Abstract
Aim
The ability to identify indicators of poor health-related quality of life (HRQoL) is crucial for both improving clinical care and determining targets of intervention for the prevention and treatment of disease. The main objectives of this study were to assess the HRQoL profile of the hypertensive population from Palestine, and to determine the socio-demographic and clinical characteristics associated with poor HRQoL.
Subject and methods
A cross sectional study was conducted, adopting the EuroQoL-5 Dimensions scale (EQ-5D-5 L) for the assessment of HRQoL. Hypertensive patients attending outpatients’ clinics at Al-Makhfyah primary health care clinic and from Alwatani Hospital, Nablus, Palestine were approached for study.
Results
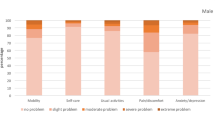
Four hundred and ten hypertensive patients were enrolled in the study. Of these, 213 patients (52 %) were female. The average age of the study population was 58.38 ± 10.65 years. HRQoL was good, with a mean EQ-5D-5 L index value and EQ visual analogue scale (EQ-VAS) score of 0.80 ± 0.16 and 74.1 ± 15.6 respectively. There was a significant positive correlation (r = 0.56; p < 0.001) between the EQ-5D-5 L index values and the reported EQ-VAS scores. A significant difference in EQ-5D-5 L index values was found among participants when grouped according to age, occupation, marital status, income, educational level, duration of disease, total number of chronic diseases, and total number of medications (Kruskal–Wallis test; p-value < 0.05), as well as gender and therapy type (Mann–Whitney test, p-value < 0.05).
Conclusions
This study highlighted that specific socio-demographic and disease-related characteristics of hypertensive patients as well as treatment factors were strongly associated with HRQoL. The study findings could be helpful in clinical practice, mainly in the early treatment of hypertensive patients, at a point where improving HRQoL is still possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aburuz S, Bulatova N, Twalbeh M, Gazawi M (2009) The validity and reliability of the Arabic version of the EQ-5D: a study from Jordan. Ann Saudi Med 29(4):304–308. doi:10.4103/0256-4947.55313
Al Habashneh R, Khader YS, Salameh S (2012) Use of the Arabic version of oral health impact profile-14 to evaluate the impact of periodontal disease on oral health-related quality of life among Jordanian adults. J Oral Sci 54(1):113–120
Al Sayah F, Ishaque S, Lau D, Johnson JA (2013) Health related quality of life measures in Arabic speaking populations: a systematic review on cross-cultural adaptation and measurement properties. Qual Life Res 22(1):213–229. doi:10.1007/s11136-012-0129-3
Al-Shehri AH, Taha AZ, Bahnassy AA, Salah M (2008) Health-related quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients. Ann Saudi Med 28(5):352–360
Altaweel W, Alharbi M (2012) Urinary incontinence: prevalence, risk factors, and impact on health related quality of life in Saudi women. Neurourol Urodyn 31(5):642–645. doi:10.1002/nau.22201
Arslantas D, Ayranci U, Unsal A, Tozun M (2008) Prevalence of hypertension among individuals aged 50 years and over and its impact on health related quality of life in a semi-rural area of western Turkey. Chin Med J (Engl) 121(16):1524–1531
Bani-Issa W (2011) Evaluation of the health-related quality of life of Emirati people with diabetes: integration of sociodemographic and disease-related variables. East Mediterr Health J 17(11):825–830
Daniel WW (2010) Biostatistics: basic concepts and methodology for the health sciences. Wiley, New York
Erickson SR, Williams BC, Gruppen LD (2004) Relationship between symptoms and health-related quality of life in patients treated for hypertension. Pharmacotherapy 24(3):344–350. doi:10.1592/phco.24.4.344.33177
EuroQol Group (1990) EuroQol: a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 16(3):199–208. doi:10.1016/0168-8510(90)90421-9
EuroQOL Group (2011) EQ-5D-5 L user guide: basic information on how to use the EQ-5D-5 L instrument. http://www.euroqol.org/fileadmin/user_upload/Documenten/PDF/Folders_Flyers/UserGuide_EQ-5D-5L.pdf. Accessed 7 January 2013
Giacaman R, Khatib R, Shabaneh L, Ramlawi A, Sabri B, Sabatinelli G, Khawaja M, Laurance T (2009) Health status and health services in the occupied Palestinian territory. Lancet 373(9666):837–849. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60107-0
Goins RT, John R, Hennessy CH, Denny CH, Buchwald D (2006) Determinants of health-related quality of life among older American Indians and Alaska Natives. J Appl Gerontol 25(1 suppl):73S–88S. doi:10.1177/0733464805283037
Goncalves CB, Moreira LB, Gus M, Fuchs FD (2007) Adverse events of blood-pressure-lowering drugs: evidence of high incidence in a clinical setting. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63(10):973–978. doi:10.1007/s00228-007-0352-y
Husseini A, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Mikki N, Ramahi TM, Ghosh HA, Barghuthi N, Khalili M, Bjertness E, Holmboe-Ottesen G, Jervell J (2009) Cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, and cancer in the occupied Palestinian territory. Lancet 373(9668):1041–1049. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60109-4
Khosravi A, Ramezani MA, Toghianifar N, Rabiei K, Jahandideh M, Yousofi A (2010) Association between hypertension and quality of life in a sample of Iranian adults. Acta Cardiol 65(4):425–430. doi:10.2143/AC.65.4.2053901
Khoudri I, Ali Zeggwagh A, Abidi K, Madani N, Abouqal R (2007) Measurement properties of the short form 36 and health-related quality of life after intensive care in Morocco. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 51(2):189–197. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2006.01225.x
