Abstract
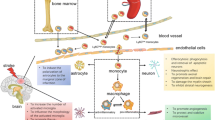
Stroke is one of the leading causes of mortality and morbidity in the world. The activation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL) plays an important role in the inflammatory response after ischemic stroke. However, in the current literature, there are few studies discussing the process and role of peripheral PMNL activation. Here, we give a comprehensive description of peripheral PMNL activation after ischemic stroke and discuss their potential roles in the process of ischemic injury. Based on our analysis, peripheral PMNL activation is supposed to be attributed to systemic inflammatory response to cerebral ischemic insult, not reflecting the activity of PMNL in local ischemic brain. Inhibiting peripheral PMNL activation in stroke animals has been effective in reducing infarction and improving behavioral outcome; thus, the same approach of inhibiting peripheral PMNL activation is a promising therapeutic strategy for stroke patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PMNL:
-
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1 beta
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- CAM:
-
Cell adhesion molecules
- PSGL-1:
-
P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1
- SLe x:
-
Sialyl Lewis x
- CD11a:
-
Cluster of differentiation molecule 11a
- LFA-1:
-
Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1
- Mac-1:
-
Macrophage-1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1
- NGAL:
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
- NP4:
-
Neutrophil proteinase 4
- ROCK:
-
Rho-associated protein kinase
- CDC42:
-
Cell division control protein 42
- MACO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- GM-CSF:
-
Granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- NIHSS:
-
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
- dMRI:
-
Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Kriz J, Lalancette-Hebert M (2009) Inflammation, plasticity and real-time imaging after cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 117(5):497–509. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0496-1
Nilupul Perera M, Ma HK, Arakawa S, Howells DW, Markus R, Rowe CC, Donnan GA (2006) Inflammation following stroke. J Clin Neurosci: Official J Neurosurg Soc Australasia 13(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2005.07.005
Htun P, Fateh-Moghadam S, Tomandl B, Handschu R, Klinger K, Stellos K, Garlichs C, Daniel W, Gawaz M (2006) Course of platelet activation and platelet–leukocyte interaction in cerebrovascular ischemia. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 37(9):2283–2287. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000236638.75591.61
Huang J, Upadhyay UM, Tamargo RJ (2006) Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surg Neurol 66(3):232–245. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2005.12.028
Smith CJ, Emsley HC, Gavin CM, Georgiou RF, Vail A, Barberan EM, del Zoppo GJ, Hallenbeck JM, Rothwell NJ, Hopkins SJ, Tyrrell PJ (2004) Peak plasma interleukin-6 and other peripheral markers of inflammation in the first week of ischaemic stroke correlate with brain infarct volume, stroke severity and long-term outcome. BMC Neurol 4:2. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-4-2
Petrault O, Ouk T, Gautier S, Laprais M, Gele P, Bastide M, Bordet R (2005) Pharmacological neutropenia prevents endothelial dysfunction but not smooth muscle functions impairment induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Br J Pharmacol 144(8):1051–1058. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706124
Buck BH, Liebeskind DS, Saver JL, Bang OY, Yun SW, Starkman S, Ali LK, Kim D, Villablanca JP, Salamon N, Razinia T, Ovbiagele B (2008) Early neutrophilia is associated with volume of ischemic tissue in acute stroke. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 39(2):355–360. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.490128
Elneihoum AM, Falke P, Axelsson L, Lundberg E, Lindgarde F, Ohlsson K (1996) Leukocyte activation detected by increased plasma levels of inflammatory mediators in patients with ischemic cerebrovascular diseases. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 27(10):1734–1738
Frijns CJ, Kappelle LJ (2002) Inflammatory cell adhesion molecules in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 33(8):2115–2122
Kostulas N, Kivisakk P, Huang Y, Matusevicius D, Kostulas V, Link H (1998) Ischemic stroke is associated with a systemic increase of blood mononuclear cells expressing interleukin-8 mRNA. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 29(2):462–466
