Abstract
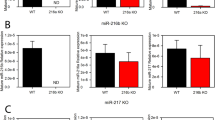
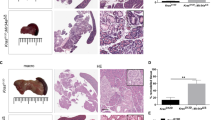
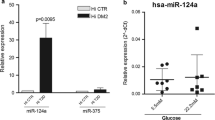
Mice harboring a G12D activating Kras mutation are among the most heavily studied models in the field of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) research. miRNAs are differentially expressed in PDAC from patients and mouse models of PDAC. To better understand the relationship that Kras activation has on miRNA expression, we profiled the expression of 629 miRNAs in RNA isolated from the pancreas of control, young, and old P48+/Cre;LSL-KRASG12D as well as PDX-1-Cre;LSL-KRASG12D mice. One hundred of the differentially expressed miRNAs had increased expression in the advanced disease (old) P48+/Cre;LSL-KRASG12D compared to wild-type mice. Interestingly, the expression of three miRNAs, miR-216a, miR-216b, and miR-217, located within a ∼30-kbp region on 11qA3.3, decreased with age (and phenotype severity) in these mice. miR-216/-217 expression was also evaluated in another acinar-specific ELa-KrasG12D mouse model and was downregulated as well. As miR-216/-217 are acinar enriched, reduced in human PDAC and target KRAS, we hypothesized that they may maintain acinar differentiation or represent tumor suppressive miRNAs. To test this hypothesis, we deleted a 27.9-kbp region of 11qA3.3 containing the miR-216/-217 host gene in the mouse’s germ line. We report that germ line deletion of this cluster is embryonic lethal in the mouse. We estimate that lethality occurs shortly after E9.5. qPCR analysis of the miR-216b and miR-217 expression in the heterozygous animals showed no difference in expression, suggesting haplosufficiency by some type of compensatory mechanism. We present the differential miRNA expression in KrasG12D transgenic mice and report lethality from deletion of the miR-216/-217 host gene in the mouse’s germ line.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Banerjee S, Logna F, Bao B, Philip PA, Korc M, Sarkar FH (2012) Inactivation of Ink4a/Arf leads to deregulated expression of miRNAs in K-Ras transgenic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. J Cell Physiol 227:3373–3380. doi:10.1002/jcp.24036
Azevedo-Pouly AC, Elgamal OA, Schmittgen TD (2014) RNA isolation from mouse pancreas: a ribonuclease-rich tissue. Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE. e51779. doi: 10.3791/51779
Bardeesy N, Cheng KH, Berger JH, Chu GC, Pahler J, Olson P, Hezel AF, Horner J, Lauwers GY, Hanahan D, DePinho RA (2006) Smad4 is dispensable for normal pancreas development yet critical in progression and tumor biology of pancreas cancer. Genes Dev 20:3130–3146. doi:10.1101/gad.1478706
Bassett AR, Akhtar A, Barlow DP, Bird AP, Brockdorff N, Duboule D, Ephrussi A, Ferguson-Smith AC, Gingeras TR, Haerty W, Higgs DR, Miska EA, Ponting CP (2014) Considerations when investigating lncRNA function in vivo. Elife 3:e03058. doi:10.7554/eLife.03058
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 297:1901–1908
Bravo-Egana V, Rosero S, Molano RD, Pileggi A, Ricordi C, Dominguez-Bendala J, Pastori RL (2008) Quantitative differential expression analysis reveals miR-7 as major islet microRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 366:922–926. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.12.052
Brembeck FH, Schreiber FS, Deramaudt TB, Craig L, Rhoades B, Swain G, Grippo P, Stoffers DA, Silberg DG, Rustgi AK (2003) The mutant K-ras oncogene causes pancreatic periductal lymphocytic infiltration and gastric mucous neck cell hyperplasia in transgenic mice. Cancer Res 63:2005–2009
Cleaver O, MacDonald RJ (2010) Developmental molecular biology of the pancreas. In: Neoptolemos RUJP, Abbruzzese JL, Buchler MW (eds) Pancreatic cancer. Springer, New York, pp 71–117.
