Abstract.
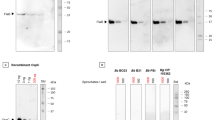
In order to determine the prevalence of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis (HGE) in Belgium, the sera of 216 patients previously diagnosed with Borrelia burgdorferi infection were analysed for possible coinfection with the agent of HGE. For this purpose, an indirect immunofluorescence assay was applied, and positive results were confirmed by Western blot using a 44-kilodalton recombinant protein (rP44) specific for the agent of HGE. Sixteen of the 216 (7.4%) sera tested were positive for the HGE agent using indirect immunofluorescence assay, and seven (3%) of them were confirmed positive by Western blot. These data suggest the agent for HGE is present in Belgium and may cause coinfection in patients infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, as has been reported in the USA and elsewhere in Europe. This is the first report documenting the identification of this agent in Belgium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guillaume, .B., Heyman, .P., Lafontaine, .S. et al. Seroprevalence of Human Granulocytic Ehrlichiosis Infection in Belgium. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 21, 397–400 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-002-0720-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-002-0720-6