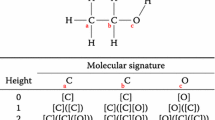
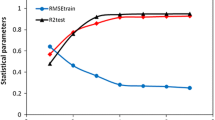
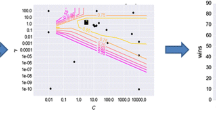
Abstract
Parathyroid hormone is the most important endocrine regulator of calcium concentration. Its N-terminal fragment (1–34) has sufficient activity for biological function. Recently, site-directed mutagenesis studies demonstrated that substitutions at several positions within shorter analogues (1–14) can enhance the bioactivity to greater than that of PTH (1–34). However, designing the optimal sequence combination is not simple due to complex combinatorial problems. In this study, support vector machines were introduced to predict the biological activity of modified PTH (1–14) analogues using mono-substituted experimental data and to analyze the key physicochemical properties at each position that correlated with bioactivity. This systematic approach can reduce the time and effort needed to obtain desirable molecules by bench experiments and provide useful information in the design of simpler activating molecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aurora, R., and Rose, G.D. (1998). Helix capping. Protein Sci. 7, 21–38.
Barazza, A., Wittelsberger, A., Fiori, N., Schievano, E., Mammi, S., Toniolo, C., Alexander, J.M., Rosenblatt, M., Peggion, E., and Chorev, M. (2005). Bioactive N-terminal undecapeptides derived from parathyroid hormone: the role of alpha-helicity. J. Pept. Res. 65, 23–35.
Bhasin, M., and Raghava, G.P. (2004). Analysis and prediction of affinity of TAP binding peptides using cascade SVM. Protein Sci. 13, 596–607.
Bhaskaran, R., and Ponnuswamy, P.K. (1988). Positional flexibilities of amino acid residues in globular proteins. Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 32, 241–255.
Bisello, A., Adams, A.E., Mierke, D.F., Pellegrini, M., Rosenblatt, M., Suva, L.J., and Chorev, M. (1998). Parathyroid hormone-receptor interactions identified directly by photocross-linking and molecular modeling studies. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 22498–22505.
Chorev, M. (2002). Parathyroid hormone 1 receptor: insights into structure and function. Receptors Channels 8, 219–242.
Crammer, K., and Singer, Y. (2001). On the algorithm implementation of multi-class SVM. J.M.L.R. 2, 265–292.
Cristianini, N., and Shawe-Taylor, J. (2000). An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods (New York: Cambridge University Press).
Dubey, A., Realff, M.J., Lee, J.H., and Bommarium, A.S. (2004). Support vector machines for learning to identify the critical position of a protein. J. Theor. Biol. 234, 351–361.
Jin, L., Briggs, S.L., Chandrasekhar, S., Chirgadze, N.Y., Clawson, D.K., Schevitz, R.W., Smiley, D.L., Tashjian, A.H., and Zhang, F. (2000). Crystal structure of human parathyroid hormone 1-34 at 0.9-A resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 27238–27244.
Joachims, T. (1999). Making large-scale SVM learning practical. In B. Scholkopf, ed., Advances in kernel methods - support vector learning, (Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press).
Karle, I.L., and Balaram, P. (1990). Structural characteristics of alpha-helical peptide molecules containing Aib residues. Biochemistry 29, 6747–6756.
Kawashima, S., Ogata, H., and Kanehisa, M. (1999). AAindex: amino acid index database. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 368–369.
Klein, P., Kanehisa, M., and DeLisi, C. (1984). Prediction of protein function from sequence properties. Discriminant analysis of a data base. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 787, 221–226.
Kowalczyk, W., Prahl, A., Dawidowska, O., Derdowska, I., Sobolewski, D., Hartrodt, B., Neubert, K., Slaninova, J., and Lammek, B. (2005). The influence of 1-aminocyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid at position 2 or 3 of AVP and its analogues on their pharmacological properties. J. Pept. Sci. 11, 584–588.
Krigbaum, W.R., and Komoriya, A. (1979). Local interactions as a structure determinant for protein molecules: II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 576, 204–248.
Levitt, M. (1976). A simplified representation of protein conformations for rapid simulation of protein folding. J. Mol. Biol. 104, 59–107.
