Abstract
Background
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a novel clinical disease entity characterized by elevated serum IgG4 concentration and tumefaction or tissue infiltration by IgG4+ plasma cells. Although IgG4-RD is not rare and is clinically important, its clinical diagnostic criteria have not been established. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD, including the involvement of various organs, are intended for the practical use of general physicians and nonspecialists.
Methods
Two IgG4-RD study groups, the Umehara and Okazaki teams, were organized by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare Japan. As IgG4-RD comprises a wide variety of diseases, these groups consist of physicians and researchers in various disciplines, including rheumatology, hematology, gastroenterology, nephrology, pulmonology, ophthalmology, odontology, pathology, statistics, and basic and molecular immunology throughout Japan, with 66 and 56 members of the Umehara and Okazaki teams, respectively. Collaborations of the two study groups involved detailed analyses of clinical symptoms, laboratory results, and biopsy specimens of patients with IgG4-RD, resulting in the establishment of comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD.
Results
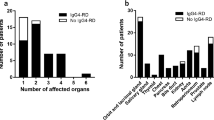
Although many patients with IgG4-RD have lesions in several organs, either synchronously or metachronously, and the pathological features of each organ differ, consensus has been reached on two diagnostic criteria for IgG4RD: (1) serum IgG4 concentration >135 mg/dl, and (2) >40% of IgG+ plasma cells being IgG4+ and >10 cells/high powered field of biopsy sample. Although the comprehensive diagnostic criteria are not sufficiently sensitive for the diagnosis of type 1 IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis (IgG4-related AIP), they are adequately sensitive for IgG4-related Mikulicz’s disease (MD) and kidney disease (KD). In addition, the comprehensive diagnostic criteria, combined with organ-specific diagnostic criteria, have increased the sensitivity of diagnosis to 100% for IgG4-related MD, KD, and AIP.
Conclusion
Our comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD are practically useful for general physicians and nonspecialists.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IgG4-RD:
-
IgG4-related disease
- MD:
-
Mikulicz’s disease
- AIP:
-
Autoimmune pancreatitis
- KD:
-
Kidney disease
- TIN:
-
Tubulointerstitial nephritis
- SS:
-
Sjögren’s syndrome
- MHLW:
-
Japan Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare Japan; familial multifocal fibrosclerosis
- RPF:
-
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
- TIN:
-
Tubulointerstitial nephritis
- MOLPS:
-
Multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome
- SIPS:
-
Systemic IgG4 plasmacytic syndrome
References
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol 2011; [Epub ahead of print]
Yamamoto M, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Takahashi H, et al. Elevated IgG4 concentrations in serum of patients with Mikulicz’s disease. Scand J Rhumatol. 2004;33:432–3.
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N, Kitagawa K, Morikawa Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multi-organ lymphoproliferative syndrome: Analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;63:1310–5.
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Koyabu M, Miyoshi H, Takaoka M. Recent advances in the concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46(3):277–88.
Dahlgren M, Khosroshahi A, Nielsen GP, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Riedel’s thyroiditis and multifocal fibrosclerosis are part of the IgG4-related systemic disease spectrum. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62(9):1312–8.
Zen Y, Inoue D, Kitao A, Onodera M, Abo H, Miyayama S, et al. IgG4-related lung and pleural disease: a clinicopathologic study of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33(12):1886–93.
Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, Gabata T, Demachi H, Kobayashi T, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: CT findings with pathologic correlations. Radiology. 2009;251(1):260–70.
Saeki T, Saito A, Yamazaki H, Emura I, Imai N, Ueno M, et al. Tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with IgG4-related systemic disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2007;11(2):168–73.
Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Kawano M, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010;78(10):1016–23.
Sato Y, Kojima M, Takata K, Morito T, Asaoku H, Takeuchi T, et al. Systemic IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: a clinical and pathologic comparison to multicentric Castleman’s disease. Mod Pathol. 2009;22(4):589–99.
Sato Y, Notohara K, Kojima M, Takata K, Masaki Y, Yoshino T. IgG4-related disease: historical overview and pathology of hematological disorders. Pathol Int. 2010;60(4):247–58.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, Unno H, Shiba N, Wajiki M, et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet. 2002;359(9315):1403–4.
Zen Y, Onodera M, Inoue D, Kitao A, Matsui O, Nohara T, et al. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: a clinicopathologic study with respect to immunoglobulin G4. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33(12):1833–9.
Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Hilgenberg A, Spooner A, Isselbacher EM, Stone JR. IgG4-related systemic disease and lymphoplasmacytic aortitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(10):3139–45.
Kamisawa T, Nakajima H, Egawa N, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing disease incorporating sclerosing pancreatitis, cholangitis, sialadenitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis with lymphadenopathy. Pancreatology 2006;6:132–7.
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(10):982–4.
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Hasebe K, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Hayashi T, et al. The analysis of interleukin-6 in patients with systemic IgG4-related plasmacytic syndrome-expansion of SIPS to the territory of Castleman’s disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48:860–2.
Kamisawa T, Chen PY, Tu Y, Nakajima H, Egawa N, Tsuruta K, et al. Pancreatic cancer with a high serum IgG4 concentration. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(38):6225–8.
Joo M, Chang SH, Kim H, Gardner JM, Ro JY. Primary gastrointestinal clear cell sarcoma: report of 2 cases, one case associated with IgG4-related sclerosing disease, and review of literature. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2009;13(1):30–5.
