Abstract
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory spinal and large-joint arthritic and potentially disabling condition, mainly affecting males of young age groups. Extensive literature based on the results of various genetic, microbiological, molecular and immunological studies carried out by independent research groups suggests that Klebsiella pneumoniae is the main microbial agent being implicated as a triggering and/or perpetuating factor in the etiopathogenesis of AS. Novel diagnostic markers and criteria based on the association with high anti-Klebsiella antibodies could be used in the detection of AS patients during early stages of the disease, and together with the current treatments might help in implementing the use of new therapeutic anti-microbial measures in the management of AS. Prospective longitudinal studies with the use of anti-microbial measures in patients with AS are required to establish the therapeutic benefit of this microbe–disease association.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boonen A, de Vet H, van der Heijde D, van der Linden S (2001) Work status and its determinants among patients with ankylosing spondylitis. A systematic literature review. J Rheumatol 28:1056–1062
Sims AM, Wordsworth BP, Brown MA (2004) Genetic susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Mol Med 4:13–20
Caffrey M, James DC (1973) Human lymphocyte antigen association in ankylosing spondylitis. Nature 242:121
Brewerton DA, Hart FD, Nicholls A, Caffrey M, James DC, Sturrock RD (1973) Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet i:904–907
Schlosstein L, Terasaki PI, Bluestone E, Pearson CM (1973) High association of an HLA antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med 288:704–706
Sheehan NJ (2004) The ramifications of HLA-B27. J R Soc Med 97:10–14
Vazquez MN, Lopez de Castro JA (2005) Similar cell surface expression of beta2-microglobulin-free heavy chains by HLA-B27 subtypes differentially associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 52:3290–3299
Linssen A (1990) B27 positive versus B27 negative disease. Scand J Rheumatol 87:111–119 (Suppl)
Taurog JD, Richardson JA, Croft JT, Simmons WA, Zhou M, Fernandez-Sueiro JL et al (1994) The germfree state prevents development of gut and joint inflammatory disease in HLA-B27 transgenic rats. J Exp Med 180:2359–2364
Eastmond CJ, Woodrow JC (1977) Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins. Ann Rheum Dis 36:360–364
Brown MA, Kennedy LG, MacGregor AJ, Darke C, Duncan E, Shatford JL et al (1997) Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in twins: the role of genes, HLA and the environment. Arthritis Rheum 40:1823–1828
Leirisalo-Repo M (2005) Reactive arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 34:251–259
Martinez A, Pacheco-Tena C, Vazquez-Mellado J, Burgos-Vargas R (2004) Relationship between disease activity and infection in patients with spondyloarthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1338–1340
Ebringer A, Cowling P, Ngwa-Suh N, James DCO, Ebringer RW (1976) Cross-reactivity between Klebsiella aerogenes species and B27 lymphocyte antigens as an aetiological factor in ankylosing spondylitis. In: Dausset J, Svegaard A (eds) HLA and disease. Paris, INSERM, pp 58:27
Welsh J, Avakian H, Cowling P, Ebringer A, Wooley P, Panayi G et al (1980) Ankylosing spondylitis, HLA-B27 and Klebsiella. I: Cross-reactivity studies with rabbit antisera. Br J Exp Pathol 61:85–91
Avakian H, Welsh J, Ebringer A, Entwistle CC (1980) Ankylosing spondylitis, HLA-B27 and Klebsiella. II. Cross-reactivity studies with human tissue typing sera. Br J Exp Pathol 61:92–96
Van Bohemen CG, Grumet FC, Zanen HC (1984) Identification of HLA-B27M1 and -M2 cross-reactive antigens in Klebsiella, Shigella and Yersinia. Immunology 52:607–610
Ogasawara M, Kono DH, Yu DTY (1986) Mimicry of human histocompatibility HLA-B27 antigens by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun 51:901–908
Schwimmbeck PL, Yu DTY, Oldstone MBA (1987) Autoantibodies to HLA-B27 in the sera of HLA-B27 patients with ankylosing spondylitis and Reiter’s syndrome: molecular mimicry with Klebsiella pneumoniae as potential mechanism of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 166:173–181
Husby G, Tsuchiya N, Schwimmbeck PL, Keat A, Pahle JA, Oldstone MB et al (1989) Cross-reactive epitope with Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase in articular tissue of HLA-B27+ patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 32:437–445