Fiszer U, Korczak-Kowalska G, Palasik W, Korlak J, Gorski A, Czlonkowska A (1998) Increased expression of adhesion molecule CD18 (LFA-1beta) on the leukocytes of peripheral blood in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol Scand 97(4):221–224
Violi F, Rasura M, Alessandri C, Intiso D, Germani M, Servi M, Fieschi C, Balsano F (1988) Leukocyte response in patients suffering from acute stroke. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 19(10):1283–1284
Santos-Silva A, Rebelo I, Castro E, Belo L, Catarino C, Monteiro I, Almeida MD, Quintanilha A (2002) Erythrocyte damage and leukocyte activation in ischemic stroke. Clinica Chimica Acta Int J Clin Chem 320(1–2):29–35
Tsai NW, Chang WN, Shaw CF, Jan CR, Huang CR, Chen SD, Chuang YC, Lee LH, Lu CH (2009) The value of leukocyte adhesion molecules in patients after ischemic stroke. J Neurol 256(8):1296–1302. doi:10.1007/s00415-009-5117-3
Harrison MJ, Marshall J (1987) Does the peripheral blood leukocyte count predict the risk of transient ischaemic attacks and strokes? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50(11):1558–1559
Ross AM, Hurn P, Perrin N, Wood L, Carlini W, Potempa K (2007) Evidence of the peripheral inflammatory response in patients with transient ischemic attack. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 16(5):203–207. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2007.05.002
Zeller JA, Lenz A, Eschenfelder CC, Zunker P, Deuschl G (2005) Platelet–leukocyte interaction and platelet activation in acute stroke with and without preceding infection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(7):1519–1523. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000167524.69092.16
Yoon SS, Dambrosia J, Chalela J, Ezzeddine M, Warach S, Haymore J, Davis L, Baird AE (2004) Rising statin use and effect on ischemic stroke outcome. BMC Med 2:4. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-2-4
Balestrino M, Partinico D, Finocchi C, Gandolfo C (1998) White blood cell count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate correlate with outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 7(2):139–144
Kozuka K, Kohriyama T, Nomura E, Ikeda J, Kajikawa H, Nakamura S (2002) Endothelial markers and adhesion molecules in acute ischemic stroke—sequential change and differences in stroke subtype. Atherosclerosis 161(1):161–168
Kakkar AK, Lefer DJ (2004) Leukocyte and endothelial adhesion molecule studies in knockout mice. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4(2):154–158. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2004.01.003
Carlos TM, Harlan JM (1994) Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood 84(7):2068–2101
Kim JS, Chopp M, Chen H, Levine SR, Carey JL, Welch KM (1995) Adhesive glycoproteins CD11a and CD18 are upregulated in the leukocytes from patients with ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attacks. J Neurol Sci 128(1):45–50
Kawamura T, Umemura T, Kanai A, Nagashima M, Nakamura N, Uno T, Nakayama M, Sano T, Hamada Y, Nakamura J, Hotta N (2006) Soluble adhesion molecules and C-reactive protein in the progression of silent cerebral infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metab Clin Exp 55(4):461–466. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2005.10.007
Fassbender K, Mossner R, Motsch L, Kischka U, Grau A, Hennerici M (1995) Circulating selectin- and immunoglobulin-type adhesion molecules in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 26(8):1361–1364
Chamorro A, Cervera A, Castillo J, Davalos A, Aponte JJ, Planas AM (2002) Unfractionated heparin is associated with a lower rise of serum vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neurosci Lett 328(3):229–232
Kubo Y, Ogasawara K, Kakino S, Kashimura H, Tomitsuka N, Sugawara A, Ogawa A (2008) Serum inflammatory adhesion molecules and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein correlates with delayed ischemic neurologic deficits after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 69(6):592–596. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2008.02.014 (discussion 596)
Wu G, Li F, Li P, Ruan C (1993) Detection of plasma alpha-granule membrane protein GMP-140 using radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies in thrombotic diseases. Haemostasis 23(2):121–128
Olofsson AM, Arfors KE, Ramezani L, Wolitzky BA, Butcher EC, von Andrian UH (1994) E-selectin mediates leukocyte rolling in interleukin-1-treated rabbit mesentery venules. Blood 84(8):2749–2758
Bleecker JD, Coulier I, Fleurinck C, Reuck JD (1998) Circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin in acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 7(3):192–195
Bevilacqua MP, Nelson RM, Mannori G, Cecconi O (1994) Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules in human disease. Annu Rev Med 45:361–378. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.45.1.361
