Abstract
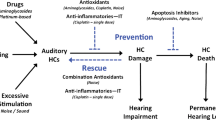
Mechanisms that lead to the death of hair cells are reviewed. Exposure to noise, the use of ototoxic drugs that damage the cochlea and old age are accompanied by hair cell death. Outer hair cells are often more susceptible than inner hair cells, partly because of an intrinsically greater susceptibility; high frequency cells are also more vulnerable. A common factor in hair cell loss following age-related changes and exposure to ototoxic drugs or high noise levels is the generation of reactive oxygen species, which can trigger intrinsic apoptosis (the mitochondrial pathway). However, hair cell death is sometimes produced via an extracellular signal pathway triggering extrinsic apoptosis. Necrosis and necroptosis also play a role and, in various situations in which cochlear damage occurs, a balance exists between these possible routes of cell death, with no one mechanism being exclusively activated. Finally, the numerous studies on these mechanisms of hair cell death have led to the identification of many potential therapeutic agents, some of which have been used to attempt to treat people exposed to damaging events, although clinical trials are not yet conclusive. Continued work in this area is likely to lead to clinical treatments that could be used to prevent or ameliorate hearing loss.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alharazneh A, Luk L, Huth M, Monfared A, Steyger PS, Cheng AG, Ricci AJ (2011) Functional hair cell mechanotransducer channels are required for aminoglycoside ototoxicity. PLoS One 6:e22347
Baker K, Staecker H (2012) Low dose oxidative stress induces mitochondrial damage in hair cells. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 295:1868–1876
Bannister LH, Dodson HC, Astbury AR, Douek EE (1988) The cortical lattice: a highly ordered system of subsurface filaments in guinea pig cochlear outer hair cells. Prog Brain Res 74:213–219
Bas E, Van De Water TR, Gupta C, Dinh J, Vu L, Martínez-Soriano F, Láinez JM, Marco J (2012) Efficacy of three drugs for protecting against gentamicin-induced hair cell and hearing losses. Br J Pharmacol 166:1888–1904
Bleicken S, Landeta O, Landajuela A, Basañez G, García-Sáez AJ (2013) Proapoptotic Bax and Bak proteins form stable protein-permeable pores of tunable size. J Biol Chem 288:33241–33252
Bodmer D, Brors D, Bodmer M, Pak K, Ryan AF (2003a) Fas ligand expression in the organ of Corti. Audiol Neurootol 8:243–249
Bodmer D, Brors D, Pak K, Bodmer M, Ryan AF (2003b) Gentamicin-induced hair cell death is not dependent on the apoptosis receptor Fas. Laryngoscope 113:452–455
Bohne BA, Harding GW, Lee SC (2007) Death pathways in noise-damaged outer hair cells. Hear Res 223:61–70
Candé C, Cohen I, Daugas E, Ravagnan L, Larochette N, Zamzami N, Kroemer G (2002) Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria. Biochimie 84:215–222
Chen Q, Mahendrasingam S, Tickle JA, Hackney CM, Furness DN, Fettiplace R (2012) The development, distribution and density of the plasma membrane calcium ATPase 2 calcium pump in rat cochlear hair cells. Eur J Neurosci 36:2302–2310
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J, Ford LP (2005) Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:1290–1297
De Freitas MR, Figueiredo AA, Brito GA, Leitao RF, Carvalho Junior JV, Gomes Junior RM, Ribeiro Rde A (2009) The role of apoptosis in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 75(5):745–752
Deltenre P, Van Maldergem L (2013) Hearing loss and deafness in the pediatric population: causes, diagnosis, and rehabilitation. Handb Clin Neurol 113:1527–1538
Devarajan P, Savoca M, Castaneda MP, Park MS, Esteban-Cruciani N, Kalinec G, Kalinec F (2002) Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in auditory cells: role of death receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Hear Res 174:45–54