Costinean S, Zanesi N, Pekarsky Y, Tili E, Volinia S, Heerema N, Croce CM (2006) Pre-B cell proliferation and lymphoblastic leukemia/high-grade lymphoma in E(mu)-miR155 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:7024–7029
Crowley JJ, Collins AL, Lee RJ, Nonneman RJ, Farrell MS, Ancalade N, Mugford JW, Agster KL, Nikolova VD, Moy SS, Sullivan PF (2015) Disruption of the microRNA 137 primary transcript results in early embryonic lethality in mice. Biol Psychiatry 77:e5–e7. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.05.022
Deng M, Tang H, Zhou Y, Zhou M, Xiong W, Zheng Y, Ye Q, Zeng X, Liao Q, Guo X, Li X, Ma J, Li G (2011) miR-216b suppresses tumor growth and invasion by targeting KRAS in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cell Sci 124:2997–3005. doi:10.1242/jcs.085050
Deng S, Zhu S, Wang B, Li X, Liu Y, Qin Q, Gong Q, Niu Y, Xiang C, Chen J, Yan J, Deng S, Yin T, Yang M, Wu H, Wang C, Zhao G (2014) Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer demonstrate active epithelial-mesenchymal transition profile, regulated by miR-217-SIRT1 pathway. Cancer Lett 355:184–191. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.08.007
Desai BM, Oliver-Krasinski J, De Leon DD, Farzad C, Hong N, Leach SD, Stoffers DA (2007) Preexisting pancreatic acinar cells contribute to acinar cell, but not islet beta cell, regeneration. J Clin Invest 117:971–977. doi:10.1172/JCI29988
Farmer DT, Shariat N, Park CY, Liu HJ, Mavropoulos A, McManus MT (2013) Partially penetrant postnatal lethality of an epithelial specific microRNA in a mouse knockout. PLoS One 8:e76634. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076634
Grippo PJ, Nowlin PS, Demeure MJ, Longnecker DS, Sandgren EP (2003) Preinvasive pancreatic neoplasia of ductal phenotype induced by acinar cell targeting of mutant Kras in transgenic mice. Cancer Res 63:2016–2019
Guerra C, Schuhmacher AJ, Canamero M, Grippo PJ, Verdaguer L, Perez-Gallego L, Dubus P, Sandgren EP, Barbacid M (2007) Chronic pancreatitis is essential for induction of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by K-ras oncogenes in adult mice. Cancer Cell 11:291–302. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.01.012
Habbe N, Shi G, Meguid RA, Fendrich V, Esni F, Chen H, Feldmann G, Stoffers DA, Konieczny SF, Leach SD, Maitra A (2008) Spontaneous induction of murine pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (mPanIN) by acinar cell targeting of oncogenic Kras in adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:18913–18918. doi:10.1073/pnas.0810097105
Hale MA, Kagami H, Shi L, Holland AM, Elsasser HP, Hammer RE, MacDonald RJ (2005) The homeodomain protein PDX1 is required at mid-pancreatic development for the formation of the exocrine pancreas. Dev Biol 286:225–237. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.07.026
Hingorani SR, Petricoin EF, Maitra A, Rajapakse V, King C, Jacobetz MA, Ross S, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Hitt BA, Kawaguchi Y, Johann D, Liotta LA, Crawford HC, Putt ME, Jacks T, Wright CV, Hruban RH, Lowy AM, Tuveson DA (2003) Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell 4:437–450
Hingorani SR, Wang L, Multani AS, Combs C, Deramaudt TB, Hruban RH, Rustgi AK, Chang S, Tuveson DA (2005) Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Cell 7:469–483. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.04.023
Hsu SH, Wang B, Kota J, Yu J, Costinean S, Kutay H, Yu L, Bai S, La Perle K, Chivukula RR, Mao H, Wei M, Clark KR, Mendell JR, Caligiuri MA, Jacob ST, Mendell JT, Ghoshal K (2012) Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver. J Clin Invest 122:2871–2883. doi:10.1172/JCI63539
Ijichi H, Chytil A, Gorska AE, Aakre ME, Fujitani Y, Fujitani S, Wright CV, Moses HL (2006) Aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice caused by pancreas-specific blockade of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cooperation with active Kras expression. Genes Dev 20:3147–3160. doi:10.1101/gad.1475506
Jiang J, Azevedo-Pouly AC, Redis RS, Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Allard D, Sutaria DS, Badawi M, Elgamal OA, Lerner MR, Brackett DJ, Calin GA, Schmittgen TD (2016) Globally increased ultraconserved noncoding RNA expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10242