Wysocka J, Lipartowska R, Lipska A (2001) Granules of neutrophils. Postepy higieny i medycyny doswiadczalnej 55(1):177–188
Vermeiren GL, Claeys MJ, van Bockstaele D, Grobben B, Slegers H, Bossaert L, Jorens PG (2000) Reperfusion injury after focal myocardial ischaemia: polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation and its clinical implications. Resuscitation 45(1):35–61
Kjeldsen L, Johnsen AH, Sengelov H, Borregaard N (1993) Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem 268(14):10425–10432
Ohlsson K, Linder C, Rosengren M (1990) Monoclonal antibodies specific for neutrophil proteinase 4. Production and use for isolation of the enzyme. Bio Chem Hoppe-Seyler 371(7):549–555
Harlan JM (1987) Neutrophil-mediated vascular injury. Acta medica Scandinavica Supplementum 715:123–129
Elneihoum AM, Falke P, Hedblad B, Lindgarde F, Ohlsson K (1997) Leukocyte activation in atherosclerosis: correlation with risk factors. Atherosclerosis 131(1):79–84
Cojocaru IM, Cojocaru M, Burcin C (2006) Evaluation of granulocyte elastase as a sensitive diagnostic parameter of inflammation in first ischemic stroke. Romanian J Intern Med 44(3):317–321
Trapp T, Olah L, Holker I, Besselmann M, Tiesler C, Maeda K, Hossmann KA (2001) GTPase RhoB: an early predictor of neuronal death after transient focal ischemia in mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 17(5):883–894. doi:10.1006/mcne.2001.0971
Brabeck C, Mittelbronn M, Bekure K, Meyermann R, Schluesener HJ, Schwab JM (2003) Effect of focal cerebral infarctions on lesional RhoA and RhoB expression. Arch Neurol 60(9):1245–1249. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.9.1245
Yano K, Kawasaki K, Hattori T, Tawara S, Toshima Y, Ikegaki I, Sasaki Y, Satoh S, Asano T, Seto M (2008) Demonstration of elevation and localization of Rho-kinase activity in the brain of a rat model of cerebral infarction. Eur J Pharmacol 594(1–3):77–83. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.045
Feske SK, Sorond FA, Henderson GV, Seto M, Hitomi A, Kawasaki K, Sasaki Y, Asano T, Liao JK (2009) Increased leukocyte ROCK activity in patients after acute ischemic stroke. Brain Res 1257:89–93. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.12.045
Shimokawa H (2002) Rho-kinase as a novel therapeutic target in treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 39(3):319–327
Fukata Y, Amano M, Kaibuchi K (2001) Rho-Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(1):32–39
Frankfurt O, Tallman MS (2011) The hematopoietic growth factors in acute leukemia: US perspective. Cancer Treat Res 157:307–337. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-7073-2_18
Paczkowska E, Larysz B, Rzeuski R, Karbicka A, Jalowinski R, Kornacewicz-Jach Z, Ratajczak MZ, Machalinski B (2005) Human hematopoietic stem/progenitor-enriched CD34(+) cells are mobilized into peripheral blood during stress related to ischemic stroke or acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Haematol 75(6):461–467. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0609.2005.00536.x
Offner H, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD (2009) Effect of experimental stroke on peripheral immunity: CNS ischemia induces profound immunosuppression. Neuroscience 158(3):1098–1111. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.033
Franzen R, Bouhy D, Schoenen J (2004) Nervous system injury: focus on the inflammatory cytokine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. Neurosci Lett 361(1–3):76–78. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.018
Tarkowski E, Rosengren L, Blomstrand C, Wikkelso C, Jensen C, Ekholm S, Tarkowski A (1997) Intrathecal release of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines during stroke. Clin Exp Immunol 110(3):492–499
Ridker PM (1998) C-reactive protein and risks of future myocardial infarction and thrombotic stroke. Eur Heart J 19(1):1–3
Elkind MS, Cheng J, Boden-Albala B, Paik MC, Sacco RL (2001) Elevated white blood cell count and carotid plaque thickness: the northern Manhattan stroke study. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 32(4):842–849
Loimaala A, Rontu R, Vuori I, Mercuri M, Lehtimaki T, Nenonen A, Bond MG (2006) Blood leukocyte count is a risk factor for intima-media thickening and subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in middle-aged men. Atherosclerosis 188(2):363–369. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.11.021
Price CJ, Menon DK, Peters AM, Ballinger JR, Barber RW, Balan KK, Lynch A, Xuereb JH, Fryer T, Guadagno JV, Warburton EA (2004) Cerebral neutrophil recruitment, histology, and outcome in acute ischemic stroke: an imaging-based study. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 35(7):1659–1664. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000130592.71028.92