Ding D, Jiang H, Wang P, Salvi R (2007) Cell death after co-administration of cisplatin and ethacrynic acid. Hear Res 226:129–139
Duan M, Qiu J, Laurell G, Olofsson A, Counter SA, Borg E (2004) Dose and time-dependent protection of the antioxidant N-L-acetylcysteine against impulse noise trauma. Hear Res 192:1–9
Engel J, Braig C, Rüttiger L, Kuhn S, Zimmermann U, Blin N, Sausbier M, Kalbacher H, Münkner S, Rohbock K, Ruth P, Winter H, Knipper M (2006) Two classes of outer hair cells along the tonotopic axis of the cochlea. Neuroscience 143:837–849
Esterberg R, Hailey DW, Rubel EW, Raible DW (2014) ER-mitochondrial calcium flow underlies vulnerability of mechanosensory hair cells to damage. J Neurosci 34:9703–9719
Fetoni AR, De Bartolo P, Eramo SL, Rolesi R, Paciello F, Bergamini C, Fato R, Paludetti G, Petrosini L, Troiani D (2013) Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) as a target of oxidative stress-mediated damage: cochlear and cortical responses after an increase in antioxidant defense. J Neurosci 33:4011–4023
Fetoni AR, Bielefeld EC, Paludetti G, Nicotera T, Henderson D (2014) A putative role of p53 pathway against impulse noise induced damage as demonstrated by protection with pifithrin-alpha and a Src inhibitor. Neurosci Res 81–82:30–37
Fettiplace R, Hackney CM (2006) The sensory and motor roles of auditory hair cells. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:19–29
Forge A (1985) Outer hair cell loss and supporting cell expansion following chronic gentamicin treatment. Hear Res 19:171–182
Fredelius L, Rask-Andersen H (1990) The role of macrophages in the disposal of degeneration products within the organ of Corti after acoustic overstimulation. Acta Otolaryngol 109:76–82
Fredelius L, Johansson B, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Wersäll J (1987) Qualitative and quantitative changes in the guinea pig organ of Corti after pure tone acoustic overstimulation. Hear Res 30:157–167
Fujimoto C, Yamasoba T (2014) Oxidative stresses and mitochondrial dysfunction in age-related hearing loss. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:582849
Furness DN, Hackney CM (1986) Morphological changes to the stereociliary bundles in the guinea pig cochlea after kanamycin treatment. Br J Audiol 20:253–259
García-Berrocal JR, Nevado J, Ramírez-Camacho R, Sanz R, González-García JA, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Cantos B, España P, Verdaguer JM, Trinidad Cabezas A (2007) The anticancer drug cisplatin induces an intrinsic apoptotic pathway inside the inner ear. Br J Pharmacol 152:1012–1020
Guicciardi ME, Gores GJ (2009) Life and death by death receptors. FASEB J 23:1625–1637
Hackney CM, Furness DN (2013) The composition and role of cross links in mechanoelectrical transduction in vertebrate sensory hair cells. J Cell Sci 126:1721–1731
Han W, Shi X, Nuttall AL (2006) AIF and endoG translocation in noise exposure induced hair cell death. Hear Res 211:85-95
Harrison RV, Evans EF (1979) Cochlear fibre responses in guinea pigs with well defined cochlear lesions. Scand Audiol Suppl 9:83–92
He L, He X, Lim LP, Stanchina E de, Xuan Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, Jackson AL, Linsley PS, Chen C, Lowe SW, Cleary MA, Hannon GJ (2007) A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 13:1130–1134
He Y, Yu H, Cai C, Sun S, Chai R, Li H (2014) Inhibition of H3K4me2 demethylation protects auditory hair cells from neomycin-induced apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol (in press)
Hu BH, Zheng GL (2008) Membrane disruption: an early event of hair cell apoptosis induced by exposure to intense noise. Brain Res 1239:107-118
Hu BH, Guo W, Wang PY, Henderson D, Jiang SC (2000) Intense noise-induced apoptosis in hair cells of guinea pig cochleae. Acta Otolaryngol 120:19–24
Hu BH, Cai Q, Manohar S, Jiang H, Ding D, Coling DE, Zheng G, Salvi R (2009) Differential expression of apoptosis-related genes in the cochlea of noise-exposed rats. Neuroscience 161:915–925
