Abstract
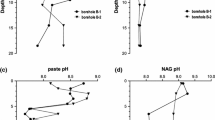
Flotation tailings associated with the extraction of Pb and Zn in the Touiref mining district, Tunisia, contain galena, sphalerite, pyrite, and marcasite in a carbonate gangue. The geochemical behaviour of oxidized and unoxidised tailings were consistent with their mineralogical and chemical characteristics. The leaching proceeded under neutral to slightly alkaline condition (pH 7.3–8.5), and positive Eh (250–470 mV). The concentrations of sulfate and Ca released during the leaching tests were associated with the neutralization of acidity by carbonates and the dissolution of gypsum initially present in the tailings. The iron precipitated, but significant amounts of Zn (5–3,300 μg/L), Cd (3–18 μg/L), and Pb (28–83 μg/L) were released during leaching, with the latter two exceeding international environmental norms (5 μg/L for Cd and 10 μg/L for Pb).
Zusammenfassung
Die Flotationsabgänge der Pb–Zn-Aufbereitung im Touiref Bergbau-Distrikt, Tunesien enthalten Galenit, Sphalerit, Pyrit und Markasit in karbonatischer Gangart. Das geochemische Verhalten oxidierter bzw. nicht-oxidierter Tailings stand im Einklang mit ihren mineralogischen und chemischen Eigenschaften. Die Laugungstests wurden unter neutralen bis schwach alkalischen pH-Bedingungen (pH 7,3–8,5) und positivem Redoxpotenzial (250-470 mV) durchgeführt. Die während der Laugungstests ausgetragenen Sulfat- und Kalziumkonzentrationen werden mit Neutralisationsreaktionen durch Karbonate sowie die Auflösung von in den Tailings bereits ursprünglich enthaltenem Gips in Verbindung gebracht. Während Eisen im Rahmen der Laugungsversuche ausfiel, wurden signifikante Mengen an Zn (5 - 3300 μg/L), Cd (3 - 18 μg/L) und Pb (28 - 83 μg/L) freigesetzt, wobei die Cd- und Pb-Konzentrationen internationale Umweltnormen (5 μg/L für Cd, 10 μg/L für Pb) überschritten.
Resumen
Las colas de flotación asociadas con la extracción de Pb y Zn en el distrito minero de Touiref, Túnez, contienen galena, esfalerita, pirita y marcasita en una ganga de carbonatos. El comportamiento geoquímico de las colas oxidadas y no oxidadas fue consistente con sus características mineralógicas y químicas. La lixiviación procedió bajo condiciones neutras o ligeramente alcalinas (pH 7,3 – 8,5) y valores positivos de Eh (250 a 470 mV). Las concentraciones de sulfato y calcio liberados durante los tests de lixiviación fueron asociados con la neutralización de la acidez por carbonatos y la disolución de yeso inicialmente presente en las colas. El hierro precipitó pero cantidades significativas de Zn (5 a 3300 μg/L), Cd (3 a 18 μg/L) y Pb (28 a 83 μg/L) fueron liberadas durante la lixiviación, con los últimos dos superando las normas ambientales internacionales (5 μg/L para Cd y 10 μg/L para Pb).
