments and model, a fluid carrying polymer nanoparticles is injected into a parallel-plate flow cell in which a biofilm has grown over the bottom plate. The model consists of a system of transport equations describing the deposition and diffusion of nanoparticles. Standard asymptotic techniques that exploit the aspect ratio of the flow cell are applied to reduce the model to two coupled partial differential equations. We perform numerical simulations using the reduced model. We compare the experimental observations with the simulation results to estimate the nanoparticle sticking coefficient and the diffusion coefficient of the nanoparticles in the biofilm. The distributions of nanoparticles through the thickness of the biofilm are consistent with diffusive transport, and uniform distributions through the thickness are achieved in about four hours. Nanoparticle deposition does not appear to be strongly influenced by the flow rate in the cell for the low flow rates considered.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramoff, M. D., P. J. Magelhaes, and S. J. Ram. Image processing with imagej. J. Biophotonics 11:36–42, 2004.
Asgharian, B., W. Hofmann, and R. Bergmann. Particle deposition in a multiple-path model of the human lung. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 34(4):332–339, 2001.
Bolte, S., and F. P. Cordeliéres. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 224:213–232, 2006.
Bouwer, E. J. Theoretical investigation of particle deposition in biofilm systems. Water Res. 21(12):1489–1498, 1987.
Cogan, N. G., and J. P. Keener. The role of the biofilm matrix in structural development. Math. Med. Biol. A J. IMA 21(2):147–166, 2004.
Costerton, J., S. Stewart, and E. Greenberg. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284(5418):1318–1322, 1999.
Dailey, L. A., E. Kleemann, M. Wittmar, T. Gessler, T. Schmehl, C. Roberts, W. Seeger, and T. Kissel. Surfactant-free, biodegradable nanoparticles for aerosol therapy based on the branched polyesters, DEAPA-PVAL-g-PLGA. Pharm. Res. 20:2011–2020, 2003.
Dailey, L. A., T. Schmehl, T. Gessler, M. Wittmar, F. Grimminger, W. Seeger, and T. Kissel. Nebulization of biodegradable nanoparticles: impact of nebulizer technology and nanoparticle characteristics on aerosol features. J. Controlled Release 86:131–144, 2003.
Desai, T. R., R. E. W. Hancock, and W. H. Finlay. A facile method of delivery of liposomes by nebulization. J. Controlled Release 84:69–78, 2002.
Ditto, A. DNA-LPEI complexes encapsulation in LTP nanospheres as a non-viral gene therapy vector. Technical report, Akron: Biomedical Engineering, The University of Akron, 2006.
Ditto, A. J., P. N. Shah, S. T. Lopina, and Y. H. Yun. Nanospheres formulated from l-tyrosine polyphosphate as a potential intracellular delivery device. Int. J. Pharm. 368(1–2):199–206, 2009.
Drury, W., P. Stewart, and W. Characklis. Transport of 1 micrometer latex particles in pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 42(1):111–117, 1993.
Drury, W. J., W. G. Characklis, and P. S. Stewart. Interactions of 1 μm latex particles with pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Water Res. 27(7):1119–1126, 1993.
Emami, J., H. Hamishehkar, A. R. Najafabadi, K. Gilani, M. Minaiyan, H. Mahdavi, H. Mirzadeh, A. Fakhari, and A. Nokhodchi. Particle size design of plga microspheres for potential pulmonary drug delivery using response surface methodology. J. Microencapsul. 26(1):1–8, 2009.
Ensign, L. M., R. Cone, and J. Hanes. Oral drug delivery with polymeric nanoparticles: the gastrointestinal mucus barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64(6):557–570, 2012.
Frijlink, H. W., and A. H. De Boer. Dry powder inhalers for pulmonary drug delivery. Expert Opinion On Drug Deliv. 1(1):67–86, 2004.
Gibson, R., J. Burns, and B. Ramsey. Pathophysiology and management of respiratory infections in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 168(8):918–951, 2003.
Griesenbach, U., S. Ferrari, D. M. Geddes, and E. W. Alton. Gene therapy progress and prospects: cystic fibrosis. Gene Ther. 9:1344–1350, 2002.
Gupta, A. S., and S. T. Lopina. L-tyrosine-based backbone-modified poly(amino acids). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 13(10):1093–1104, 2002.
Hall-Stoodley, L., J. W. Costerton, and P. Stoodley. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2(2):95–108, 2004.
Heyder, J. Deposition of inhaled particles in the human respiratory tract and consequences for regional targeting in respiratory drug delivery. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 1(4):315–320, 2004.
Heydorn, A., B. K. Ersbøll, M. Hentzer, M.R. Parsek, M. Givskov, and S. Molin. Experimental reproducibility in flow-chamber biofilms. Microbiology 146:2409–2416, 2000.
Heydorn, A., A. T. Nielsen, M. Hentzer, C. Sternberg, M. Givskov, B. K. Ersbøll, and S. Molin. Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program comstat. Microbiology 146:2395–2407, 2000.