Huang T, Cheng AG, Stupak H, Liu W, Kim A, Staecker H, Lefebvre PP, Malgrange B, Kopke R, Moonen G, Van De Water TR (2000) Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of cochlear sensory cells: otoprotective strategies. Int J Dev Neurosci 18:259–720
Jacob S, Johansson C, Fridberger A (2013) Noise-induced alterations in cochlear mechanics, electromotility, and cochlear amplification. Pflugers Arch 465:907–917
Jamesdaniel S, Ding D, Kermany MH, Davidson BA, Knight PR 3rd, Salvi R, Coling DE (2008) Proteomic analysis of the balance between survival and cell death responses in cisplatin-mediated ototoxicity. J Proteome Res 7:3516–3524
Jensen-Smith HC, Hallworth R, Nichols MG (2012) Gentamicin rapidly inhibits mitochondrial metabolism in high-frequency cochlear outer hair cells. PLoS One 7:e38471
Jiang D, Furness DN, Hackney CM, Lopez DE (1993) Microslicing of the resin-embedded cochlea in comparison with the surface preparation technique for analysis of hair cell number and morphology. Br J Audiol 27:195–203
Jiang H, Sha SH, Forge A, Schacht J (2006) Caspase-independent pathways of hair cell death induced by kanamycin in vivo. Cell Death Differ 13:20–30
Joris PX (2003) Interaural time sensitivity dominated by cochlea-induced envelope patterns. J Neurosci 23:6345–6350
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Riquet F, Duprez L, Vanden Berghe T, Takahashi N, Vandenabeele P (2014) Necroptosis, in vivo detection in experimental disease models. Semin Cell Dev Biol 35:2-13
Jovanovic M, Hengartner MO (2006) miRNAs and apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene 25:6176–6187
Kashio A, Sakamoto T, Suzukawa K, Asoh S, Ohta S, Yamasoba T (2007) A protein derived from the fusion of TAT peptide and FNK, a Bcl-x(L) derivative, prevents cochlear hair cell death from aminoglycoside ototoxicity in vivo. J Neurosci Res 85:1403–1412
Kashio A, Sakamoto T, Kakigi A, Suzuki M, Suzukawa K, Kondo K, Sato Y, Asoh S, Ohta S, Yamasoba T (2012) Topical application of the antiapoptotic TAT-FNK protein prevents aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity. Gene Ther 19:1141–1149
Kopke RD, Weisskopf PA, Boone JL, Jackson RL, Wester DC, Hoffer ME, Lambert DC, Charon CC, Ding DL, McBride D (2000) Reduction of noise-induced hearing loss using L-NAC and salicylate in the chinchilla. Hear Res 149:138–146
Kopke RD, Jackson RL, Coleman JK, Liu J, Bielefeld EC, Balough BJ (2007) NAC for noise: from the bench top to the clinic. Hear Res 226:114–125
Ladrech S, Wang J, Simonneau L, Puel JL, Lenoir M (2007) Macrophage contribution to the response of the rat organ of Corti to amikacin. J Neurosci Res 85:1970–1979
Lavrik IN (2014) Systems biology of death receptor networks: live and let die. Cell Death Dis 5:e1259
Lee JH, Park C, Kim SJ, Kim HJ, Oh GS, Shen A, So HS, Park R (2013) Different uptake of gentamicin through TRPV1 and TRPV4 channels determines cochlear hair cell vulnerability. Exp Mol Med 45:e12
Li LY, Luo X, Wang X (2001) Endonuclease G is an apoptotic DNase when released from mitochondria. Nature 412:95-99
Li-Korotky HS (2012) Age-related hearing loss: quality of care for quality of life. Gerontologist 52:265–271
Lin CY, Wu JL, Shih TS, Tsai PJ, Sun YM, Ma MC, Guo YL (2010) N-Acetyl-cysteine against noise-induced temporary threshold shift in male workers. Hear Res 269:42–47
Mahendrasingam S, Macdonald JA, Furness DN (2011) Relative time course of degeneration of different cochlear structures in the CD/1 mouse model of accelerated aging. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 12:437–453
Mammano F (2011) Ca2+ homeostasis defects and hereditary hearing loss. Biofactors 37:182–188
Marques-Fernandez F, Planells-Ferrer L, Gozzelino R, Galenkamp KMO, Reix S, Llecha-Cano N, Lopez-Soriano J, Yuste VJ, Moubarak RS, Comella JX (2013) TNFα induces survival through the FLIP-L-dependent activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway. Cell Death Dis 4:e493
