Abstract
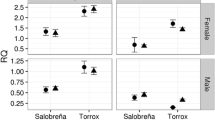
The genetic inertness of supernumerary (B) chromosomes has recently been called into question after finding several cases of gene activity on them. The grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans harbors B chromosomes containing large amounts of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) units, some of which are eventually active, but the amount of rRNA transcripts contributed by B chromosomes, compared to those of the standard (A) chromosomes, is unknown. Here, we address this question by means of quantitative PCR (qPCR) for two different ITS2 amplicons, one coming from rDNA units located in both A and B chromosomes (ITS2A+B) and the other being specific to B chromosomes (ITS2B). We analyzed six body parts in nine males showing rDNA expression in their B chromosomes in the testis. Amplification of the ITS2B amplicon was successful in RNA extracted from all six body parts analyzed, but showed relative quantification (RQ) values four orders of magnitude lower than those obtained for the ITSA+B amplicon. RQ values differed significantly between body parts for the two amplicons, with testis, accessory gland and wing muscle showing threefold higher values than head, gastric cecum and hind leg. We conclude that the level of B-specific rDNA expression is extremely low even in individuals where B chromosome rDNA is not completely silenced. Bearing in mind that B chromosomes carry the largest rDNA cluster in the E. plorans genome, we also infer that the relative contribution of B chromosome rRNA genes to ribosome biogenesis is insignificant, at least in the body parts analyzed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banaei-Moghaddam AM, Meier K, Karimi-Ashtiyani R, Houben A (2013) Formation and expression of pseudogenes on the B chromosome of rye. Plant Cell 25:2536–2544
Cabrero J, Alché JD, Camacho JPM (1987) Effects of B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans on nucleolar organizer regions activity. Activation of a latent NOR on a B chromosome fused to an autosome. Genome 29:116–121
Cabrero J, López-León MD, Bakkali M, Camacho JPM (1999) Common origin of B chromosomes variants in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Heredity 83:435–439
Camacho JPM (2005) B chromosomes. In: Gregory TR (ed) The evolution of the genome. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 223–286
Camacho JPM, Shaw MW, López-León MD, Pardo MC, Cabrero J (1997) Population dynamics of a selfish B chromosome neutralized by the standard genome in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Am Nat 149:1030–1050
Camacho JPM, Cabrero J, López-León MD, Bakkali M, Perfectti F (2003) The B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans and the intragenomic conflict. Genetica 117:77–84
Carchilan M, Kumke K, Mikolajewski S, Houben A (2009) Rye B chromosomes are weakly transcribed and might alter the transcriptional activity of A chromosome sequences. Chromosoma 118:607–616
Chapuis MP, Tohidi-Esfahani D, Dodgson T, Blondin L, Ponton F, Cullen D, Simpson SJ, Sword GA (2011) Assessment and validation of a suite of reverse transcription-quantitative PCR reference genes for analyses of density-dependent behavioural plasticity in the Australian plague locust. BMC Mol Biol 12:7
Gunderson JH, Sogin ML, Wollett G, Hollingdale M, de la Cruz VF, Waters AP, McCutchan TF (1987) Structurally distinct, stage-specific ribosomes occur in Plasmodium. Science 238:933–937
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hannan KM, Hannan RD, Rothblum LI (1998) Transcription by RNA polymerase I. Front Biosci 3:376–398
Heitz E (1931) Die Ursache der gesetzmässigen Zahl, Lage, From und Grösse pflanzlicher Nukleolen. Planta 12:775–844
Hothorn T, Bretz F, Westfall P (2008) Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom J 50:346–363
Leach CR, Houben A, Bruce F, Pistrick K, Demidov D, Timmis JN (2005) Molecular evidence for transcription of genes on a B chromosome in Crepis capillaris. Genetics 171:269–278
Long EO, David IB (1980) Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem 49:727–764
López-León MD, Neves N, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS, Hewitt GM, Camacho JPM (1994) Possible origin of B chromosome deduced from its DNA composition using double FISH technique. Chromosom Res 2:87–92
McClintock DJL (1934) The relation of a particular chromosomal element to the development of the nucleoli in Zea mays. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 21:294–328
Montiel EE, Cabrero J, Camacho JPM, López-León MD (2012) Gypsy, RTE and Mariner transposable elements populate Eyprepocnemis plorans genome. Genetica 140:365–374