Hindi, K. M., A. J. Ditto, M. J. Panzner, D. A. Medvetz, C. E. Hovis, D. S. Han, J. K. Hilliard, J. B. Taylor, Y. H. Yun, C. L. Cannon, and W. J. Youngs. The antimicrobial efficacy of sustained release silver carbene complex-loaded l-tyrosine polyphosphate nanoparticles: characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomaterials 30:3771–3779, 2009.
Jackson, K., R. Keyser, and D. Wozniak. The role of biofilms in airway disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 24(6):663–670, 2003.
Katz, S., I. Adatia, E. Louca, K. Leung, T. Humpl, J. T. Reyes, and A. L. Coates. Nebulized therapies for childhood pulmonary hypertension: an in vitro model. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 41:666–673, 2006.
Kleemann, E., Dailey, H. G. Abdelhady, T. Gessler, T. Schmehl, C. J. Roberts, M. C. Davies, W. Seeger, and T. Kissel. Modified polyethyleneimines as non-viral gene delivery systems for aerosol gene therapy: investigations of the complex structure and stability during air-jet and ultrasonic nebulization. J. Controlled Release 100:437–450, 2004
Koping-Hoggard, M., M. M. Issa, T. Kohler, K. M. Varum, and P. Artursson. A miniaturized nebulization catheter for improved gene delivery to the mouse lung. J. Gene Med. 7(9):1215–1222, 2005.
Lambiase, A., V. Raia, M. Pezzo, A. Sepe, V. Carnovale, and F. Rossano. Microbiology of airway disease in a cohort of patients with cystic fibrosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 6(1):4, 2006.
Leid, J. G., A. J. Ditto, A. Knapp, P. N. Shah, B. D. Wright, R. Blust, L. Christensen, C. B. Clemons, J. P. Wilber, G. W. Young, A. G. Kang, M. J. Panzner, C. L. Cannon, Y. H. Yun, W. J. Youngs, N. M. Seckinger, and E. K. Cope. In vitro antimicrobial studies of silver carbene complexes: activity of free and nanoparticle carbene formulations against clinical isolates of pathogenic bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 67(1):138–148, 2012.
Li, Z., C. Kleinstreuer, and Z. Zhang. Particle deposition in the human tracheobronchial airways due to transient inspiratory flow patterns. J. Aerosol Sci. 38(6):625–644, 2007.
Longest, P., and M. Oldham. Numerical and experimental deposition of fine respiratory aerosols: development of a two-phase drift flux model with near-wall velocity corrections. J. Aerosol Sci. 39(1):48–70, 2008.
P. W. Longest, S. Vinchurkar, and T. Martonen. Transport and deposition of respiratory aerosols in models of childhood asthma. J. Aerosol Sci. 37(10):1234–1257, 2006.
Nassar, D., A. E. Stine, C. B. Clemons, K. M. Miller, J. P. Wilber, G. W. Young, M. C. Deblock, M. J. Panzner, W. J. Youngs, A. J. Ditto, Y. H. Yun, A. Milsted, J. G. Leid, and C. L. Cannon. Delivery of silver-based antimicrobials to the lung via nebulized nanoparticles. 2012, in preparation.
Neubig, R. Penetration of nanoparticles into a biofilm from a bulk fluid. Masters Thesis. The University of Akron, 2011.
Palmer, K. L., L. M. Aye, and M. Whiteley. Nutritional cues control pseudomonas aeruginosa multicellular behavior in cystic fibrosis sputum. J. Bacteriol. 189:8079–8087, 2007.
Pandey, R., A. Sharma, A. Zahoor, S. Sharma, G. K. Khuller, and B. Prasad. Poly (dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticle based inhalable sustained drug delivery system for experimental tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52:981–986, 2003.
Panzner M.J., A. Deeraksa, A. Smith, B. D. Wright, K. M. Hindi, A. Kascatan-Nebioglu, A. G. Torres, B. M. Judy, C. E. Hovis, J. K. Hilliard, R. J. Mallett, E. Cope, D. M. Estes, C. L. Cannon, J. G. Leid, and W. J. Youngs. Synthesis and in vitro efficacy studies of silver carbene complexes on biosafety level 3 bacteria. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 13:1739–1745, 2009.
Ramsey, B. Management of pulmonary disease in patients with cystic fibrosis (vol 335, pg 179, 1996). N. Engl. J. Med. 335(15):1167–1167, 1996.
Rudolph C., R. H. Muller, and J. Rosenecker. Jet nebulization of PEI/DNA polyplexes: physical stability and in vitro gene delivery efficiency. J. Gene Med. 4:66–74, 2002.
Rybak, M. J. Pharmacodynamics: relation to antimicrobial resistance. Am. J. Infect. Control 34(5):S38–S45, 2006.
Searcy, K. E., A. I. Packman, E. R. Atwill, and T. Harter. Capture and retention of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72(9):6242–6247, 2006.
Sen Gupta, A. S., and S. T. Lopina. Properties of l-tyrosine based polyphosphates pertinent to potential biomaterial applications. Polymer 46:2133–2140, 2005.
