Abstract
Purpose
Altered cellular metabolism has received increased attention as an important hallmark of cancer. Activation of FASN has been found to be involved in many human tumors. Despite extensive research in FASN function on cancer, the underlying mechanism is not entirely understood yet.
Methods
Cerulenin was used to suppress the FASN expression in human colorectal cancer cell lines (HT29 and LoVo). Expression of PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, mTOR, p-mTOR, FASN, and AZGP1 was measured using western blotting and qPCR. ATP and lactic acid were assessed to investigate the activation of energy metabolism. Cell cytotoxicity assay was studied by cell counting kit-8 assay. The capacity of cell proliferation and migration was investigated by clonogenic and invasion assay. Analysis of apoptosis and the cell cycle was detected by flow cytometry.
Results
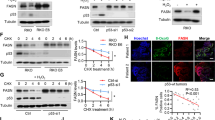
We found that the expression of FASN was down-regulated, while the expression of PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR, and AZGP1 was down-regulated in HT29 and LoVo cells treated with FASN inhibitor. Proliferation was reduced in FASN inhibitor-treated cells, which is consistent with an increased apoptosis rate. Furthermore, the migration of FASN inhibitor-treated cells was decreased and the content of ATP and lactic acid was also dropped.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that inhibited FASN suppresses the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells by down-regulating energy metabolism and mTOR signaling pathway. The results have paved the way to understand the relations of FASN, mTOR signaling pathway, and energy metabolism in colorectal cancer cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FASN:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- Akt:
-
Serine/threonine kinase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate
- OXPHOS:
-
Oxidative phosphorylation
- AZGP1:
-
Zn-alpha-2-glycoprotein 1
References
Alo’ PL, Visca P, Marci A, Mangoni A, Botti C, Di TU (1996) Expression of fatty acid synthase (FAS) as a predictor of recurrence in stage I breast carcinoma patients. Cancer 77(3):474–482
Bandyopadhyay S, Zhan R, Wang Y, Pai SK, Hirota S, Hosobe S et al (2006) Mechanism of apoptosis induced by the inhibition of fatty acid synthase in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66(11):5934–5940
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di CA, Testa JR (2005) Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: implications for therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res 94:29–86
Bongaerts GP, van Halteren HK, Verhagen CA, Wagener DJ (2006) Cancer cachexia demonstrates the energetic impact of gluconeogenesis in human metabolism. Med Hypotheses 67(5):1213–1222
Chang L, Tian X, Lu Y, Jia M, Wu P, Huang P (2014) Alpha-2-glycoprotein 1(AZGP1) regulates biological behaviors of LoVo cells by down-regulating mTOR signaling pathway and endogenous fatty acid synthesis. PLoS One 9(6):e99254
Chiang CT, Way TD, Tsai SJ, Lin JK (2007) Diosgenin, a naturally occurring steroid, suppresses fatty acid synthase expression in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells through modulating Akt, mTOR and JNK phosphorylation. FEBS Lett 581(30):5735–5742
Chiaradonna F, Moresco RM, Airoldi C, Gaglio D, Palorini R, Nicotra F et al (2012) From cancer metabolism to new biomarkers and drug targets. Biotechnol Adv 30(1):30–51
Chuang HY, Chang YF, Hwang JJ (2011) Antitumor effect of orlistat, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, is via activation of caspase-3 on human colorectal carcinoma-bearing animal. Biomed Pharmacother 65(4):286–292
Dashnamoorthy R, Abermil N, Behesti A, Kozlowski P, Lansigan F, Kinlaw WB et al (2014) The lipid addiction of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and potential treatment strategies with novel fatty acid synthase (FASN) small molecule inhibitors. Blood 124(21):4490
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB (2008) The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab 7(1):11–20
Deepa PR, Vandhana S, Jayanthi U, Krishnakumar S (2012) Therapeutic and toxicologic evaluation of anti-lipogenic agents in cancer cells compared with non-neoplastic cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 110:494–503
Duvel K, Yecies JL, Menon S, Raman P, Lipovsky AI, Souza AL et al (2010) Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Mol Cell 39:171–183
Epstein JI, Carmichael M, Partin AW (1995) OA-519 (fatty acid synthase) as an independent predictor of pathologic state in adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Urology 45(1):81–86
Fako V, Wu X, Pflug B, Liu YJ, Zhang JT (2015) Repositioning proton pump inhibitors as anti-cancer drugs by targeting the thioesterase domain of human fatty acid synthase. J Med Chem 58(2):778–784
Flavin R, Peluso S, Nguyen PL, Loda M (2010) Fatty acid synthase as a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Future Oncol 6(4):551–562
Francipane MG, Lagasse E (2014) mTOR pathway in colorectal cancer: an update. Oncotarget 5(1):49–66
Gago G, Diacovich L, Arabolaza A, Tsai SC, Gramajo H (2011) Fatty acid biosynthesis in actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35(3):475–497