抽象
在突尼斯Touiref矿区,铅-锌浮选尾矿的碳酸盐类矸石含有方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铁矿和白铁矿。氧化与未氧化尾矿的地球化学行为与它们的矿物学和化学特征吻合。溶滤试验在中性-弱碱性(pH = 7.3 ~ 8.5)和正氧化-还原电位(Eh = 250 ~ 470 mV)条件下进行。溶滤试验释放的硫酸盐和钙离子浓度与尾矿最初的碳酸盐中和作用及石膏溶解作用有关。铁离子发生了沉淀,大量锌(5-3300 μg/L)、镉(3-18 μg/L)和铅(28-83 μg/L)释放出来,而且后两离子浓度超过了国际环境标准(镉5 μg/L,铅10 μg/L)。












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubertin M, Bussière B, Chapuis RP (1996) Hydraulic conductivity of homogenized tailings from hard rock mines. Can Geotech J 33(3):470–482
Aubertin M, Bussiere B, Bernier L (2002) Environnement et gestion de résidus miniers. Presses Internationales de Polytechnique, Corporation de l’École Polytechnique de Montréal, Montréal, Canada
Benzaazoua M, Bussière B, Dagenais AM (2001) Comparison of kinetic tests for sulphide mine tailings. Proc, Tailings and Mine Waste, Fort Collins, CO, USA, pp 263–272
Benzaazoua M, Bussière B, Dagenais AM, Archambeault M (2004) Kinetic tests comparison and interpretation for prediction of the Joutel tailings acid generation potential. Environ Geol 46:1086–1110
Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Jambor JL (1994) Remediation and prevention of low-quality drainage from mine wastes. In: Blowes DW, Jambor JL (eds) The environmental geochemistry of sulfide mine-wastes, vol 2. Mineralogical Association of Canada, Nepean, pp 365–380
Blowes DW, Jambor JL, Hanton-Fong ChJ (1998) Geochemical, mineralogical and microbiological characterization of a sulphide-bearing carbonate-rich gold mine tailings impoundment, Joutel, Québec. Appl Geochem 13(6):687–705
Bussière B (2007) Colloquium 2004: hydrogeotechnical properties of hard rock tailings from metal mines and emerging geoenvironmental disposal approaches. Can Geotech J 44(9):1019–1052
Bussiere B, Benzaazoua M (1999) Essais cinétiques en colonnes réalisés sur cinq échantillons provenant du site Joutel. Unité de recherche et de service en technologie minérale (rapport de service non publié), Rouyn-Noranda
Bussiere B, Aubertin M, Zagoury M, Potvin R, Benzaazoua M (2005) Principaux défis et pistes de solution pour la restauration des sites miniers abandonnés. Actes du Symposium sur l’ Environnement et les mines, Rouyn-Noranda
Bussière B, Benzaazoua M, Aubertin M, Mbonimpa M (2004) A laboratory study of covers made of low-sulphide tailings to prevent acid mine drainage. Environ Geol 45(5):609–622
Cox Matthew R (1998) The effectiveness of in situ limestone treatment of acid mine drainage. Environ Eng Geosci 4(1):3–14
Cruz R, Méndez BA, Monroy M, Gonzalez I (2001) Cyclic voltametry applied to evaluate reactivity in sulfide mining residues. Appl Geochem 16:1631–1640
Day SJ, Bowell RJ (2005) Atypical and typical zinc geochemistry in a carbonate setting, Sa Dena Hes Mine, Yukon Territory, Canada. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 5(3):255–266
De Giudicci G (2008) Abandoned mining wastes and their impact on the environment: some case study from South West of Sardinia (Italy). In: Proc, Symp 2008 sur la gestion des déchets solides & développements durable, Hammamet, Tunisia, pp 229–230
Down CG, Stock J (1977) Environmental impact of mining. Lohn Sons, New York City
Felmy AR, Griven JB, Jenne EA (1984) MINTEQ : a computer program for calculating aqueous geochemical equilibria. National Technical Information Services, Springfield
Hakkou R, Benzaazoua M, Bussiere B (2008a) Acid mine drainage at the abandoned Kettara Mine (Morocco): 1. Environmental characterization. Mine Water Environ 27:145–159
Hakkou R, Benzaazoua M, Bussiere B (2008b) Acid mine drainage at the abandoned Kettara Mine (Morocco): 2. Mine waste geochemical behavior. Mine Water Environ 27:160–170
Heikkinen P, Raisanen M, Johnson R (2009) Geochemical characterization of seepage and drainage water quality from two sulphide mine tailings impoundments: acid mine drainage vs. neutral mine drainage. Mine Water Environ 28:30–49
Holmström H, Ljungberg J, Öhlander B (1999) Role of carbonates in mitigation of metal release from mining waste. Evidence from humidity cell tests. Environ Geol 37(4):267–280
INM (Institut National de Météorolgie de Tunisie), (2004) Archives des données de pluviométrie, température, évaporation, précipitation et vent de la région d’El Kef. INM, Tunis
