Abstract
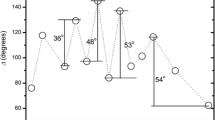
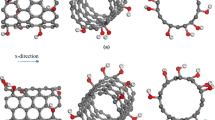
In situ transmission electron microscopy nanoindentation tests are used to measure the compressive fracture and mechanical properties of individual titanium oxide (TiO2) capped nanotubes. The average critical loads ranged from 3.6 to 9.6 μN. Individual TiO2 capped nanotubes with lengths of 8–10 μm were found to have Young’s modulus values of ~2.2–9.4 GPa and work energy values of ~3.1–6.6 × 10−13 J. The results indicate that the Young’s modulus and tensile strength depend on capped nanotube length.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balaur E, Macak JM, Tsuchiya H, Schmuki P (2005) Wetting behaviour of layers of TiO2 nanotubes with different diameters. J Mater Chem 15:4488–4491
Chang WY, Fang TH, Chiu ZW, Hsiao YJ, Ji LW (2011) Nanomechanical properties of array TiO2 nanotubes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 145:87–92
Crawford GA, Chawla N, Das K, Bose S, Bandyopadhyay A (2007) Microstructure and deformation behavior of biocompatible TiO2 nanotubes on titanium substrate. Acta Biomater 3:359–367
Fox RL, Kapoor MP (1968) Rates of change of eigenvalues and eigenvectors. J AIAA 6:2426–2429
Gong D, Grimes CA, Varghese OK, Hu W, Singh RS, Chen Z, Dickey EC (2001) Titanium oxide nanotube arrays prepared by anodic oxidation. J Mater Res 16:3331–3334
Greer JR, De Hosson JTM (2011) Plasticity in small-sized metallic systems: intrinsic versus extrinsic size effect. Prog Mater Sci 56:654–724
Han SC, Doh JM, Yoon JK, Kim GH, Byun JY, Han SH, Hong KT, Kwun SI (2009) Highly ordered self-organized TiO2 nanotube arrays prepared by a multi-step anodic oxidation process. Met Mater Int 15:493–499
Haslach HW Jr, Armstrong RW (2004) Deformable bodies and their material behavior. Wiley, New York, p 496
Kang SH, Kim HS, Kim JY, Sung YE (2009) An investigation on electron behavior employing vertically-aligned TiO2 nanotube electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 20:355307
Kang SH, Fang TH, Chen TH, Kuo CH (2013) Size effect on nanomechanical properties of ZnO cones using in situ transmission electron microscopy. Curr Appl Phys 13:1689–1696
Kim YJ, Son K, Choi IC, Choi IS, Park WI, Jang JI (2011) Exploring nanomechanical behavior of silicon nanowires: AFM bending versus nanoindentation. Adv Funct Mater 21:279–286
Li SQ, Zhang GM, Guo DZ, Yu LG, Zhang W (2009) Anodization fabrication of highly ordered. TiO2 nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 113:12759–12765
Mor GK, Varghese OK, Paulose M, Mukherjee N, Grimes CA (2003) Fabrication of tapered, conical-shaped titania nanotubes. J Mater Res 18:2588–2593
Mor GK, Varghese OK, Paulose M, Shankar K, Grimes CA (2006) A review on highly-ordered TiO2 nanotube-arrays: fabrication, material properties, and solar energy applications. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:2011–2075
Rahai AR, Kazemi S (2008) Buckling analysis of non-prismatic columns based on modified vibration modes. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 13:1721–1735
Roy P, Dey T, Schmuki P (2010) Scanning electron microscopy observation of nanoscopic wetting of TiO2 nanotubes and ODS modified nanotubes using ionic liquids. Electrochem Solid State Lett 13:E11–E13
Shokuhfar T, Arumugam GK, Heiden PA, Yassar RS, Friedrich C (2009) Direct mechanical behavior measurements of individual titanium oxide nanotubes. ACS Nano 3:3098–3102
Sreekantan S, Lockman Z, Hazan R, Tasbihi M, Tong LK, Mohamed AR (2009) Influence of electrolyte pH on TiO2 nanotube formation by Ti anodization. J Alloy Compd 485:478–483
Varghese OK, Gong D, Paulose M, Ong KGC, Grimes A (2003) Hydrogen sensing using titania nanotubes. Sens Actuators B 93:338–344
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Science Council of Taiwan under grants NSC 100-2811-E-151-001 and NSC 100-2628-E-151-003-MY3 and by the Center for Micro/Nano Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, SH., Fang, TH., Chen, TH. et al. Size effect on mechanical properties of TiO2 capped nanotubes investigated using in situ transmission electron microscopy. Microsyst Technol 20, 515–520 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1939-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1939-0