McFadden SL, Ding D, Reaume AG, Flood DG, Salvi RJ (1999) Age-related cochlear hair cell loss is enhanced in mice lacking copper/zinc superoxide dismutase. Neurobiol Aging 20:1–8
Morgan MJ, Liu Z (2011) Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res 21:103–115
Nagańska E, Matyja E (2001) Ultrastructural characteristics of necrotic and apoptotic mode of neuronal cell death in a model of anoxia in vitro. Folia Neuropathol 39:129–139
Nakagawa T, Yamane H, Takayama M, Sunami K, Nakai Y (1998) Apoptosis of guinea pig cochlear hair cells following chronic aminoglycoside treatment. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 255:127–131
Nieminen AI, Eskelinen VM, Haikala HM, Tervonen TA, Yan Y, Partanen JI, Klefström J (2013) Myc-induced AMPK-phospho p53 pathway activates Bak to sensitize mitochondrial apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:E1839–E1848
Nishizaki K, Yoshino T, Orita Y, Nomiya S, Masuda Y (1999) TUNEL staining of inner ear structures may reflect autolysis, not apoptosis. Hear Res 130:131–136
Nouvian R, Ruel J, Wang J, Guitton MJ, Pujol R, Puel JL (2003) Degeneration of sensory outer hair cells following pharmacological blockade of cochlear KCNQ channels in the adult guinea pig. Eur J Neurosci 17:2553–2562
Ohinata Y, Miller JM, Altschuler RA, Schacht J (2000) Intense noise induces formation of vasoactive lipid peroxidation products in the cochlea. Brain Res 878:163–173
Ojano-Dirain CP, Antonelli PJ, Le Prell CG (2014) Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ reduces gentamicin-induced ototoxicity. Otol Neurotol 35:533–539
Op de Beeck K, Schacht J, Van Camp G (2011) Apoptosis in acquired and genetic hearing impairment: the programmed death of the hair cell. Hear Res 281:18–27
Park MK, Lee BD, Chae SW, Chi J, Kwon SK, Song JJ (2012) Protective effect of NecroX, a novel necroptosis inhibitor, on gentamicin-induced ototoxicity. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:1265–1269
Quint E, Furness DN, Hackney CM (1998) The effect of explantation and neomycin on hair cells and supporting cells in organotypic cultures of the adult guinea-pig utricle. Hear Res 118:157–167
Rask-Andersen H, Liu W, Erixon E, Kinnefors A, Pfaller K, Schrott-Fischer A, Glueckert R (2012) Human cochlea: anatomical characteristics and their relevance for cochlear implantation. Anat Rec 295:1791–1811
Rauchegger H, Spoendlin H (1981) Damage of the basilar membrane by acoustic stimulation. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 232:117–122
Ravi R, Somani SM, Rybak LP (1995) Mechanism of cisplatin ototoxicity: antioxidant system. Pharmacol Toxicol 76:386–394
Richardson GP, Russell IJ (1991) Cochlear cultures as a model system for studying aminoglycoside induced ototoxicity. Hear Res 53:293–311
Rizzi MD, Hirose K (2007) Aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 15:352–357
Roshan R, Shridhar S, Sarangdhar MA, Banik A, Chawla M, Garg M, Singh VP, Pillai B (2014) Brain-specific knockdown of miR-29 results in neuronal cell death and ataxia in mice. RNA 20:1287–1297
Ryan A, Dallos P (1975) Effect of absence of cochlear outer hair cells on behavioural auditory threshold. Nature 253:44–46
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Mukherjea D, Ramkumar V (2007) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear Res 226:157–167
Sha SH, Schacht J (1999) Stimulation of free radical formation by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Hear Res 128:112–118
Sha SH, Taylor R, Forge A, Schacht J (2001) Differential vulnerability of basal and apical hair cells is based on intrinsic susceptibility to free radicals. Hear Res 155:1–8
Someya S, Xu J, Kondo K, Ding D, Salvi RJ, Yamasoba T, Rabinovitch PS, Weindruch R, Leeuwenburgh C, Tanokura M, Prolla TA (2009) Age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6J mice is mediated by Bak-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19432–19437