Baines M, Ebringer A, Avakian H, Samuel D, James DC (1990) The use of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) and radiobinding assay to investigate the cross-reactivity of Klebsiella antigens and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis patients and healthy controls. Scand J Rheumatol 19:341–349
Fielder M, Pirt SJ, Tarpey I, Wilson C, Cunningham P, Ettelaie C et al (1995) Molecular mimicry and ankylosing spondylitis: possible role of a novel sequence in pullulanase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. FEBS Lett 369:243–248
Tani Y, Sato H, Tanaka N, Mori K, Doida Y, Hukuda S (1997) Serum IgA1 and IgA2 subclass antibodies against collagens in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Scand J Rheumatol 26:380–382
Maki-Ikola O, Penttinen M, von Essen R, Gripenberg-Lerche C, Isomaki H, Granfors K (1997) IgM, IgG and IgA class enterobacterial antibodies in serum and synovial fluid in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 36:1051–1053
Wilson C, Rashid T, Tiwana H, Beyan H, Hughes L, Bansal S et al (2003) Cytotoxicity responses to peptide antigens in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 30:972–978
Ebringer A, Rashid T, Wilson C, Ptaszynska T, Fielder M (2006) Ankylosing spondylitis as an auto-immune disease linked to intestinal Klebsiella infection: prospects for a new therapeutic approach. Curr Rheumatol Rev 2:55–68
Stone MA, Payne U, Schentag C, Rahman P, Pacheco-Tena C, Inman RD (2004) Comparative immune responses to candidate arthritogenic bacteria do not confirm a dominant role for Klebsiella pneumonia in the pathogenesis of familial ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 43:148–155
Tani Y, Tiwana H, Hukuda S, Nishioka J, Fielder M, Wilson C et al (1997) Antibodies to Klebsiella, Proteus and HLA-B27 peptides in Japanese patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 24:109–114
Ebringer R, Cooke D, Cawdell DR, Cowling P, Ebringer A (1977) Ankylosing spondylitis: Klebsiella and HLA-B27. Rheumatol Rehabil 16:190–196
Eastmond CJ, Willshaw HE, Burgess SE, Shinebaum R, Cook EM, Wright V (1980) Frequency of faecal Klebsiella aerogenes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and controls with respect to individual features of the disease. Ann Rheum Dis 39:118–123
Hunter T, Harding GK, Kaprove RE, Schroeder ML (1981) Fecal carriage of various Klebsiella and Enterobacter species in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 24:106–108
Kuberski TT, Morse HG, Rate RG, Bonnell MD (1983) Increased recovery of Klebsiella from the gastrointestinal tract of Reiter’s syndrome and ankylosing spondylitis patients. Br J Rheumatol 22(Suppl 2):85–90
Van Kregten E, Huber-Bruning O, Vandenbroucke JP, Willers JMN (1991) No conclusive evidence of an epidemiological relation between Klebsiella and ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 18:384–388
Smith GW, Blackwell CC, Nuki G (1997) Faecal flora in spondyloarthropathy. Br J Rheumatol 36:850–854
Maki-Ikola O, Leirisalo-Repo M, Turunen U, Granfors K (1997) Association of gut inflammation with increased serum IgA class Klebsiella antibody concentrations in patients with axial ankylosing spondylitis (AS): implication for different aetiopathogenetic mechanisms for axial and peripheral AS? Ann Rheum Dis 56:180–183
Maki-Ikola O, Hallgren R, Kanerud L, Feltelius N, Knutsson L, Granfors K (1997) Enhanced jejunal production of antibodies to Klebsiella and other Enterobacteria in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 56:421–425
Mielants H, Veys EM, Cuvelier C, De Vos M (1988) Ileocolonoscopic findings in seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Br J Rheumatol 27(Suppl 2):95–105
Martinez-Gonzalez O, Cantero-Hinojosa J, Paule-Sastre P, Gomez-Magan JC, Salvatierra-Rios D (1994) Intestinal permeability in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and their healthy relatives. Br J Rheumatol 33:644–647
Lahesmaa R, Skurnik M, Granfors K, Mottonen T, Saario R, Toivanen A et al (1992) Molecular mimicry in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthropathies. A critical appraisal of cross-reactivity between microbial antigens and HLA-B27. Br J Rheumatol 31:221–229
Toivanen A, Stahlberg TH, Granfors K, Ebringer A (1986) Absence of antibodies to Yersinia enterocolitica in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in London. Lancet 2:1400–1401
Cauli A, Dessole G, Fiorillo MT, Vacca A, Mameli A, Bitti P et al (2002) Increased level of HLA-B27 expression in ankylosing spondylitis patients compared with healthy HLA-B27 positive subjects: a possible further susceptibility factor for the development of disease. Rheumatology 41:1375–1379
Cowling P, Ebringer R, Cawdell D, Ischii M, Ebringer A (1980) C-reactive protein, ESR, and Klebsiella in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 39:45–49
