Abstract
Study design
A retrospective review
Purpose
This study was designed to compare postoperative changes in neural foramen between transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) and posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF).
Methods
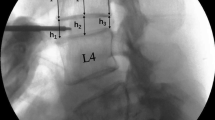
A retrospective analysis of 67 patients was compared to the change of neural foraminal morphometry of the two techniques. 33 patients (40 levels) had TLIF and 34 patients (39 levels) had PLIF. The two groups had similar demographic profiles. Radiological parameters including anterior and posterior disc height, foraminal height (FH), and segmental Cobb angle (SCA) were measured by sagittally reconstructed computed tomography images before and after surgery. Cage position was designated as contralateral, middle, and ipsilateral in the TLIF group. Surgical results were assessed by Odom criteria, visual analog scale (VAS), and Oswestry disability index (ODI) scores.
Results
The TLIF and PLIF group showed no bilateral difference in FH. The TLIF group had increased contralateral SCA compared to the ipsilateral side postoperatively. FH differed according to cage position in the TLIF group. When a cage was inserted deeply into the contralateral side, contralateral FH increased significantly. However, when a cage was inserted into the ipsilateral side, contralateral FH decreased significantly. Back pain was significantly lower in the TLIF group at 1 and 6 months than in the PLIF group. However, ODI and Odom scale scores were not different between the groups.
Conclusions
TLIF may induce uneven changes in foraminal morphometry. Cage position may be the major determinant of this result.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stonecipher T, Wright S (1989) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with facet-screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 14:468–471
Lowe TG, Tahernia AD, O’Brien MF, Smith DA (2002) Unilateral transforaminal posterior lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF): indications, technique, and 2-year results. J Spinal Disord Tech 15:31–38
Grob D (2009) Surgery for degenerative lumbar disease: transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J 18:1991–1992. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-1222-3
Humphreys SC, Hodges SD, Patwardhan AG, Eck JC, Murphy RB, Covington LA (2001) Comparison of posterior and transforaminal approaches to lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:567–571
Yan DL, Pei FX, Li J, Soo CL (2008) Comparative study of PILF and TLIF treatment in adult degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17:1311–1316. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0739-1
Rosenberg WS, Mummaneni PV (2001) Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: technique, complications, and early results. Neurosurgery 48:569–574 (discussion 574–565)
Hunt T, Shen FH, Shaffrey CI, Arlet V (2007) Contralateral radiculopathy after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J 16(Suppl 3):311–314. doi:10.1007/s00586-007-0387-x
Harms J, Rolinger H (1982) A one-stager procedure in operative treatment of spondylolistheses: dorsal traction-reposition and anterior fusion (author’s transl). Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 120:343–347. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1051624
Foley KT, Lefkowitz MA (2002) Advances in minimally invasive spine surgery. Clin Neurosurg 49:499–517
Lin PM (1977) A technical modification of Cloward’s posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurgery 1:118–124
Evans JH (1985) Biomechanics of lumbar fusion. Clin Orthop Relat Res (193):38–46
Voor MJ, Mehta S, Wang M, Zhang YM, Mahan J, Johnson JR (1998) Biomechanical evaluation of posterior and anterior lumbar interbody fusion techniques. J Spinal Disord 11:328–334
Steffee AD, Sitkowski DJ (1988) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion and plates. Clin Orthop Relat Res 227:99–102
Hsieh PC, Koski TR, O’Shaughnessy BA, Sugrue P, Salehi S, Ondra S, Liu JC (2007) Anterior lumbar interbody fusion in comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: implications for the restoration of foraminal height, local disc angle, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine 7:379–386. doi:10.3171/spi-07/10/379
Hasegawa T, An HS, Haughton VM, Nowicki BH (1995) Lumbar foraminal stenosis: critical heights of the intervertebral discs and foramina. A cryomicrotome study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:32–38
Xu H, Ju W, Xu N, Zhang X, Zhu X, Zhu L, Qian X, Wen F, Wu W, Jiang F (2013) Biomechanical comparison of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with one or two cages by finite element analysis. Neurosurgery. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000430320.39870.f7
Tsuang YH, Chiang YF, Hung CY, Wei HW, Huang CH, Cheng CK (2009) Comparison of cage application modality in posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterior instrumentation–a finite element study. Med Eng Phys 31:565–570. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.11.012
Iwata T, Miyamoto K, Hioki A, Fushimi K, Ohno T, Shimizu K (2013) Morphological changes in contralateral lumbar foramen in unilateral cantilever transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using kidney-type intervertebral spacers. J Spinal Disord Tech. doi:10.1097/BSD.0b013e318286bb14
Anand N, Hamilton JF, Perri B, Miraliakbar H, Goldstein T (2006) Cantilever TLIF with structural allograft and RhBMP2 for correction and maintenance of segmental sagittal lordosis: long-term clinical, radiographic, and functional outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:E748–E753. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000240211.23617.ae
Dimar JR 2nd, Glassman SD, Vemuri VM, Esterberg JL, Howard JM, Carreon LY (2011) Lumbar lordosis restoration following single-level instrumented fusion comparing 4 commonly used techniques. Orthopedics 34:e760–e764. doi:10.3928/01477447-20110922-14
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dong-Su Jang, B.A. (Research Assistant, Department of Anatomy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea), for his help with the figures. No funds were received in support of this work. No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
PGC: nothing to disclose. SHP: nothing to disclose. BJM: nothing to disclose. KNK: nothing to disclose. YH: nothing to disclose. DHY: nothing to disclose. DSJ: nothing to disclose. DAS: nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, P.G., Park, S.H., Kim, K.N. et al. A morphometric analysis of contralateral neural foramen in TLIF. Eur Spine J 24, 783–790 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3783-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3783-7