Gansler TS, Hardman W 3rd, Hunt DA, Schaffel S, Hennigar RA (1997) Increased expression of fatty acid synthase (OA-519) in ovarian neoplasms predicts shorter survival. Hum Pathol 28(6):686–692
Garrido-Sanchez L, Vendrell J, Fernandez-Garcia D, Ceperuelo-Mallafre V, Chacon MR, Ocana-Wilhelmi L et al (2012) De novo lipogenesis in adipose tissue is associated with course of morbid obesity after bariatric surgery. PLoS One 7(2):e31280
Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ (2004) Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis. Nat Rev Cancer 4(11):891–899
Grube S, Dunisch P, Freitag D, Klausnitzer M, Sakr Y, Walter J et al (2014a) The mTOR inhibitor rapamycin synergizes with a fatty acid synthase inhibitor to induce cytotoxicity in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer cells. PLoS One 9(5):e97697
Grube S, Dünisch P, Freitag D, Klausnitzer M, Sakr Y, Walter J et al (2014b) Overexpression of fatty acid synthase in human gliomas correlates with the WHO tumor grade and inhibition with Orlistat reduces cell viability and triggers apoptosis. J Neurooncol 118(2):277–287
Hadad SM, Hardie DG (2014) Appleyard V, Thompson AM. Effects of metformin on breast cancer cell proliferation, the AMPK pathway and the cell cycle. Clin Transl Oncol 16(8):746–752
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1):57–70
Hassan B, Akcakanat A, Holder AM, Meric-Bernstam F (2013) Targeting the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 22(4):641–664
Hilvo M, Denkert C, Lehtinen L, Muller B, Brockmoller S, Seppanen-Laakso T et al (2011) Novel theranostic opportunities offered by characterization of altered membrane lipid metabolism in breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 71(9):3236–3245
Hsieh AC, Liu Y, Edlind MP, Ingolia NT, Janes MR, Sher A et al (2012) The translational landscape of mTOR signalling steers cancer initiation and metastasis. Nature 485(7396):55–61
Huang P, Zhu S, Lu S, Dai Z, Jin Y (2000) An experimental study on cerulenin induced apoptosis of human colonic cancer cells. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 29(2):115–118
Innocenzi D, Alò PL, Balzani A, Sebastiani V, Silipo V, La Torre G et al (2003) Fatty acid synthase expression in melanoma. J Cutan Pathol 30(1):23–28
Janku F, Tsimberidou AM, Garrido-Laguna I, Wang X, Luthra R, Hong DS et al (2011) PIK3CA mutations in patients with advanced cancers treated with PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther 10(3):558–565
Jeong NY, Lee JS, Yoo KS, Oh S, Choe E, Lee HJ et al (2013) Fatty acid synthase inhibitor cerulenin inhibits topoisomerase I catalytic activity and augments SN-38-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 18(2):226–237
Kroemer G, Pouyssegur J (2008) Tumor cell metabolism: cancer’s Achilles’ heel. Cancer Cell 13(6):472–482
Kuhajda FP (2000) Fatty-acid synthase and human cancer: new perspectives on its role in tumor biology. Nutrition 16(3):202–208
Kuhajda FP, Jenner K, Wood FD, Hennigar RA, Jacobs LB, Dick JD et al (1994) Fatty acid synthesis: a potential selective target for antineoplastic therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(14):6379–6383
Kusakabe T, Nashimoto A, Honma K, Suzuki T (2002) Fatty acid synthase is highly expressed in carcinoma, adenoma and in regenerative epithelium and intestinal metaplasia of the stomach. Histopathology 40(1):71–79
Li J, Kim SG, Blenis J (2014) Rapamycin: one drug, many effects. Cell Metab 19(3):373–379
Linehan WM, Rouault TA (2013) Molecular pathways: fumarate hydratase-deficient kidney cancer–targeting the Warburg effect in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19(13):3345–3352
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Long XH, Mao JH, Peng AF, Zhou Y, Huang SH, Liu ZL (2013) Tumor suppressive microRNA-424 inhibits osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion via targeting fatty acid synthase. Exp Ther Med 5(4):1048–1052
Long QQ, Yi YX, Qiu J, Xu CJ, Huang PL (2014) Fatty acid synthase (FASN) levels in serum of colorectal cancer patients: correlation with clinical outcomes. Tumour Biol 35(4):3855–3859
LoPiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB, Dennis PA (2008) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: effective combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Updates 11(1–2):32–50
Mashima T, Seimiya H, Tsuruo T (2009) De novo fatty-acid synthesis and related pathways as molecular targets for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer 100(9):1369–1372
Menendez JA, Lupu R (2007) Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 7(10):763–777
Migita T, Ruiz S, Fornari A, Fiorentino M, Priolo C, Zadra G et al (2009) Fatty acid synthase: a metabolic enzyme and candidate oncogene in prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(7):519–532
Milgraum LZ, Witters LA, Pasternack GR, Kuhajda FP (1997) Enzymes of the fatty acid synthesis pathway are highly expressed in in situ breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 3(11):2115–2120
Nosho K, Kawasaki T, Ohnishi M, Suemoto Y, Kirkner GJ, Zepf D et al (2008) PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer: relationship with genetic and epigenetic alterations. Neoplasia 10(6):534–541
Pelicano H, Martin DS, Xu RH, Huang P (2006a) Glycolysis inhibition for anticancer treatment. Oncogene 25(34):4633–4646