Gill J, Angelo N, Yeong ML, McIvor N. Salivary duct carcinoma arising in IgG4-related autoimmune disease of the parotid gland. Hum Pathol. 2009;40(6):881–6.
Straub BK, Esposito I, Gotthardt D, Radeleff B, Antolovic D, Flechtenmacher C, et al. IgG4-associated cholangitis with cholangiocarcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2011;458(6):761–5.
Cheuk W, Yuen HK, Chan AC, Shih LY, Kuo TT, Ma MW, et al. Ocular adnexal lymphoma associated with IgG4+ chronic sclerosing dacryoadenitis: a previously undescribed complication of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32(8):1159–67.
Kubota T, Moritani S, Yoshino T, Nagai H, Terasaki H. Ocular adnexal marginal zone B cell lymphoma infiltrated by IgG4-positive plasma cells. J Clin Pathol. 2010;63(12):1059–65.
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Tabeya T, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Ishigami K, et al. Risk of malignancies in IgG4-related disease. Mod Rheumatol 2011; [Epub ahead of print]
Masaki Y, Sugai S, Umehara H. IgG4-related diseases including Mikulicz’s disease and sclerosing pancreatitis: diagnostic insights. J Rheum. 2010;37:1380–5.
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Naruse S, Tanaka S, Nishimori I, et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: revised proposal. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41(7):626–31.
Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, Nishi S, Yamaguchi Y, Hisano S, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 2011; 15(5):615–26.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–8.
Strehl JD, Hartmann A, Agaimy A. Numerous IgG4-positive plasma cells are ubiquitous in diverse localised non-specific chronic inflammatory conditions and need to be distinguished from IgG4-related systemic disorders. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64(3):237–43.
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Naishiro Y, Isshiki H, Ohara M, Suzuki C, et al. Mikulicz’s disease and systemic IgG4-related plasmacytic syndrome (SIPS). Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2008;31(1):1–8.
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Fukui T. Recent advances in autoimmune pancreatitis: concept, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. J Gastroenterol. 2008;43(6):409–18.
Takuma K, Kamisawa T, Igarashi Y. Autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(1):80–7.
Fujinaga Y, Kadoya M, Kawa S, Hamano H, Ueda K, Momose M, et al. Characteristic findings in images of extra-pancreatic lesions associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Radiol. 2010;76(2):228–38.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Intractable Diseases, the Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants from Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan. We sincerely thank the many contributing researchers and collaborators who participated in the All Japan IgG4 team.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
For the All Japan IgG4 team.
Professional collaborators of the All Japan G4 team are given in the Appendix.
H. Umehara and K. Okazaki equally contributed to this work.
Appendix
Appendix
The authors thank the many patients who participated in this registry. In addition to the listed authors, other professional collaborators of the All Japan G4 team in the Research Program for Intractable Disease by Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) Japan, include: Atsushi Azumi (Kobe Kaisei Hospital); Keiji Kubo, and Hiroshi Yamamoto (Shinshu University); Daisuke Kawabata (Kyoto University); Seijiro Minamoto (Osaka Respiratory and Allergy Center); Susumu Nishiyama (Kurashiki Hospital); Kazuo Tsubota and Yoko Ogawa (Keio University); Shintaro Hirata (University of Occupational and Environmental Health); Tomoki Origuchi (Nagasaki University); Yasuharu Sato (Okayama University); Susumu Sugai (Kudou Hospital); Hiroki Takahashi (Sapporo Medical University); Hiroto Tsuboi (Tsukuba University); Dai Inoue, Masayuki Takahira and Yuko Waseda (Kanazawa University); Masaru Kojima (Dokkyo University School of Medicine); Norifumi Tsukamoto (Gunma University); Morio Matsumoto (Nishigunma National Hospital); Kayoko Murayama (Gunma Prefectural Cancer Center); Ritsuro Suzuki and Shigeru Ko (Nagoya University); Takahiro Nakazawa and Osamu Hasebe (Nagoya City University); Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa (Kuma Hospital); Masao Seto and Nobumasa Mizuno (Aichi Cancer Center; Yosuke Matsumoto (Kyoto Prefecture University); Tokuhide Oyama (Niigata University); Akira Sakai (Hiroshima University); Yoshiaki Imamura (Fukui University); Keita Fujikawa (Isahaya hospital); Yoshihiro Yakushijin (Ehime University); Akira Sakai (Hiroshima University); Takayoshi Nishino (Tokyo Womens Medical University), Kenji Hirano (Tokyo University), Hitoshi Yoshida (Showa University), Tatsuo Kinashi, Kazushige Uchida (Kansai Medical University), Kunihiko Itoh (University of Shizuoka) and Kazuko Kitagawa, Tsutomu Takegami, Naohisa Tomosugi, Hisanori Tonami, Nozomu Kurose, Yasuhito Ishigaki, Takayuki Nojima, Hitoshi Yokoyama, Toshihiro Fukushima, Masao Tanaka, Yoshimasa Fujita, Toshioki Sawaki, Takafumi Kawanami, Miyuki Miki, Haruka Iwao, Akio Nakajima, and Takuji Nakamura (Kanazawa Medical University).
About this article
Cite this article
Umehara, H., Okazaki, K., Masaki, Y. et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol 22, 21–30 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0571-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0571-z