Montiel EE, Cabrero J, Ruiz-Estévez M, Burke WD, Eickbush TH, Camacho JPM, López-León MD (2014) Preferential occupancy of R2 retroelements on the B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. PLoS ONE 9(3):e91820
Mosgoeller W (2004) Nucleolar ultrastructure in vertebrates. In: Olson MOJ (ed) The Nucleolus. Kluwer, New York, pp 10–20
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, The R Development Core Team (2013) nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-113
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. In: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org
Reeder RH (1999) Regulation of RNA polymerase I transcription in yeast and vertebrates. Prog Nucl Acid Res Mol Biol 62:293–327
Rufas JS, Iturra P, de Souza W, Esponda P (1982) Simple silver staining procedure for the localization of nucleolus and nucleolar organizer under light and electron microscopy. Arch Biol 93:267–274
Ruiz-Estévez M, López-León MD, Cabrero J, Camacho JPM (2012) B-chromosome ribosomal DNA is functional in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. PLoS One 7(5):e36600. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036600
Ruiz-Estévez M, López-León MD, Cabrero J, Camacho JPM (2013) Ribosomal DNA is active in different B chromosome variants of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Genetica 141:337–345
Sollner-Webb B, Tower J (1986) Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Genet 55:801–830
Teruel M (2009) Origen, expresión y efectos fenotípicos de un parásito genómico. Universidad de Granada, PhD
Teruel M, Cabrero J, Perfectti F, Camacho JPM (2007) Nucleolus size variation during meiosis and NOR activity of a B chromosome in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Chromosom Res 15:755–765
Teruel M, Cabrero J, Perfectti F, Camacho JPM (2009) Quantitative analysis of NOR expression in a B chromosome of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Chromosoma 118:291–300
Teruel M, Ruíz-Ruano F, Marchal JA, Sánchez-Baca A, Cabrero J, Camacho JPM, Perfectti F (2014) Disparate molecular evolution of two types of repetitive DNA in the genome of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Heredity 112:531–542
Trifonov VA, Dementyeva PV, Larkin DM, O’Brien PCM, Perelman PL, Yang F, Ferguson-Smith MA, Graphodatsky AS (2013) Transcription of a protein-coding gene on B chromosomes of the Siberian roe deer (Capreolus pygargus). BMC Biol 11:90
Van Hiel MB, Van Wielendaele P, Temmerman L, Van Soest S, Vuerinckx K, Huybrechts R, Broeck JV, Simonet G (2009) Identification and validation of housekeeping genes in brains of the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria under different development conditions. BMC Mol Biol 10:56
van Vugt JFA, Salverda M, de Jong H, Stouthamer R (2003) The paternal sex ratio chromosome in the parasitic wasp Trichogramma kaykai condenses the paternal chromosomes into a dense chromatin mass. Genome 46:580–587
Van Wormhoudt A, Gaume B, Le Bras Y, Roussel V, Huchette S (2011) Two different and functional nuclear rDNA genes in the abalone Haliotis tuberculata: tissue differential expression. Genetica 139:1217–1227
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3. RESEARCH0034.1-0034.11
Zhou Q, Zhu H, Huang Q, Zhao L, Zhang G, Roy SW, Vicoso B, Xuan Z, Ruan J, Zhang Y, Zhao R, Ye C, Zhang X, Wang J, Wang W, Bachtrog D (2012) Deciphering neo-sex and B chromosome evolution by the draft genome of Drosophila albomicans. BMC Genom 13:109
Zurita S, Cabrero J, López-León MD, Camacho JPM (1998) Polymorphism regeneration for a neutralized selfish B chromosome. Evolution 52:274–277
Acknowledgments
We thank an anonymous reviewer for helpful suggestions that substantially improved the manuscript, and Karl Meunier for language revision. This study was supported by a grant from the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (CGL2009-11917) and Plan Andaluz de Investigación (CVI-6649), and was partially performed by FEDER funds. M Ruíz-Estévez was supported by a FPU fellowship from the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the KU Leuven Research Foundation (GOA/11/02) and the Research Foundation of Flanders (Belgium) for financial support.
Integrity of research
All experiments comply with the current Spanish and Belgian laws. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Estévez, M., Badisco, L., Broeck, J.V. et al. B chromosomes showing active ribosomal RNA genes contribute insignificant amounts of rRNA in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans . Mol Genet Genomics 289, 1209–1216 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0880-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0880-y