Kawaguchi Y, Cooper B, Gannon M, Ray M, MacDonald RJ, Wright CVE (2002) The role of the transcriptional regulator Ptf1a in converting intestinal to pancreatic progenitors. Nat Genet 32:128–134. doi:10.1038/ng959
Kuhnert F, Mancuso MR, Hampton J, Stankunas K, Asano T, Chen CZ, Kuo CJ (2008) Attribution of vascular phenotypes of the murine Egfl7 locus to the microRNA miR-126. Development 135:3989–3993. doi:10.1242/dev.029736
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD (2007) Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 120:1046–1054
Liu N, Bezprozvannaya S, Williams AH, Qi X, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN (2008) microRNA-133a regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation and suppresses smooth muscle gene expression in the heart. Genes Dev 22:3242–3254. doi:10.1101/gad.1738708
Medina PP, Nolde M, Slack FJ (2010) OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature 467:86–90. doi:10.1038/nature09284
Morris JP, Greer R, Russ HA, von Figura G, Kim GE, Busch A, Lee J, Hertel KJ, Kim S, McManus M, Hebrok M (2014) Dicer regulates differentiation and viability during mouse pancreatic cancer initiation. PLoS One 9:e95486. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095486
Park CY, Jeker LT, Carver-Moore K, Oh A, Liu HJ, Cameron R, Richards H, Li Z, Adler D, Yoshinaga Y, Martinez M, Nefadov M, Abbas AK, Weiss A, Lanier LL, de Jong PJ, Bluestone JA, Srivastava D, McManus MT (2012) A resource for the conditional ablation of microRNAs in the mouse. Cell Rep 1:385–391. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.02.008
Piovan C, Amari F, Lovat F, Chen Q, Coppola V (2014) Generation of mouse lines conditionally over-expressing microRNA using the Rosa26-Lox-Stop-Lox system. Methods Mol Biol 1194:203–224. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-1215-5_11
Rachagani S, Macha MA, Menning MS, Dey P, Pai P, Smith LM, Mo YY, Batra SK (2015) Changes in microRNA (miRNA) expression during pancreatic cancer development and progression in a genetically engineered KrasG12D;Pdx1-Cre mouse (KC) model. Oncotarget 6:40295–40309. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5641
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM (2014) Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 74:2913–2921. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155
Schmittgen TD, Lee EJ, Jiang J, Sarkar A, Yang L, Elton TS, Chen C (2008) Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA. Methods 44:31–38
Schultz NA, Werner J, Willenbrock H, Roslind A, Giese N, Horn T, Wojdemann M, Johansen JS (2012) MicroRNA expression profiles associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and ampullary adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 25:1609–1622. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2012.122
Shakya R, Gonda T, Quante M, Salas M, Kim S, Brooks J, Hirsch S, Davies J, Cullo A, Olive K, Wang TC, Szabolcs M, Tycko B, Ludwig T (2013) Hypomethylating therapy in an aggressive stroma-rich model of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 73:885–896. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1880
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65:5–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21254
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, Cannon T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, Labourier E, Hahn SA (2007) MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 26:4442–4452
Szafranska AE, Doleshal M, Edmunds HS, Gordon S, Luttges J, Munding JB, Barth RJ Jr, Gutmann EJ, Suriawinata AA, Marc Pipas J, Tannapfel A, Korc M, Hahn SA, Labourier E, Tsongalis GJ (2008) Analysis of microRNAs in pancreatic fine-needle aspirates can classify benign and malignant tissues. Clin Chem 54:1716–1724. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2008.109603
Tirmenstein MA, Nicholls-Grzemski FA, Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA, Fariss MW (2000) Characterization of nitric oxide production following isolation of rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Sci 53:56–62
