Abstract
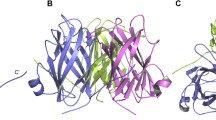
White spot disease is a devastating disease of shrimp Penaeus monodon in which the shrimp receptor protein PmRab7 interacts with viral envelop protein VP28 to form PmRab7–VP28 complex, which causes initiation of the disease. The molecular mechanism implicated in the disease, the dynamic behavior of proteins as well as interaction between both the biological counterparts that crafts a micro-environment feasible for entry of virus into the shrimp is still unknown. In the present study, we applied molecular modeling (MM), molecular dynamics (MD) and docking to compute surface mapping of infective amino acid residues between interacting proteins. Our result showed that α-helix of PmRab7 (encompassing Ser74, Ile143, Thr184, Arg53, Asn144, Thr184, Arg53, Arg79) interacts with β-sheets of VP28 (containing Ser74, Ile143, Thr184, Arg53, Asn144, Thr184, Arg53, Arg79) and Arg69-Ser74, Val75-Ile143, Leu73-Ile143, Arg79-Asn144, Ala198-Ala182 bonds contributed in the formation of PmRab7–VP28 complex. Further studies on the amino acid residues and bonds may open new possibilities for preventing PmRab7–VP28 complex formation, thus reducing chances of WSD. The quantitative predictions provide a scope for experimental testing in future as well as endow with a straightforward evidence to comprehend cellular mechanisms underlying the disease.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Escobedo-Bonilla CM, Alday-Sanz V, Wille M, Sorgeloos P, Pensaert MB, Nauwynck HJ (2008) A review on the morphology, molecular characterization, morphogenesis and pathogenesis of white spot syndrome virus. J Fish Dis 31(1):1–18
Lightner DV (1996) Epizootiology, distribution and the impact on international trade of two penaeid shrimp viruses in the Americas. Rev Sci Tech 15(2):579–601
Huang HT, Leu JH, Huang PY, Chen LL (2012) A putative cell surface receptor for white spot syndrome virus is a member of a transporter superfamily. PLoS One 7(3):e33216
Kushwaha SK, Shakya M (2010) Protein interaction network analysis–approach for potential drug target identification in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Theor Biol 262(2):284–294
Awale M, Kumar V, Saravanan P, Mohan CG (2010) Homology modeling and atomic level binding study of Leishmania MAPK with inhibitors. J Mol Model 16(3):475–488
Gutiérrez-de-Terán H, Nervall M, Ersmark K, Liu P, Janka LK, Dunn B, Hallberg A, Aqvist J (2006) Inhibitor binding to the plasmepsin IV aspartic protease from Plasmodium falciparum. Biochemistry 45(35):10529–10541
Ode H, Nakashima M, Kitamura S, Sugiura W, Sato H (2012) Molecular dynamics simulation in virus research. Front Microbiol 3:258
Yang F, He J, Lin X, Li Q, Pan D, Zhang X, Xu X (2001) Complete genome sequence of the shrimp white spot bacilliform virus. J Virol 75(23):11811–11820
Lu L, Kwang J (2004) Identification of a novel shrimp protein phosphatase and its association with latency-related ORF427 of white spot syndrome virus. FEBS Lett 577(1–2):141–146
Sieczkarski SB, Whittaker GR (2002) Dissecting virus entry via endocytosis. J Gen Virol 83(Pt 7):1535–1545
Seabra MC, Mules EH, Hume AN (2002) Rab GTPases, intracellular traffic and disease. Trends Mol Med 8(1):23–30
Stein MP, Dong J, Wandinger-Ness A (2003) Rab proteins and endocytic trafficking: potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55(11):1421–1437
Sritunyalucksana K, Wannapapho W, Lo CF, Flegel TW (2006) PmRab7 is a VP28-binding protein involved in white spot syndrome virus infection in shrimp. J Virol 80(21):10734–10742
van Hulten MC, Witteveldt J, Snippe M, Vlak JM (2001) White spot syndrome virus envelope protein VP28 is involved in the systemic infection of shrimp. Virology 285(2):228–233
Chang YS, Liu WJ, Lee CC, Chou TL, Lee YT, Wu TS, Huang JY, Huang WT, Lee TL, Kou GH, Wang AH, Lo CF (2010) A 3D model of the membrane protein complex formed by the white spot syndrome virus structural proteins. PLoS One 5(5):e10718
Tang X, Wu J, Sivaraman J, Hew CL (2007) Crystal structures of major envelope proteins VP26 and VP28 from white spot syndrome virus shed light on their evolutionary relationship. J Virol 81(12):6709–6717
Eswar N, John B, Mirkovic N, Fiser A, Ilyin VA, Pieper U, Stuart AC, Marti-Renom MA, Madhusudhan MS, Yerkovich B, Sali A (2003) Tools for comparative protein structure modeling and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3375–3380
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):235–242