Luck, M.D., Carter, P.H., and Gardella, T.J. (1999). The (1-14) fragment of parathyroid hormone (PTH) activates intact and amino-terminally truncated PTH-1 receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 13, 670–680.
Martinez, W.L., and Martinez, A.R. (2002). Computational statistics handbook with MATLAB. (Boca Raton, London, New York, Washington D.C.: Chapman and Hall/CRC).
Maxfield, F.R., and Scheraga, H.A. (1976). Status of empirical methods for the prediction of protein backbone topography. Biochemistry 15, 5138–5153.
Meirovitch, H., Rackovsky, S., and Scheraga, H.A. (1980). Empirical studies of hydrophobicity: 1. Effect of protein size on the hydrophobic behavior of amino acids. Macromolecules 13, 1398–1405.
Mita, K., Ichimura, S., and Zama, M. (2004). Conformation of poly(L-homoarginine). Biopolylmers 19, 1123–1135.
Ponnuswamy, P.K., Prabhakaran, M., and Manavalan, P. (1980). Hydrophobic packing and spatial arrangement of amino acid residues in globular proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 623, 301–316.
Potts, J.T. (2005). Parathyroid hormone: past and present. J. Endocrinol. 187, 311–325.
Prabhakaran, M., and Ponnuswamy, P.K. (1982). Shape and surface features of globular proteins. Macromolecules 15, 314–320.
Rackovsky, S., and Scheraga, H.A. (1977). Hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, and the radial and orientational distributions of residues in native proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 5248–5251.
Richardson, J.S., and Richardson, D.C. (1988). Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science 240, 1648–1652.
Rölz, C., Pellegrini, M., and Mierke, D.F. (1999). Molecular characterization of the receptor-ligand complex for parathyroid hormone. Biochemistry 38, 6397–6405.
Sali, A., and Blundell, T.L. (1993). Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 234, 779–815.
Sarda, D., Chua, G.H., Li, K.B., and Krishnan, A. (2005). pSLIP: SVM based protein subcellular localization prediction using multiple physicochemical properties. BMC Bioinformatics 6, 152.
Scholkopf, B.,and Smola, A.J. (2002). Learning with Kernels (Cambridge: The MIT Press).
Shimizu, M., Potts, J.T., Jr., and Gardella, T.J. (2000). Minimiz. of parathyroid hormone. Novel amino-terminal parathyroid hormone fragments with enhanced potency in activating the type-1 parathyroid hormone receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21836–21843.
Shimizu, M., Carter, P.H., Khatri, A., Potts, J.T., Jr., and Gardella, T.J. (2001). Enhanced activity in parathyroid hormone-(1-14) and -(1-11): novel peptides for probing ligand-receptor interactions. Endocrinology 142, 3068–3074.
Supper, J. (2005). Predicting MHC class I binding peptides based on amino acid properties using decision trees and support vector machines (Tübingen: Department for Simulation of Biological Systems, University of Tübingen).
Tanaka, S., and Scheraga, H.A. (1977). Statistical mechanical treatment of protein conformation. 5. A multistate model for specific-sequence copolymers of amino acids. Macromolecules 10, 9–20.
Toschantaridis, I., Hofmann, T., Joachims, T., and Altun, Y. (2004). Support vector machine learning for interdependent and structured output spaces. (Banff, Canada: 21st International Conference on Machine Learning).
Tsomaia, N., Pellegrini, M., Hyde, K., Gardella, T.J., and Mierke, D.F. (2004). Toward parathyroid hormone minimization: conformational studies of cyclic PTH(1-14) analogues. Biochemistry 43, 690–699.
Vapnik, V.N. (1995). The Natural of Statistical Learning Theory (New York: Springer Verlag).
Wilce, M.C., Aguilar, M.I., and Hearn, M.T. (1995). Physicochemical basis of amino acid hydrophobicity scales: evaluation of four new scales of amino acid hydrophobicity coefficient derived from RP-HPLC of peptides. Anal. Chem. 67, 1210–1219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, A., Ko, S., Lim, SK. et al. Prediction of parathyroid hormone signalling potency using SVMs. Mol Cells 27, 547–556 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0082-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0082-3