Abstract
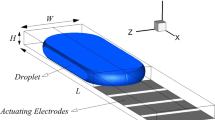
In this article, an electrohydrodynamic approach is used to study the microdroplet actuation in contemporary digital microfluidic biochips. The model is employed to analyze the microdroplet motion, and investigate the effects of the key parameters on the devices performance. The modeling results are compared to the experimental observations, and it is shown that the model provides an accurate representation of digital microfluidic transport. An extensive parametric variation is used to derive the maximum actuation switching frequency for ranges of the microdroplet size, gap spacing between the top and bottom plates and electrode pitch size. As a result, scalability of the devices is investigated, and it is shown that the microdroplet transfer rates change inversely with the system size, and microdroplet average velocity is nearly the same for different system scales. As a result of this study, an adjustable force-based actuation switching frequency implementation is proposed, and it is shown that faster microdroplet motion is obtained by in situ adjusting of the switching frequency. Finally, it has been observed that fastest microdroplet motion, despite similar studies conducted in the literature, is not achieved via actuating the next electrode as soon as the microdroplet touches it. Indeed, the switching frequency spectrum is dependent on the physical and geometrical properties of the system.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelgawad M, Wheeler AR (2008) Low-cost, rapid-prototyping of digital microfluidics devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 4(4):349–355
Abdelgawad M, Wheeler AR (2009) The digital revolution: a new paradigm for microfluidics. Adv Mater 21(8):920–925
Afkhami S, Bussmann M (2008) Height functions for applying contact angles to 2D VOF simulations. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 57(4):453–472
Ahmadi A, Najjaran H, Holzman JF, Hoorfar M (2009) Two-dimensional flow dynamics in digital microfluidic systems. J Micromech Microeng 19(6):065003
Ahmadi A, Holzman JF, Najjaran H, Hoorfar M (2011) Electrohydrodynamic modeling of microdroplet transient dynamics in electrocapillary-based digital microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 10(5):1019–1032
Arzpeyma A, Bhaseen S, Dolatabadi A, Wood-Adams P (2008) A coupled electro-hydrodynamic numerical modeling of droplet actuation by electrowetting. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 323(1–3):28–35
Bahadur V, Garimella SV (2006) An energy-based model for electrowetting-induced droplet actuation. J Micromech Microeng 16(8):1494–1503
Baird E, Young P, Mohseni K (2007) Electrostatic force calculation for an EWOD-actuated droplet. Microfluid Nanofluid 3(6):635–644
Bhattacharjee B, Najjaran H (2010) Simulation of droplet position control in digital microfluidic systems. J Dyn Syst Meas Control 132(1):014501-3
Blake T, Coninck JD (2002) The influence of solid liquid interactions on dynamic wetting. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 96(1–3):21–36
Brassard D, Malic L, Normandin F, Tabrizian M, Veres T (2008) Water-oil core–shell droplets for electrowetting-based digital microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 8(8):1342–1349
Buehrle J, Herminghaus S, Mugele F (2003) Interface profiles near three-phase contact lines in electric fields. Phys Rev Lett 91(8):086101
Bussmann M, Mostaghimi J, Chandra S (1999) On a three-dimensional volume tracking model of droplet impact. Phys Fluids 11:1406–1417
Chang YH, Lee GB, Huang FC, Chen YY, Lin JL (2006) Integrated polymerase chain reaction chips utilizing digital microfluidics. Biomed Microdevices 8(3):215–225
Cho SK, Moon H, Kim CJ (2003) Creating, transporting, cutting, and merging liquid droplets by electrowetting-based actuation for digital microfluidic circuits. J Microelectromech Syst 12(1):70–80
Cooney CG, Chen CY, Emerling MR, Nadim A, Sterling JD (2006) Electrowetting droplet microfluidics on a single planar surface. Microfluid Nanofluid 2(5):435–446
Fair RB (2007) Digital microfluidics: is a true lab-on-a-chip possible. Microfluid Nanofluid 3(3):245–281
Fair RB (2010) Scaling fundamentals and applications of digital microfluidic microsystems. Microfluid Based Microsyst 0:285–304
Fair RB, Khlystov A, Tailor TD, Ivanov V, Evans RD, Griffin PB, Srinivasan V, Pamula VK, Pollack MG, Zhou J (2007) Chemical and biological applications of digital-microfluidic devices. IEEE Des Test Comput 24(1):10–24