Rak A, Pylypenko O, Niculae A, Pyatkov K, Goody RS, Alexandrov K (2004) Structure of the Rab7:REP-1 complex: insights into the mechanism of Rab prenylation and choroideremia disease. Cell 117(6):749–760
Sali A, Potterton L, Yuan F, Vlijmen H, Karplus M (1995) Evaluation of comparative protein modeling by MODELLER. Proteins 23(3):318–326
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Cryst 26:283–291
Colovos C, Yeates TO (1993) Verification of protein structures: patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci 2(9):1511–1519
Vriend G (1990) WHAT IF: a molecular modeling and drug design program. J Mol Graph 8(1):52–56, 29
Wiederstein M, Sippl MJ (2007) ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W407–W410
Bowie JU, Luthy R, Eisenberg D (1991) A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science 253(5016):164–170
Pettersen EF, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
Orengo CA, Michie AD, Jones S, Jones DT, Swindells MB, Thornton JM (1997) CATH–a hierarchic classification of protein domain structures. Structure 5(8):1093–1108
Berendsen HJC, Van der Spoel D, Van Drunen R (1995) GROMACS—a message passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Phys Commun 91:43–56
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJC, Fraaije JGEM (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 16:273–284
Miyamoto S, Kollman PA (1992) SETTLE: an analytical version of the SHAKE and RATTLE algorithms for rigid water models. J Comput Chem 13:952–962
Corpet F (1988) Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res 16(22):10881–10890
Hirokawa T, Boon-Chieng S, Mitaku S (1998) SOSUI: classification and secondary structure prediction system for membrane proteins. Bioinformatics 14(4):378–379
Schneidman-Duhovny D, Inbar Y, Nussinov R, Wolfson HJ (2005) PatchDock and SymmDock: servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W363–W367
Sharma A, Nigam A (2010) Structure modeling of novel DNA glycosylase enzyme from oral pathogen Streptococcus sanguinis. Bioinformation 5(3):136–140
Srinivasan K, Stalin T, Sivakumar K (2012) Spectral and electrochemical study of host-guest inclusion complex between 2,4-dinitrophenol and β-cyclodextrin. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 94:89–100
Subramaniam S, Mohmmed A, Gupta D (2009) Molecular modeling studies of the interaction between Plasmodium falciparum HslU and HslV subunits. J Biomol Struct Dyn 26(4):473–479
Verma S, Singh A, Mishra A (2012) Dual inhibition of chaperoning process by taxifolin: molecular dynamics simulation study. J Mol Graph Model 37:27–38
Verma S, Singh A, Mishra A (2012) The effect of fulvic acid on pre- and postaggregation state of Aβ(17–42): molecular dynamics simulation studies. Biochim Biophys Acta PMID:22940640
Venugopal S, Mohan R (2012) In silico docking studies of staphylococcus aureus virulent proteins with antimicrobial peptides. Int J Pharm Res Dev 3(12):79–86
Gupta S, Misra G, Pant MC, Seth PK (2011) Prediction of a new surface binding pocket and evaluation of inhibitors against huntingtin interacting protein 14: an insight using docking studies. J Mol Model 17(12):3047–3056
Gupta S, Misra G, Pant MC, Seth PK (2012) Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor: exploring the potential of novel inhibitor N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6, 7-bis (2-methoxyethoxy) quinolin-4-amine using docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Protein Pept Lett 19(9):955–968
Gupta S, Misra G, Pant MC, Seth PK (2012) Identification of novel potent inhibitors aginst Bcl-XL anti-apoptotic protein using docking studies. Protein Pept Lett 19(12):1302-1317
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to National Agricultural Bioinformatics Grid Project under National Agricultural Innovation Project, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi for providing financial support. We also gratefully acknowledge the necessary facilities provided by the Director, National Bureau of Fish Genetic Resources, Lucknow and the Chief Executive Officer, Biotech Park, Lucknow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, A.K., Gupta, S., Verma, S. et al. Interaction between shrimp and white spot syndrome virus through PmRab7-VP28 complex: an insight using simulation and docking studies. J Mol Model 19, 1285–1294 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1672-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-012-1672-0