Kazmierski R, Guzik P, Ambrosius W, Kozubski W (2001) Leukocytosis in the first day of acute ischemic stroke as a prognostic factor of disease progression. Wiad Lek 54(3–4):143–151
Christensen H, Boysen G (2004) C-reactive protein and white blood cell count increases in the first 24 hours after acute stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 18(3):214–219. doi:10.1159/000079944
Pozzilli C, Lenzi GL, Argentino C, Bozzao L, Rasura M, Giubilei F, Fieschi C (1985) Peripheral white blood cell count in cerebral ischemic infarction. Acta Neurol Scand 71(5):396–400
Netz U, Perry Z, Weitzman S (2008) Characteristics of morbidity and mortality from stroke in the Negev population in the years 1995 and 1999. Harefuah 147(11):842–846, 944
di Napoli M, Papa F (2002) Inflammation, hemostatic markers, and antithrombotic agents in relation to long-term risk of new cardiovascular events in first-ever ischemic stroke patients. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 33(7):1763–1771
Heinel LA, Rubin S, Rosenwasser RH, Vasthare US, Tuma RF (1994) Leukocyte involvement in cerebral infarct generation after ischemia and reperfusion. Brain Res Bull 34(2):137–141
Emerich DF, Dean RL 3rd, Bartus RT (2002) The role of leukocytes following cerebral ischemia: pathogenic variable or bystander reaction to emerging infarct? Exp Neurol 173(1):168–181. doi:10.1006/exnr.2001.7835
Matsuo Y, Onodera H, Shiga Y, Nakamura M, Ninomiya M, Kihara T, Kogure K (1994) Correlation between myeloperoxidase-quantified neutrophil accumulation and ischemic brain injury in the rat. Effects of neutrophil depletion. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 25(7):1469–1475
Chu LS, Wei EQ, Yu GL, Fang SH, Zhou Y, Wang ML, Zhang WP (2006) Pranlukast reduces neutrophil but not macrophage/microglial accumulation in brain after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27(3):282–288. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00290.x
La M, Tailor A, D’Amico M, Flower RJ, Perretti M (2001) Analysis of the protection afforded by annexin 1 in ischaemia-reperfusion injury: focus on neutrophil recruitment. Eur J Pharmacol 429(1–3):263–278
Soriano SG, Lipton SA, Wang YF, Xiao M, Springer TA, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Hickey PR (1996) Intercellular adhesion molecule-1-deficient mice are less susceptible to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ann Neurol 39(5):618–624. doi:10.1002/ana.410390511
Chen H, Chopp M, Zhang RL, Bodzin G, Chen Q, Rusche JR, Todd RF 3rd (1994) Anti-CD11b monoclonal antibody reduces ischemic cell damage after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Ann Neurol 35(4):458–463. doi:10.1002/ana.410350414
Chopp M, Li Y, Jiang N, Zhang RL, Prostak J (1996) Antibodies against adhesion molecules reduce apoptosis after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat brain. J Cerebral Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cerebral Blood Flow Metab 16(4):578–584. doi:10.1097/00004647-199607000-00007
Zaleska MM, Mercado ML, Chavez J, Feuerstein GZ, Pangalos MN, Wood A (2009) The development of stroke therapeutics: promising mechanisms and translational challenges. Neuropharmacology 56(2):329–341. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.10.006
Bednar MM, Gross CE, Russell SR, Fuller SP, Ellenberger CL, Schindler E, Klingbeil C, Vexler V (1998) Humanized anti-l-selectin monoclonal antibody DREG200 therapy in acute thromboembolic stroke. Neurol Res 20(5):403–408
Krams M, Lees KR, Hacke W, Grieve AP, Orgogozo JM, Ford GA (2003) Acute stroke therapy by inhibition of neutrophils (ASTIN): an adaptive dose–response study of UK-279,276 in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke J Cerebral Circ 34(11):2543–2548. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000092527.33910.89
Becker KJ (2002) Anti-leukocyte antibodies: LeukArrest (Hu23F2G) and Enlimomab (R6.5) in acute stroke. Curr Med Res Opin 18(Suppl 2):s18–s22
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Medjaden Bioscience Limited for careful edition and proofread work. We also acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (81171239).
Conflict of interest
There is no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, X., Li, T., Ji, G. et al. Peripheral polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation as a systemic inflammatory response in ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci 34, 1509–1516 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1447-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1447-0