Abstract
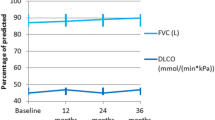
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a noteworthy condition in the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc) because of its associated mortality and morbidity; however, the efficacy of various treatments for ILD has been controversial in previous reports. In this study, we examined the efficacy and safety of intravenous cyclophosphamide (IVCY) pulse therapy with prednisolone (PSL) for the treatment of ILD with SSc. A total of 121 patients with SSc were screened and evaluated for ILD, using high-resolution computed tomography of the chest, pulmonary function testing, and bronchoalveolar lavage. Thirteen patients with active ILD were enrolled in this study. The treatment protocol for ILD was 0.4 g/m2 of body surface area of IVCY monthly plus 0.8 mg/kg of body weight of PSL daily. Two to six doses of IVCY were administered, depending on the remission of ILD. Initial PSL doses were maintained for a month and then gradually tapered to 10 mg daily. An activity index of ILD showed improvements in all patients in the 12 months after the initial intervention; however, four patients experienced recurrence of ILD after 24 months, and one additional patient had recurrence of ILD after 36 months. Seven patients reached the 48-month point with no recurrence of ILD. This long observational study for 48 months showed the efficacy of IVCY with PSL for active alveolitis in the first year. However, because five patients had recurrence of ILD more than 1 year after the treatment, it would be necessary to consider maintenance therapy for ILD beyond 1 year.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheema GS, Quismorio FP Jr. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2001;7(5):283–90.
Silver RM, Warrick JH, Kinsella MB, Staudt LS, Baumann MH, Strange C. Cyclophosphamide and low-dose prednisone therapy in patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) with interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(5):838–44.
Steen VD, Lanz JK Jr, Conte C, Owens GR, Medsger TA Jr. Therapy for severe interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. A retrospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37(9):1290–6.
Wells AU, Cullinan P, Hansell DM, Rubens MB, Black CM, Newman-Taylor AJ, Du Bois RM. Fibrosing alveolitis associated with systemic sclerosis has a better prognosis than lone cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149(6):1583–90.
Vallance DK, Lynch JP 3rd, McCune WJ. Immunosuppressive treatment of the pulmonary manifestations of progressive systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1995;7(3):174–82.
Schnabel A, Reuter M, Gross WL. Intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide in the treatment of interstitial lung disease due to collagen vascular diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(7):1215–20.
Varai G, Earle L, Jimenez SA, Steiner RM, Varga J. A pilot study of intermittent intravenous cyclophosphamide for the treatment of systemic sclerosis associated lung disease. J Rheumatol. 1998;25(7):1325–9.
Liossis SN, Bounas A, Andonopoulos AP. Mycophenolate mofetil as first-line treatment improves clinically evident early scleroderma lung disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(8):1005–8.
Tsukamoto H, Nagafuji K, Horiuchi T, Miyamoto T, Aoki K, Takase K, Henzan H, Himeji D, Koyama T, Miyake K, et al. A phase I-II trial of autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of refractory autoimmune disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(4):508–14.
White B, Moore WC, Wigley FM, Xiao HQ, Wise RA. Cyclophosphamide is associated with pulmonary function and survival benefit in patients with scleroderma and alveolitis. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132(12):947–54.
Griffiths B, Miles S, Moss H, Robertson R, Veale D, Emery P. Systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease: a pilot study using pulse intravenous methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide to assess the effect on high resolution computed tomography scan and lung function. J Rheumatol. 2002;29(11):2371–8.
Airo P, Danieli E, Parrinello G, Antonioli CM, Cavazzana I, Toniati P, Franceschini F, Cattaneo R. Intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy for systemic sclerosis. A single-center experience and review of the literature with pooled analysis of lung function test results. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22(5):573–8.
Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, Goldin J, Roth MD, Furst DE, Arriola E, Silver R, Strange C, Bolster M, et al. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(25):2655–66.
Nadashkevich O, Davis P, Fritzler M, Kovalenko W. A randomized unblinded trial of cyclophosphamide versus azathioprine in the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25(2):205–12.
Hoyles RK, Ellis RW, Wellsbury J, Lees B, Newlands P, Goh NS, Roberts C, Desai S, Herrick AL, McHugh NJ, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of corticosteroids and intravenous cyclophosphamide followed by oral azathioprine for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(12):3962–70.
Kowal-Bielecka O, Landewe R, Avouac J, Chwiesko S, Miniati I, Czirjak L, Clements P, Denton C, Farge D, Fligelstone K, et al. EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: a report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR). Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(5):620–8.
Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1980,23(5):581–90.
Clements P, Lachenbruch P, Siebold J, White B, Weiner S, Martin R, Weinstein A, Weisman M, Mayes M, Collier D. Inter and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan TSS) in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1995;22(7):1281–5.
Tashkin DP, Elashoff R, Clements PJ, Roth MD, Furst DE, Silver RM, Goldin J, Arriola E, Strange C, Bolster MB, et al. Effects of 1-year treatment with cyclophosphamide on outcomes at 2 years in scleroderma lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176(10):1026–34.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Systemic Sclerosis Research Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tochimoto, A., Kawaguchi, Y., Hara, M. et al. Efficacy and safety of intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy with oral prednisolone in the treatment of interstitial lung disease with systemic sclerosis: 4-year follow-up. Mod Rheumatol 21, 296–301 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-010-0403-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-010-0403-6