Lazenby M, Khatib J (2012) Associations among patient characteristics, health-related quality of life, and spiritual well-being among Arab Muslim cancer patients. J Palliat Med 15(12):1321–1324. doi:10.1089/jpm.2012.0208
Li W, Liu L, Puente JG, Li Y, Jiang X, Jin S, Ma H, Kong L, Ma L, He X, Ma S, Chen C (2005) Hypertension and health-related quality of life: an epidemiological study in patients attending hospital clinics in China. J Hypertens 23(9):1667–1676. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000174971.64589.39
Maatouk I, Wild B, Herzog W, Wesche D, Schellberg D, Schottker B, Muller H, Rothenbacher D, Stegmaier C, Brenner H (2012) Longitudinal predictors of health-related quality of life in middle-aged and older adults with hypertension: results of a population-based study. J Hypertens 30(7):1364–1372. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e328353d81b
McGrath C, Alkhatib MN, Al-Munif M, Bedi R, Zaki AS (2003) Translation and validation of an Arabic version of the UK oral health related quality of life measure (OHQoL-UK) in Syria, Egypt and Saudi Arabia. Community Dent Health 20(4):241–245
Mielck A, Reitmeir P, Vogelmann M, Leidl R (2013) Impact of educational level on health-related quality of life (HRQL): results from Germany based on the EuroQol 5D (EQ-5D). Eur J Public Health 23(1):45–49. doi:10.1093/eurpub/ckr206
Mrabet H, Mrabet A, Zouari B, Ghachem R (2004) Health-related quality of life of people with epilepsy compared with a general reference population: a Tunisian study. Epilepsia 45(7):838–843. doi:10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.56903.x
Ogunlana MO, Adedokun B, Dairo MD, Odunaiya NA (2009) Profile and predictor of health-related quality of life among hypertensive patients in south-western Nigeria. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 9:25. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-9-25
Saleem F, Hassali MA, Shafie AA (2012) A cross-sectional assessment of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among hypertensive patients in Pakistan. Health Expect. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-7625.2012.00765.x
Schwarzinger M, Dewedar S, Rekacewicz C, Abd Elaziz KM, Fontanet A, Carrat F, Mohamed MK (2004) Chronic hepatitis C virus infection: does it really impact health-related quality of life? A study in rural Egypt. Hepatology 40(6):1434–1441. doi:10.1002/hep.20468
Serhier Z, Harzy T, EL S, Diouny S, El Rhazi K, Bennani Othmani M, Salmi LR, Nejjari C (2012) Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the knee and hip health-related quality of life (OAKHQoL) in a Moroccan Arabic-speaking population. Rheumatol Int 32(4):1015–1023. doi:10.1007/s00296-010-1781-y
Stein AD, Stoyanovsky V, Mincheva V, Dimitrov E, Hodjeva D, Petkov A, Tsanova V (2000) Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in a working Bulgarian population. Eur J Epidemiol 16(3):265–270. doi:10.1023/A:1007601107752
Trevisol DJ, Moreira LB, Kerkhoff A, Fuchs SC, Fuchs FD (2011) Health-related quality of life and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hypertens 29(2):179–188. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e328340d76f
Trevisol DJ, Moreira LB, Fuchs FD, Fuchs SC (2012) Health-related quality of life and awareness of hypertension. J Hypertens 30(3):629. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32834f9bbf
ul Haq N, Hassali MA, Shafie AA, Saleem F, Aljadhey H (2012) A cross sectional assessment of health related quality of life among patients with Hepatitis-B in Pakistan. Health Qual Life Outcome 10(1):91. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-10-91
Wahass S, Khalil MS, Al Qurain AA, Yasawy MI (2006) The impact of functional dyspepsia on health-related quality of life in Saudi patients. Saudi J Gastroenterol 12(3):123–129. doi:10.4103/1319-3767.29752
Wang HM, Beyer M, Gensichen J, Gerlach FM (2008) Health-related quality of life among general practice patients with differing chronic diseases in Germany: cross sectional survey. BMC Public Health 8(1):246. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-8-246
Wang R, Zhao Y, He X, Ma X, Yan X, Sun Y, Liu W, Gu Z, Zhao J, He J (2009) Impact of hypertension on health-related quality of life in a population-based study in Shanghai, China. Public Health 123(8):534–539. doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2009.06.009
Wilson IB, Cleary PD (1995) Linking clinical variables with health-related quality of life: a conceptual model of patient outcomes. JAMA 273(1):59–65. doi:10.1001/jama.1995.03520250075037
Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM, Morisky DE (2013a) Relationship of treatment satisfaction to medication adherence: findings from a cross-sectional survey among hypertensive patients in Palestine. Health Qual Life Outcome 11(1):191. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-11-191
Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM, Wildali AH, Saleem HM, Aysa HA, Badwan MA, Awang R, Morisky DE (2013b) Health-related quality of life associated with treatment adherence in patients with hypertension: a cross-sectional study. Int J Cardiol 168(3):2981–2983. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.04.105
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Jabi, S.W., Zyoud, S.H., Sweileh, W.M. et al. Assessment of health-related quality of life among hypertensive patients: a cross-sectional study from Palestine. J Public Health 22, 277–286 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-014-0613-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-014-0613-z