Abstract
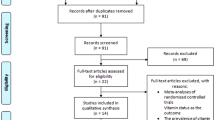
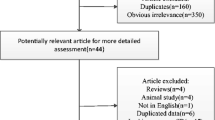
To estimate the associations between vitamin D status and Parkinson’s disease (PD). We searched electronic databases of the human literature in PubMed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library up to February, 2014 using the following keywords: ‘vitamin D’ or ‘25(OH)D’ and ‘status’ or ‘deficiency’ or ‘insufficiency’ and ‘Parkinson’s disease’. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted on observational studies that reported the association between blood vitamin D levels and PD. Seven studies met the inclusion criteria. 1,008 patients and 4,536 controls were included. Results of our meta-analysis show that PD patients had lower mean levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] than healthy controls [weighted mean difference (MD), −16.9, 95 % confidence interval (CI)], −33.5 to −0.2). Patients with vitamin D insufficiency [25(OH)D level <75 nmol/l] had an increased risk of PD (OR 1.5, 95 % CI 1.1–2.0). Patients with vitamin D deficiency [25(OH)D level <50 nmol/l] experienced a twofold increased risk of PD (OR 2.2, 95 % CI 1.5–3.4). Low vitamin D levels are associated with an increased risk of PD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dick FD, De Palma G, Ahmadi A, Scott NW, Prescott GJ, Bennett J, Semple S, Dick S, Counsell C, Mozzoni P, Haites N, Wettinger SB, Mutti A, Otelea M, Seaton A, Söderkvist P, Felice A, Geoparkinson study group (2007) Environmental risk factors for Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism: the Geoparkinson study. Occup Environ Med 64(10):666–672
Hancock DB, Martin ER, Mayhew GM, Stajich JM, Jewett R, Stacy MA, Scott BL, Vance JM, Scott WK (2008) Pesticide exposure and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a family-based case–control study. BMC Neurol 8(3):6
Henchcliffe C, Beal MF (2008) Mitochondrial biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 4(11):600–609
DeLuca GC, Kimball SM, Kolasinski J, Ramagopalan SV, Ebers GC (2013) Review: the role of vitamin D in nervous system health and disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39(5):458–484
Zittermann A, Schleithoff SS, Koerfer R (2006) Vitamin D insufficiency in congestive heart failure: why and what to do about it? Heart Fail Rev 11(1):25–33
Chaudhuri JR, Mridula KR, Alladi S, Anamika A, Umamahesh M, Balaraju B, Swath A, Bandaru VS (2014) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency in ischemic stroke and subtypes in Indian patients. J Stroke 16(1):44–50
Brøndum-Jacobsen P, Nordestgaard BG, Schnohr P, Benn M (2013) 25-hydroxyvitamin D and symptomatic ischemic stroke: an original study and meta-analysis. Ann Neurol 73(1):38–47
Martinelli V, Dalla Costa G, Colombo B, Dalla Libera D, Rubinacci A, Filippi M, Furlan R, Comi G (2014) Vitamin D levels and risk of multiple sclerosis in patients with clinically isolated syndromes. Mult Scler 20(2):147–155
Guzmán-Fulgencio M, García-Álvarez M, Berenguer J, Jiménez-Sousa MÁ, Cosín J, Pineda-Tenor D, Carrero A, Aldámiz T, Alvarez E, López JC, Resino S (2014) Vitamin D deficiency is associated with severity of liver disease in HIV/HCV coinfected patients. J Infect 68(2):176–184
Camargo CA Jr, Manson JE (2014) Vitamin D supplementation and risk of infectious disease: no easy answers. Am J Clin Nutr 99(1):3–4
Gorham ED, Garland CF, Garland FC, Grant WB, Mohr SB, Lipkin M, Newmark HL, Giovannucci E, Wei M, Holick MF (2007) Optimal vitamin D status for colorectal cancer prevention: a quantitative meta-analysis. Am J Prev Med 32(3):210–216
Evatt ML (2010) Beyond vitamin status: is there a role for vitamin D in Parkinson disease? Arch Neurol 67(7):795–797
Newmark HL, Newmark J (2007) Vitamin D and Parkinson’s disease––a hypothesis. Mov Disord 22(4):461–468
Evatt ML, DeLong MR, Kumari M, Auinger P, McDermott MP, Tangpricha V, Parkinson Study Group DATATOP Investigators (2011) High prevalence of hypovitaminosis D status in patients with early Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 68(3):314–319