Johnson RH, Blowes DW, Robertson WD, Jambor JL (2000) The hydrogeochemistry of the Nickel Rim mine tailings impoundment, Sudbury, Ontario. J Contam Hydrol 41:49–80
Jurjovec J, Ptacek CJ, Blowes DW (2002) Acid neutralization mechanisms and metal release in mine tailings: a laboratory column experiment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66(9):1511–1523
Lindsay MBJ, Condon PD, Jambor JL, Lear KG, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ (2009) Mineralogical, geochemical, and microbial investigation of a sulfide-rich tailings deposit characterized by neutral drainage. Appl Geochem 24(12):2212–2221
Lizarraga-Mendiola L, Gonzalez-Sandoval MR, Duran-Dominguez MC, Marquez-Herrera C (2009) Geochemical behavior of heavy metals in a Zn–Pb–Cu mining area in the state of Mexico (central Mexico). Environ Monit Assess 55:355–372
Marcus JJ (1997) Mining environmental handbook: effects of mining on the environment and American environmental controls on mining. Imperial College Press, London
Matthies R, Aplin AC, Jarvis AP (2010) Performance of a passive treatment system for net-acidic coal mine drainage over five years of operation. Sci Total Environ 408(20):4877–4885
McCreadie H, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Jambor JL (2000) The influence of reduction reactions and solids composition on pore-water arsenic concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 34:3159–3166
McGregor RG, Blowes DW, Jambor JL, Robertson WD (1998) The solid-phase controls on the mobility of heavy metals at the Copper Cliff tailings area, Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. J Contam Hydrol 33:247–271
Morin KA, Hutt NM (1997) Environmental geochemistry of mine site drainage: practical theory and case studies. MDAG Publication, Vancouver
NEDEM (Programme de Neutralisation des Eaux de Drainage dans l’Environnement Minier) (2006) Update on Cold Temperature Effects on Geochemical Weathering. MEND/NEDEM Rapport 1.61.6, Ottawa, Canada
Neff D (2003) Apport des analogues archéologiques à l’estimation des vitesses moyennes et àl’étude des mécanismes de corrosion à très long terme des aciers non alliés dans les sols. Thèse de Doctorat de l’Université de Technologie de Compiègne, p 167
Nicholson RV, Rinker M, Venhuis MA, Williams G, Swabrick B (2003). Implications of non-acidic metal leaching on mine rock management at a nickel mine in permafrost terrain: environmental baseline investigation. Mining and the Environment III, Session 5B U/Radionuclides, Sudbury, Paper on CD Rom
Othmani MA (2006) Résidus miniers et impact sur l’environnement: exemple du secteur de Touiref. Mémoire de mastère, Option Ressources Minérales: Exploration et Valorisation. Dépt de Géologie, Univ de Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Pépin G (2009) Évaluation du comportement géochimique de stériles potentiellement générateurs de drainage neutre contaminé à l’aide de cellules expérimentales in situ, MSc Thesis, Univ du Québec en Abitibi-Témiscamingue (UQAT), Canada
Percival JB, Kwong YTJ, Dumaresq CG, Michel FA (2004) Transport and attenuation of arsenic, cobalt and nickel in an alkaline environment (Cobalt, Ontario). Geological Survey of Canada OF report 1680, Ottawa, Canada
Pettit CM, Scharer JM, Chambers DB, Halbert BE, Kirkaldy JL, Bolduc L (1999) Neutral mine drainage. In: Proc, Sudbury Conf, Sudbury, ON, Canada, pp 829–838
Plante B, Benzaazoua M, Bussiere B (2010) Kinetic testing and sorption studies by modified weathering cells to characterize the potential to generate contaminated neutral drainage. Mine Water Environ 30:22–37
Rinker MJ, Nicholson RV, Venhuis MA, Swarbrick B (2003) Implication of non-acid metal leaching on mine rock management at a nickel mine in permafrost terrain: 1—mine rock evaluation. Mining and the Environment III, Sudbury, ON, Canada, paper on CD ROM
Ripley EA, Redman RE, Crowder AA (1996) Environmental effects of mining. St Lucie Press, Boca Raton