Fan SK, Hsieh TH, Lin DY (2009) General digital microfluidic platform manipulating dielectric and conductive droplets by dielectrophoresis and electrowetting. Lab Chip 9(9):1236–1242
Fouillet Y, Jary D, Chabrol C, Claustre P, Peponnet C (2008) Digital microfluidic design and optimization of classic and new fluidic functions for lab on a chip systems. Microfluid Nanofluid 4(3):159–165
Gao L, McCarthy TJ (2006) Contact angle hysteresis explained. Langmuir 22(14):6234–6237
Hua Z, Rouse JL, Eckhardt AE, Srinivasan V, Pamula VK, Schell WA, Benton JL, Mitchell TG, Pollack MG (2010) Multiplexed real-time polymerase chain reaction on a digital microfluidic platform. Anal Chem 82(6):2310–2316
Jebrail MJ, Wheeler AR (2009) Digital microfluidic method for protein extraction by precipitation. Anal Chem 81(1):330–335
Jones TB (2005) An electromechanical interpretation of electrowetting. J Micromech Microeng 15(6):1184–1187
Kang KH (2002) How electrostatic fields change contact angle in electrowetting. Langmuir 18(26):10318–10322
Keshavarz-Motamed Z, Kadem L, Dolatabadi A (2010) Effects of dynamic contact angle on numerical modeling of electrowetting in parallel plate microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 8(1):47–56
Kumari N, Bahadur V, Garimella SV (2008) Electrical actuation of dielectric droplets. J Micromech Microeng 18(8):5018
Lee J, Moon H, Fowler J, Schoellhammer T, Kim CJ (2002) Electrowetting and electrowetting-on-dielectric for microscale liquid handling. Sens Actuators A Phys 95(2–3):259–268
Lomax H, Pulliam TH, Zingg DW (2001) Fundamentals of computational fluid dynamics. Springer, Berlin
Luk VN, Wheeler AR (2009) A digital microfluidic approach to proteomic sample processing. Anal Chem 81(11):4524–4530
Malic L, Brassard D, Veres T, Tabrizian M (2010) Integration and detection of biochemical assays in digital microfluidic loc devices. Lab Chip 10(4):418–431
Miller EM, Wheeler AR (2008) A digital microfluidic approach to homogeneous enzyme assays. Anal Chem 80(5):1614–1619
Moon H, Cho SK, Garrell RL (2002) Low voltage electrowetting-on-dielectric. J Appl Phys 92(7):4080–4087
Moon H, Wheeler AR, Garrell RL, Loo JA, Kim CJ (2006) An integrated digital microfluidic chip for multiplexed proteomic sample preparation and analysis by MALDI-MS. Lab Chip 6(9):1213–1219
Nichols KP, Gardeniers HJGE (2007) A digital microfluidic system for the investigation of pre-steady-state enzyme kinetics using rapid quenching with MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 79(22):8699–8704
Pollack MG, Fair RB, Shenderov AD (2000) Electrowetting-based actuation of liquid droplets for microfluidic applications. Appl Phys Lett 77(11):1725–1726
Pollack MG, Shenderov AD, Fair RB (2002) Electrowetting-based actuation of droplets for integrated microfluidics. Lab Chip 2(2):96–101
Ren H, Fair RB, Pollack MG, Shaughnessy EJ (2002) Dynamics of electro-wetting droplet transport. Sens Actuators B Chem 87(1):201–206
SadAbadi H, Packirisamy M, Dolatabadi A, Wuthrich R (2010) Effects of electrode switching sequence on EWOD droplet manipulation: a simulation study. In: Proceedings of the ASME FEDSM-ICNMM, vol 31212, pp 1–6
Sista R, Hua Z, Thwar P, Sudarsan A, Srinivasan V, Eckhardt A, Pollack M, Pamula V (2008) Development of a digital microfluidic platform for point of care testing. Lab Chip 8(12):2091
Srinivasan V, Pamula VK, Fair RB (2004) An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab Chip 4(4):310–315
Su F, Hwang W, Chakrabarty K (2006) Droplet routing in the synthesis of digital microfluidic biochips. In: Proceedings of the conference on design, automation and test in Europe: Proceedings, European design and automation association, Munich, pp 323–328
Urbanski JP, Thies W, Rhodes C, Amarasinghe S, Thorsen T (2006) Digital microfluidics using soft lithography. Lab Chip 6(1):96–104
Wheeler AR, Moon H, Bird CA, Loo RRO, Kim CJ, Loo JA, Garrell RL (2005) Digital microfluidics with in-line sample purification for proteomics analyses with MALDI-MS. Anal Chem 77(2):534–540
Zeng J, Korsmeyer T (2004) Principles of droplet electrohydrodynamics for lab-on-a-chip. Lab Chip 4(4):265–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, A., Devlin, K.D. & Hoorfar, M. Numerical study of the microdroplet actuation switching frequency in digital microfluidic biochips. Microfluid Nanofluid 12, 295–305 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0872-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0872-8