Eyles DW, Smith S, Kinobe R, Hewison M, McGrath JJ (2005) Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1 alpha-hydroxylase in human brain. J Chem Neuroanat 29(1):21–30
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta- analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283(15):2008–2012
Duckitt K, Harrington D (2005) Risk factors for pre-eclampsia at antenatal booking: systematic review of controlled studies. BMJ 330(7491):565
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 357(3):266–281
Abou-Raya S, Helmii M, Abou-Raya A (2009) Bone and mineral metabolism in older adults with Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing 38(6):675–680
van den Bos F, Speelman AD, van Nimwegen M, van der Schouw YT, Backx FJ, Bloem BR, Munneke M, Verhaar HJ (2013) Bone mineral density and vitamin D status in Parkinson’s disease patients. J Neurol 260(3):754–760
Ding H, Dhima K, Lockhart KC, Locascio JJ, Hoesing AN, Duong K, Trisini-Lipsanopoulos A, Hayes MT, Sohur US, Wills AM, Mollenhauer B, Flaherty AW, Hung AY, Mejia N, Khurana V, Gomperts SN, Selkoe DJ, Schwarzschild MA, Schlossmacher MG, Hyman BT, Sudarsky LR, Growdon JH, Scherzer CR (2013) Unrecognized vitamin D3 deficiency is common in Parkinson disease: Harvard Biomarker Study. Neurology 81(17):1531–1537
Evatt ML, Delong MR, Khazai N, Rosen A, Triche S, Tangpricha V (2008) Prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in patients with Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 65(10):1348–1352
Knekt P, Kilkkinen A, Rissanen H, Marniemi J, Sääksjärvi K, Heliövaara M (2010) Serum vitamin D and the risk of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 67(7):808–811
Sato Y, Honda Y, Kaji M, Asoh T, Hosokawa K, Kondo I, Satoh K (2002) Amelioration of osteoporosis by menatetrenone in elderly female Parkinson’s disease patients with vitamin D deficiency. Bone 31(1):114–118
Sato Y, Honda Y, Iwamoto J, Kanoko T, Satoh K (2005) Abnormal bone and calcium metabolism in immobilized Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov Disord 20(12):1598–1603
Egan KM, Signorello LB, Munro HM, Hargreaves MK, Hollis BW, Blot WJ (2008) Vitamin D insufficiency among African–Americans in the southeastern United States: implications for cancer disparities (United States). Cancer Causes Control 19(5):527–535
Tsiaras WG, Weinstock MA (2011) Factors influencing vitamin D status. Acta Derm Venereol 91(2):115–124
Zhao Y, Sun Y, Ji HF, Shen L (2013) Vitamin D levels in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: a meta-analysis. Nutrition 29(6):828–832
Lawson DE, Paul AA, Black AE, Cole TJ, Mandal AR, Davie M (1979) Relative contributions of diet and sunlight to vitamin D state in the elderly. Br Med J 2(6185):303–305
Eyles DW, Smith S, Kinobe R, Hewison M, McGrath JJ (2005) Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1 alpha-hydroxylase in human brain. J Chem Neuroanat 29(1):21–30
Buell JS, Dawson-Hughes B (2008) Vitamin D and neurocognitive dysfunction: preventing “D”ecline? Mol Aspects Med 29(6):415–422
Han X, Xue L, Li Y, Chen B, Xie A (2012) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism and its association with Parkinson’s disease in Chinese Han population. Neurosci Lett 525(1):29–33
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Harbin Special Funds for Research of Scientific and Technological Innovative Talents (No. 2011RFQYS092) and Innovative Foundation of the Harbin Medical University (HCXS2010014).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Z. Lv and H. Qi contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Z., Qi, H., Wang, L. et al. Vitamin D status and Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci 35, 1723–1730 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1821-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1821-6