Ritcey GM (1989) Tailings management, problems and solutions in the mining industries. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Romero FM, Armienta MA, Gonzalez-Hernandez G (2007) Solid-phase control on the mobility of potentially toxic elements in an abandoned lead/zinc mine tailings impoundment, Taxco, Mexico. Appl Geochem 22:109–127
Rose AW, Cravotta CA III (1998) Geochemistry of coal mine drainage. In: Brady KBC, Smith MW, Schueck J (eds) Coal mine drainage prediction and pollution in Pennsylvania. Bureau of Mining and Reclamation, Pennsylvania Dept of Environmental Protection, Harrisburg, PA, USA, pp 1–22
Rouvier H (1977) Géologie de l’extrême Nord tunisien : tectoniques et paléogéographies superposées à l’extrémité orientale de la chaîne maghrébine, Thèse Doctorat ès Sci, Univ P et M Curie, Paris, France
Sainfeld P (1952) Les gîtes plombo-zincifères de la Tunisie. Ann. Mines et Géologie, Tunis, Tunisia
Scharer JM, Pettit CM, Kirkaldy JL, Bolduc L, Halbert BE, Chambers DB (2000) Leaching of metals sulphide mine wastes at neutral pH. In: Proc, 5th ICARD, Soc for Mining, Metallurgy, Exploration, Inc, Denver, CO, USA, pp 191–204
SERMI (Société d’Etudes et de Recherches Minières) (1965) Inventaire géologique et minier: Étude géologique et minière de la zone de Touiref—Rapport interne Office National des Mines, Tunis
Shevenell L, Connors KA, Henry CD (1999) Controls on pit lake water quality at sixteen open-pit mines in Nevada. Appl Geochem 14:669–687
Sobek AA, Schuller WA, Freeman JR, Smith RM (1978) Field and laboratory methods applicable to overburdens and minesoils. US Environmental Protection Agency report EPA-600/2–78-054, Washington DC, USA, pp 47–50
Souissi F, Souissi R, Bouchardon JL, Moutte J, Munoz M, Chakroun HK, Othmani M, Ghorbel M (2008) Mineralogical and geochemical characterization of mine tailings and the effect of Pb, Zn, Cd and Cu mobility on the quality of soils and stream sediments in northern Tunisia. Actes du Congrès International Gestion des Déchets Solides et Développement Durable, Hammamet, Tunisia, pp 313–317
Sracek O, Kříbek B, Mihaljevič M, Majer V, Veselovský F, Vencelides Z, Nyambe I (2012) Mining-related contamination of surface water and sediments of the Kafue River drainage system in the Copperbelt district, Zambia: an example of a high neutralization capacity system. J Geochem Explor 112:174–188
Stantec (2004) Review of water quality issues in neutral pH drainage: examples and emerging priorities for the mining industry in Canada. Rapport NEDEM 10.1 Natural Resources, Ottawa, ON, Canada
US NPDWS (National Primary Drinking Water Standards) (2003) US EPA Report 816-F-03-016, Office of Water (4606M), http://www.epa.gov./safewater. Accessed 12 Sept 2007
Villeneuve M (2004) Évaluation du comportement géochimique à long terme de rejets miniers à faible potentiel de génération d’acide à l’aide d’essais cinétiques. Mémoire de maîtrise en génie minéral, École Polytechnique de Montréal, QC, Canada
Villeneuve M, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M, Aubertin M, Monroy M (2003) The influence of kinetic test type on the geochemical response of low acid generating potential tailings. In: Proc, Tailings and Mine Waste 03, Sweets and Zeitlinger, Lisse, the Netherlands, pp 269–279
Xu S, Yu C, Hiroshiro Y (2010) Migration behavior of Fe, Cu, Zn, and mo in alkaline tailings from lanjiagou porphyry molybdenum deposits, Northeast China. Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering. Kyushu Univ 70(2):19–31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research and the URSTM of the University of Quebec; Rouyn-Noranda, Canada. We also thank Mathieu Villeneuve, Benoit Plante, Erol Yilmaz, and Alain Perreault for their assistance and willingness to perform the experiments and analyses, and Mohamed Ali Fedaoui and Fethi Ouerghi from the municipality of Touiref for their technical support. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments, which greatly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Othmani, M.A., Souissi, F., Benzaazoua, M. et al. The Geochemical Behaviour of Mine Tailings from the Touiref Pb–Zn District in Tunisia in Weathering Cells Leaching Tests. Mine Water Environ 32, 28–41 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-012-0210-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-012-0210-8