Abstract:
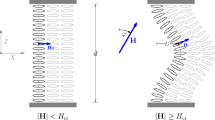
Previous studies on nematic liquid crystals containing silica particles indicated memory effects that might be due to hydrogen bonds between the individual silica particles. We made smectic liquid crystal dispersions containing silica particles with various surface properties. Using a neutron scattering technique we studied the interfacial surface effects on the structure of the silica aggregates, and on the smectic layer alignment. Our observations indicate that the stability of the memory correlates to the number of OH groups on the silica surfaces. The observations imply that, with fine-tuning of the OH content of the silica surfaces, various types of memory devices can be designed. We considered three different effects that can memorise the alignment of the liquid crystal. Measurements on tilted SmC phases indicate that surface effects become important only after repeated heating-cooling cycles, as the average size of the aggregates decrease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 31 July 1998 and Received in final form 17 December 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jákli, A., Almásy, L., Borbély, S. et al. Memory of silica aggregates dispersed in smectic liquid crystals: Effect of the interface properties. Eur. Phys. J. B 10, 509–513 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050880
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050880