Soppimath, K. S., T. M. Aminabhavi, A. R. Kulkarni, and W. E. Rudzinski. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Controlled Release 70:1–20, 2001.
Stewart, P., and J. Costerton. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 358:135–138, 2001.
Stine, A. E., D. Nassar, C. B. Clemons, K. M. Miller, J. P. Wilber, G. W. Young, W. J. Youngs, Y. H. Yun, A. Milsted, J. G. Leid, and C. L. Cannon. Modeling the response of a biofilm to silver-based antimicrobial. 2012, in preparation.
Sufya, N., D. Allsion, and P. Gilbert. Clonal variation in maximum specific growth rate and susceptibility towards antimicrobials. J. Appl. Microbiol. 95:1261–1267, 2003.
Suh, J., K. Choy, S. Lai, J. Suk, B. Tang, S. Prabhu, J. Hanes. Pegylation of nanoparticles improves their cytoplasmic transport. Int. J. Nanomed. 2(4):735–741, 2007.
Suk, J., S. Lai, Y. Wang, L. Ensign, P. Zeitlin, M. Boyle, and J. Hanes. The penetration of fresh undiluted sputum expectorated by cystic fibrosis patients by non-adhesive polymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 30(13):2591–2597, 2009.
Szomolay, B., I. Klapper, J. Dockery, and P. Stewart. Adaptive responses to antimicrobial agents in biofilms. Environ. Microbiol. 7(8):1186–1191, 2005.
Tang, B., M. Dawson, S. Lai, Y. Wang, J. Suk, M. Yang, P. Zeitlin, M. Boyle, J. Fu, and J. Hanes. Biodegradable polymer nanoparticles that rapidly penetrate the human mucus barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106(46):19268–19273, 2009.
Tolker-Nielsen, T., and C. Sternberg. Growing and analyzing biofilms in flow chambers. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. Chapter 1:Unit 1B.2, 2011.
Vadolas, J., R. Williamson, and P. A. Ioannou. Gene therapy for inherited lung disorders: an insight into pulmonary defense. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 15:61–72, 2002.
Wang, Y., S. Lai, J. Suk, A. Pace, R. Cone, and J. Hanes. Addressing the peg mucoadhesivity paradox to engineer nanoparticles that “slip” through the human mucus barrier. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47(50):9726–9729, 2008.
Wloka, M., H. Rehage, H.-C. Flemming, and J. Wingender. Structure and rheological behaviour of the extracellular polymeric substance network of mucoid pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Biofilms 2(4):275–283, 2005.
Wong, J. P., H. Yang, K. L. Blasetti, G. Schnell, J. Conley, and L. N. Schofield. Liposome delivery of ciprofloxacin against intracellular francisella tularensis infection. J. Controlled Release 92:265–273, 2003.
Xi, J., and P. Longest. Transport and deposition of micro-aerosols in realistic and simplified models of the oral airway. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35(4):560–581, 2007
Yang, L., K. B. Barken, M. E. Skindersoe, A. B. Christensen, M. Givskov, and T. Tolker-Nielsen. Effects of iron on DNA release and biofilm development by pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 153:1318–1328, 2007.
Yoon, S., R. Hennigan, G. Hilliard, U. Ochsner, K. Parvatiyar, M. Kamani, H. Allen, T. DeKievit, P. Gardner, U. Schwab, J. Rowe, B. Iglewski, T. McDermott, R. Mason, D. Wozniak, R. Hancock, M. Parsek, T. Noah, R. Boucher, and D. Hassett. Pseudomonas aeruginosa anaerobic respiration in biofilms: relationships to cystic fibrosis pathogenesis. Dev. Cell 3(4):593–603, 2002.
Youngs, W. J., C. A. Tessier, J. C. Garrison, C. A. Quezada, A. Melaiye, S. Durmus, M. J. Panzner, and A. Kascatan-Nebioglu. Medicinal applications of metal complexes of n-heterocyclic carbenes. In: Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry, edited by J. Sessler, and S. Lippard, vol. 903. 2005, pp. 414–427.
Yun, Y. H., H. Jiang, R. Chan, and W. Chen. Sustained release of PEG-g-chitosan complexed dna from poly(lactide-co-glycolide). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 16(11):1359–1378, 2005.
Zacarias, G., C. Ferreira, and J. Velasco-Hernandez. Porosity and tortuosity relations as revealed by a mathematical model of biofilm structure. J. Theor. Biol. 233:245–251, 2005.
Zhang, T., N. Cogan, and Q. Wang. Phase field models for biofilms. I. Theory and one-dimensional simulations. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 69(3):641–669, 2008.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH Grant RO1 GM086895 and the Akron Research Commercialization Corporation. The authors of this article are members of The Center for Silver Therapeutics Research at The University of Akron. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO1 tagged with gfp were a generous gift from Dr. Sren Molin. The authors thank the reviewers for many helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jennifer West oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, J.K., Neubig, R., Clemons, C.B. et al. Nanoparticle Deposition onto Biofilms. Ann Biomed Eng 41, 53–67 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0626-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0626-0