Ebringer A (1992) Ankylosing spondylitis is caused by Klebsiella. Evidence from immunogenetic, microbiologic and serologic studies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 18:105–121
Anderson IH, Levine AS, Levitt MD (1981) Incomplete absorption of the carbohydrate in all-purpose wheat flour. N Engl J Med 304:891–892
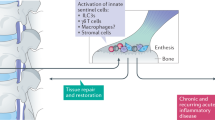
Benjamin M, McGonagle D (2001) The anatomical basis for disease localisation in seronegative spondyloarthropathy at entheses and related sites. J Anat 199:503–526
Fournier AM, Denizet D, Delagrange A (1969) La lymphographie dans la spondylarthrite ankylosante. J Radiol Electrol 50:773–784
Calin A (2004) Ankylosing spondylitis. In: Isenberg DA, Maddison PJ, Woo P, Glass DN, Breedveld FC (eds) Oxford textbook of rheumatology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 754–766
Ebringer R, Cawdell D, Ebringer A (1979) Klebsiella pneumoniae and acute anterior uveitis in ankylosing spondylitis. Br Med J 1:383
Sahly H, Podschun R, Kekow J, Nolle B, Gross WL, Ullmann U (1998) Humoral immune response to Klebsiella capsular polysaccharides in HLA-B27-positive patients with acute anterior uveitis and ankylosing spondylitis. Autoimmunity 28:209–215
Kijlstra A, Luyendijk L, van der Gaag R, van Kregten E, Linssen A, Willers JM (1986) IgG and IgA immune response against Klebsiella in HLA-B27-associated anterior uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 70:85–88
Van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368
Ebringer A, Rashid T, Wilson C, Miskejova G (2005) Pre-ankylosing spondylitis is a clinical disease entity: diagnostic criteria and therapeutic implications. Rheumatologia 18:91–96
Van der Heijde D, Dijkmans B, Geusens P, Sieper J, DeWoody K, Williamson P et al (2005) Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with anykylosing spondylitis: results of randomized, placebo-controlled trial (ASSERT). Arthritis Rheum 52:582–591
Merkesdal S, Ruof J, Mittendorf T, Zeidler H (2004) Cost-effectiveness of TNF-alpha-blocking agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5:1881–1886
Fleischmann RM, Iqbal I, Stern RL (2004) Considerations with the use of biological therapy in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Drug Saf 3:391–403
Trull A, Ebringer R, Panayi GS, Colthorpe J, James DC, Ebringer A (1983) IgA antibodies to Klebsiella pneumoniae in ankylosing spondylitis. Scand J Rheumatol 12:249–253
Trull A, Ebringer A, Panayi GS, Ebringer R, James DC (1984) HLA-B27 and the immune response to enterobacterial antigens in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Immunol 55:74–80
Ebringer A, Ptaszynska T, Corbett M, Wilson C, Macafee Y, Avakian H et al (1985) Antibodies to Proteus in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet ii:305–307
Khalafpour S, Ebringer A, Abuljadayel I, Corbett M (1988) Antibodies to Klebsiella and Proteus microorganisms in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis patients measured by ELISA. Br J Rheumatol 27(Suppl II):86–89
Maki-Ikola O, Lehtinen K, Granfors K, Vainionpaa R, Toivanen P (1991) Bacterial antibodies in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Immunol 84:472–475
Shodjai-Moradi F, Ebringer A, Abuljadayel I (1992) IgA antibody response to Klebsiella in ankylosing spondylitis measured by immunoblotting. Ann Rheum Dis 51:233–237
Tiwana H, Wilson C, Walmsley RS, Wakefield AJ, Smith MS, Cox NL et al (1997) Antibody response to gut bacteria in ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Rheumatol Int 17:11–16
Ahmadi K, Wilson C, Tiwana H, Binder A, Ebringer A (1998) Antibodies to Klebsiella pneumoniae lipopolysaccharide in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol 37:1330–1333
Blankenberg-Sprenkels SHD, Fielder M, Feldkamp TEW, Tiwana H, Wilson C, Ebringer A (1998) Antibodies to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Dutch patients with ankylosing spondylitis and acute anterior uveitis and to Proteus mirabilis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 25:743–747
Chou CT, Uksila J, Toivanen P (1998) Enterobacterial antibodies in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 16:161–164
Acknowledgement
We thank the trustees of the Middlesex Hospital, the Arthritis Research Campaign (Grant EO514) and “American Friends of King’s College London” for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashid, T., Ebringer, A. Ankylosing spondylitis is linked to Klebsiella—the evidence. Clin Rheumatol 26, 858–864 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0488-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0488-7