Song JJ, Chang J, Choi J, Im GJ, Chae SW, Lee SH, Kwon SY, Jung HH, Chung AY, Park HC, Choi J (2014) Protective role of NecroX-5 against neomycin-induced hair cell damage in zebrafish. Arch Toxicol 88:435-441
Spoendlin H (1985) Anatomy of cochlear innervation. Am J Otolaryngol 6:453-467
Strasser A, Cory S, Adams JM (2011) Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J 30:3667–3683
Szondy Z, Garabuczi E, Joós G, Tsay GJ, Sarang Z (2014) Impaired clearance of apoptotic cells in chronic inflammatory diseases: therapeutic implications. Front Immunol 5:354
Tadros SF, D'Souza M, Zhu X, Frisina RD (2008) Apoptosis-related genes change their expression with age and hearing loss in the mouse cochlea. Apoptosis 13:1303–1321
Taylor RR, Nevill G, Forge A (2008) Rapid hair cell loss: a mouse model for cochlear lesions. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 9:44–64
Torres M (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in redox signaling. Front Biosci 8:369–391
Usami S, Takumi Y, Fujita S, Shinkawa H, Hosokawa M (1997) Cell death in the inner ear associated with aging is apoptosis? Brain Res 747:147–150
Wan G, Corfas G, Stone JS (2013) Inner ear supporting cells: rethinking the silent majority. Semin Cell Dev Biol 24:448–459
Wang J, Van De Water TR, Bonny C, Ribaupierre F de, Puel JL, Zine A (2003) A peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase protects against both aminoglycoside and acoustic trauma-induced auditory hair cell death and hearing loss. J Neurosci 23:8596–8607
Wang P, Zhang P, Huang J, Li M, Chen X (2013) Trichostatin A protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by regulating expression of genes related to apoptosis and synaptic function. Neurotoxicology 37:51–62
Wang Y, Chen C, Loake GJ, Chu C (2010) Nitric oxide: promoter or suppressor of programmed cell death? Protein Cell 1:133–142
Wangemann P (2006) Supporting sensory transduction: cochlear fluid homeostasis and the endocochlear potential. J Physiol (Lond) 576:11–21
Westphal D, Dewson G, Czabotar PE, Kluck RM (2011) Molecular biology of Bax and Bak activation and action. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:521–531
Wu CC, Bratton SB (2013) Regulation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway by reactive oxygen species. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:546-558
Xiong Y, Fang JH, Yun JP, Yang J, Zhang Y, Jia WH, Zhuang SM (2010) Effects of microRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 51:836–845
Yamashita D, Miller JM, Jiang HY, Minami SB, Schacht J (2004) AIF and EndoG in noise-induced hearing loss. Neuroreport 15:2719–2722
Yoo J, Hamilton SJ, Angel D, Fung K, Franklin J, Parnes LS, Lewis D, Venkatesan V, Winquist E (2014) Cisplatin otoprotection using transtympanic L-N-acetylcysteine: a pilot randomized study in head and neck cancer patients. Laryngoscope 124:E87–E94
Yu L, Tang H, Jiang XH, Tsang LL, Chung YW, Chan HC (2010) Involvement of calpain-I and microRNA34 in kanamycin-induced apoptosis of inner ear cells. Cell Biol Int 34:1219–1225
Yuan J, Kroemer G (2010) Alternative cell death mechanisms in development and beyond. Genes Dev 24:2592–2602
Zhang Q, Liu H, McGee J, Walsh EJ, Soukup GA, He DZ (2013) Identifying microRNAs involved in degeneration of the organ of Corti during age-related hearing loss. PLoS One 8:e62786
Zheng HW, Chen J, Sha SH (2014) Receptor-interacting protein kinases modulate noise-induced sensory hair cell death. Cell Death Dis 5:e1262
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to Professor C.M. Hackney CBiol FSB for reading and commenting on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furness, D.N. Molecular basis of hair cell loss. Cell Tissue Res 361, 387–399 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2113-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2113-z