Tsai WC, Hsu SD, Hsu CS, Lai TC, Chen SJ, Shen R, Huang Y, Chen HC, Lee CH, Tsai TF, Hsu MT, Wu JC, Huang HD, Shiao MS, Hsiao M, Tsou AP (2012) MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest 122:2884–2897. doi:10.1172/JCI63455
Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM, Lintault L, Meissner A, Erkeland SJ, Newman J, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Stone JR, Jaenisch R, Sharp PA, Jacks T (2008) Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 132:875–886. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.019
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M (2011) Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 378:607–620. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62307-0
Visani M, Acquaviva G, Fiorino S, Bacchi Reggiani ML, Masetti M, Franceschi E, Fornelli A, Jovine E, Fabbri C, Brandes AA, Tallini G, Pession A, de Biase D (2015) Contribution of microRNA analysis to characterisation of pancreatic lesions: a review. J Clin Pathol 68:859–869. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2015-203246
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2257–2261
Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Kiss I, Klusova S, Hlavsa J, Prochazka V, Kala Z, Mazanec J, Hausnerova J, Kren L, Hermanova M, Lenz J, Karasek P, Vyzula R, Slaby O (2015) miR-21, miR-34a, miR-198 and miR-217 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Diagn Pathol 10:38. doi:10.1186/s13000-015-0272-6
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA, Qi X, McAnally J, Hill JA, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN (2008) The endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity and angiogenesis. Dev Cell 15:261–271. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.07.002
Xue Y, Abou Tayoun AN, Abo KM, Pipas JM, Gordon SR, Gardner TB, Barth RJ Jr, Suriawinata AA, Tsongalis GJ (2013) MicroRNAs as diagnostic markers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its precursor, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasm. Cancer Genet 206:217–221. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2013.05.020
Yu J, Li A, Hong SM, Hruban RH, Goggins M (2012) MicroRNA alterations of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias. Clin Cancer Res 18:981–992. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2347
Zhao Y, Ransom JF, Li A, Vedantham V, von Drehle M, Muth AN, Tsuchihashi T, McManus MT, Schwartz RJ, Srivastava D (2007) Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell 129:303–317. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.030
Zhao WG, Yu SN, Lu ZH, Ma YH, Gu YM, Chen J (2010) The miR-217 microRNA functions as a potential tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting Kras. Carcinogenesis 31:1726–1733. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq160
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Pelotonia idea grant from the Ohio State University to T.D.S. and E.C. A.C.P.A.P. was supported by NIH fellowship 5F31CA142238. We thank Dr. David Tuveson for providing the RNA samples from the KC and control mice. We thank Dr. Caifu Chen for his assistance with the mouse TaqMan miRNA assays and Luke Bramlage and Andrea Haughtvedt for their technical assistance. We also thank Inga Carsten of the Genetically Engineered Mouse Modeling Core for the help in mES microinjection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article forms part of a special issue of Functional & Integrative Genomics entitled “miRNA in model and complex organisms” (Issue Editors: Hikmet Budak and Baohong Zhang).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Table 1
(XLSX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azevedo-Pouly, A.C.P., Sutaria, D.S., Jiang, J. et al. miR-216 and miR-217 expression is reduced in transgenic mouse models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, knockout of miR-216/miR-217 host gene is embryonic lethal. Funct Integr Genomics 17, 203–212 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0512-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0512-1