Abstract
Background
Same-day bidirectional endoscopy is commonly performed in clinical practice. However, the optimal sequence of procedures for same-day bidirectional endoscopy has not been established. The purpose of this study was to compare colonoscopy performance and quality between patients who underwent colonoscopy before or after esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
Methods
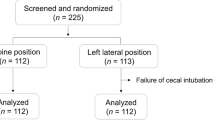
A total of 1,103 patients were prospectively randomized into either the EGD–colonoscopy or colonoscopy–EGD sequence groups. Three patients who had incomplete cecal intubation due to structural obstruction were excluded from the analysis. During colonoscopy, colonoscopic parameters including difficult cecal intubation (cecal intubation failure and prolonged insertion), insertion time, and adenoma detection rate were measured. Out of 1,100 patients, 524 patients without sedation completed a questionnaire designed to assess subjective discomfort experienced.
Results
The colonoscopy completion rate was 99.5 %, and the rate of difficult cecal intubation was 14.5 %. The time from insertion to reaching the cecum (minutes:seconds, 06:32 ± 04:26 vs. 06:40 ± 04:09, p = 0.649), difficult cecal intubation ratio (76 of 550 vs. 83 of 550, p = 0.593), and colonoscopic adenoma detection rate (29.8 vs. 25.5 %, p = 0.106) did not differ between the groups. On multivariate analysis, difficulty with cecal intubation increased specifically in women, in patients aged 55 years and over, in patients with poor bowel preparation, and in patients who had undergone previous abdominal surgery. Subjective discomfort after EGD was higher in the colonoscopy–EGD sequence group.
Conclusions
The procedural sequence did not affect colonoscopy performance and quality in same-day bidirectional endoscopy, and factors such as old age, female gender, poor bowel preparation, and previous abdominal surgery were confirmed to adversely affect colonoscopy. In addition, the EGD–colonoscopy sequence induced less subjective discomfort during EGD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Urquhart J, Eisen G, Faigel DO, Mattek N, Holub J, Lieberman DA (2009) A closer look at same-day bidirectional endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 69:271–277
Zuckerman G, Benitez J (1992) A prospective study of bidirectional endoscopy (colonoscopy and upper endoscopy) in the evaluation of patients with occult gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol 87:62–66
Alemayehu G, Järnerot G (1993) Same-day upper and lower endoscopy in patients with occult bleeding, melena, hematochezia, and/or microcytic anemia. A retrospective study of 224 patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 28:667–672
Hardwick RH, Armstrong CP (1997) Synchronous upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy is an effective method of investigating iron-deficiency anaemia. Br J Surg 84:1725–1728
Velez JP, Schwesinger WH, Stauffer J, Gaskill HV 3rd, Kazantsev GB, Sirinek KR, Strodel WE (2002) Bidirectional endoscopy in patients with fecal occult blood. Surg Endosc 16:117–120
Lieberman D, Fennerty MB, Morris CD, Holub J, Eisen G, Sonnenberg A (2004) Endoscopic evaluation of patients with dyspepsia: results from the national endoscopic data repository. Gastroenterology 127:1067–1075
Joo MK, Park JJ, Lee WW, Lee BJ, Hwang JK, Kim SH, Jung W, Kim JH, Yeon JE, Kim JS, Byun KS, Bak YT (2010) Differences in the prevalence of colorectal polyps in patients undergoing endoscopic removal of gastric adenoma or early gastric cancer and in healthy individuals. Endoscopy 42:114–120
Triadafilopoulos G, Aslan A (1991) Same-day upper and lower inpatient endoscopy: a trend for the future. Am J Gastroenterol 86:952–955
Cho JH, Kim JH, Lee YC, Song SY, Lee SK (2010) Comparison of procedural sequences in same-day bidirectional endoscopy without benzodiazepine and propofol sedation: starting at the bottom or the top. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:899–904
Hsieh YH, Lin HJ, Tseng KC (2011) Which should go first during same-day bidirectional endoscopy with propofol sedation? J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:1559–1564
Waye JD, Bashkoff E (1991) Total colonoscopy: is it always possible? Gastrointest Endosc 37:152–154
Church JM (1994) Complete colonoscopy: how often? And if not, why not? Am J Gastroenterol 89:556–560
Kim WH, Cho YJ, Park JY, Min PK, Kang JK, Park IS (2000) Factors affecting insertion time and patient discomfort during colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 52:600–605
Lee SK, Kim TI, Shin SJ, Kim BC, Kim WH (2006) Impact of prior abdominal or pelvic surgery on colonoscopy outcomes. J Clin Gastroenterol 40:711–716
Rex DK, Bond JH, Winawer S, Levin TR, Burt RW, Johnson DA, Kirk LM, Litlin S, Lieberman DA, Waye JD, Church J, Marshall JB, Riddell RH, US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer (2002) Quality in the technical performance of colonoscopy and the continuous quality improvement process for colonoscopy: recommendations of the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Am J Gastroenterol 97:1296–1308
Rex DK, Petrini JL, Baron TH, Chak A, Cohen J, Deal SE, Hoffman B, Jacobson BC, Mergener K, Petersen BT, Safdi MA, Faigel DO, Pike IM, ASGE/ACG Taskforce on Quality in Endoscopy (2006) Quality indicators for colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol 101:873–885
Lieberman D, Nadel M, Smith RA, Atkin W, Duggirala SB, Fletcher R, Glick SN, Johnson CD, Levin TR, Pope JB, Potter MB, Ransohoff D, Rex D, Schoen R, Schroy P, Winawer S (2007) Standardized colonoscopy reporting and data system: report of the Quality Assurance Task Group of the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable. Gastrointest Endosc 65:757–766
Lieberman DA, Faigel DO, Logan JR, Mattek N, Holub J, Eisen G, Morris C, Smith R, Nadel M (2009) Assessment of the quality of colonoscopy reports: results from a multicenter consortium. Gastrointest Endosc 69:645–653
Bair D, Pham J, Seaton MB, Arya N, Pryce M, Seaton TL (2009) The quality of screening colonoscopies in an office-based endoscopy clinic. Can J Gastroenterol 23:41–47
Cirocco WC, Rusin LC (1995) Factors that predict incomplete colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum 38:964–968
Acknowledgments
This research was supported (Jae Hee Cho, Hee Man Kim) in part by a research grant (11-010) by Jeil Pharmaceutical (Seoul, Korea) and by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2011-0013944, 2011-0008901).
Disclosures
Ja Sung Choi, Young Hoon Youn, Sang Kil Lee, Jin Yi Choi, Hee Man Kim, Yu Jin Kim, Ki Jun Han, Hyeon Geun Cho, Si Young Song, and Jae Hee Cho have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.S., Youn, Y.H., Lee, S.K. et al. Which should go first during same-day upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy? A randomized prospective study focusing on colonoscopy performance. Surg Endosc 27, 2209–2215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2741-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2741-2