Pelicano H, Xu RH, Du M, Feng L, Sasaki R, Carew JS et al (2006b) Mitochondrial respiration defects in cancer cells cause activation of Akt survival pathway through a redox-mediated mechanism. J Cell Biol 175(6):913–923
Piyathilake CJ, Frost AR, Manne U, Bell WC, Weiss H, Heimburger DC et al (2000) The expression of fatty acid synthase (FASE) is an early event in the development and progression of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Hum Pathol 31(9):1068–1073
Pizer ES, Chrest FJ, DiGiuseppe JA, Han WF (1998) Pharmacological inhibitors of mammalian fatty acid synthase suppress DNA replication and induce apoptosis in tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 58(20):4611–4615
Pouyssegur J, Dayan F, Mazure NM (2006) Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature 441(7092):437–443
Rashid A, Pizer ES, Moga M, Milgraum LZ, Zahurak M, Pasternack GR et al (1997) Elevated expression of fatty acid synthase and fatty acid synthetic activity in colorectal neoplasia. Am J Pathol 150(1):201–208
Santolla MF, Lappano R, De Marco P, Pupo M, Vivacqua A, Sisci D et al (2012) G protein-coupled estrogen receptor mediates the up-regulation of fatty acid synthase induced by 17beta-estradiol in cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 287(52):43234–43245
Schulze A, Harris AL (2012) How cancer metabolism is tuned for proliferation and vulnerable to disruption. Nature 491(7424):364–373
Sebastiani V, Visca P, Botti C, Santeusanio G, Galati GM, Piccini V et al (2004) Fatty acid synthase is a marker of increased risk of recurrence in endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 92(1):101–105
Shiragami R, Murata S, Kosugi C, Tezuka T, Yamazaki M, Hirano A et al (2013) Enhanced antitumor activity of cerulenin combined with oxaliplatin in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 43(2):431–438
Shurbaji MS, Kalbfleisch JH, Thurmond TS (1996) Immunohistochemical detection of a fatty acid synthase (OA-519) as a predictor of progression of prostate cancer. Hum Pathol 27(9):917–921
Suva ML, Riggi N, Bernstein BE (2013) Epigenetic reprogramming in cancer. Science 339(6127):1567–1570
Swierczynski J, Hebanowska A, Sledzinski T (2014) Role of abnormal lipid metabolism in development, progression, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 20(9):2279–2303
Swinnen JV, Roskams T, Joniau S, Van Poppel H, Oyen R, Baert L et al (2002) Overexpression of fatty acid synthase is an early and common event in the development of prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 98(1):19–22
Thupari JN, Pinn ML, Kuhajda FP (2001) Fatty acid synthase inhibition in human breast cancer cells leads to malonyl-CoA-induced inhibition of fatty acid oxidation and cytotoxicity[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285(2):217–223
Vander HMG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324(5930):1029–1033
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2(7):489–501
Wang HQ, Altomare DA, Skele KL, Poulikakos PI, Kuhajda FP, Di Cristofano A et al (2005) Positive feedback regulation between AKT activation and fatty acid synthase expression in ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncogene 24(22):3574–3582
Warburg O (1956) On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science 124(3215):269–270
Ward C, Langdon SP, Mullen P, Harris AL, Harrison DJ, Supuran CT et al (2013) New strategies for targeting the hypoxic tumour microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 39(2):171–179
Weiss L, Hoffmann GE, Schreiber R, Andres H, Fuchs E, Körber E et al (1986) Fatty-acid biosynthesis in man, a pathway of minor importance. Purification, optimal assay conditions, and organ distribution of fatty-acid synthase. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 367(9):905–912
Wu X, Qin L, Fako V, Zhang JT (2014) Molecular mechanisms of fatty acid synthase (FASN)-mediated resistance to anti-cancer treatments. Adv Biol Regul 54:214–221
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F, de Bono JS, Workman P (2008) Targeting the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8(4):393–412
Zhan Y, Ginanni N, Tota MR, Wu M, Bays NW, Richon VM et al (2008) Control of cell growth and survival by enzymes of the fatty acid synthesis pathway in HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 14(18):5735–5742
Zhou W, Simpson PJ, McFadden JM, Townsend CA, Medghalchi SM, Vadlamudi A et al (2003) Fatty acid synthase inhibition triggers apoptosis during S phase in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 63(21):7330–7337
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81150028); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK2012749); Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20120092110065).
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ligong Chang and Peng Wu have contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, L., Wu, P., Senthilkumar, R. et al. Loss of fatty acid synthase suppresses the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells by down-regulating energy metabolism and mTOR signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 59–72 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2000-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2000-8