Abstract
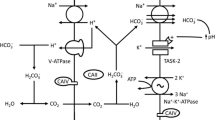
TASK-2 (K2P5.1) is a background K+ channel opened by extra- or intracellular alkalinisation that plays a role in renal bicarbonate handling, central chemoreception and cell volume regulation. Here, we present results that suggest that TASK-2 is also modulated by Gβγ subunits of heterotrimeric G protein. TASK-2 was strongly inhibited when GTP-γ-S was used as a replacement for intracellular GTP. No inhibition was present using GDP-β-S instead. Purified Gβγ introduced intracellularly also inhibited TASK-2 independently of whether GTP or GDP-β-S was present. The effects of GTP-γ-S and Gβγ subunits were abolished by neutralisation of TASK-2 C terminus double lysine residues K257–K258 or K296–K297. Use of membrane yeast two hybrid (MYTH) experiments and immunoprecipitation assays using tagged proteins gave evidence for a physical interaction between Gβ1 and Gβ2 subunits and TASK-2, in agreement with expression of these subunits in proximal tubule cells. Co-immunoprecipitation was impeded by mutating C terminus K257–K258 (but not K296–K297) to alanines. Gating by extra- or intracellular pH was unaltered in GTP-γ-S-insensitive TASK-2-K257A-K258A mutant. Shrinking TASK-2-expressing cells in hypertonic solution decreased the current to 36 % of its initial value. The same manoeuvre had a significantly diminished effect on TASK-2-K257A-K258A- or TASK-2-K296-K297-expressing cells, or in cells containing intracellular GDP-β-S. Our data are compatible with the concept that TASK-2 channels are modulated by Gβγ subunits of heterotrimeric G protein. We propose that this modulation is a novel way in which TASK-2 can be tuned to its physiological functions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
There is a discrepancy between single channel conductance for I K, vol estimated from noise analysis of macroscopic current in Ehrlich cells giving a value of 5.5 pS [46], which compares with 15 pS for TASK-2 by direct single channel current measurement [49], both at 0 mV and under quasi-physiological K+ gradient. The only difference was the lower K+ intracellular concentration used in Ehrlich cells (116 mM) compared with the expressed channel (150 mM). The difference might point to different channels, but a decision on this will have to await single channel measurements in Ehrlich cells.
References
Abel A, Wittau N, Wieland T, Schultz G, Kalkbrenner F (2000) Cell cycle-dependent coupling of the vasopressin V1a receptor to different G proteins. J Biol Chem 275:32543–32551
Barrière H, Belfodil R, Rubera I, Tauc M, Lesage F, Poujeol C, Guy N, Barhanin J, Poujeol P (2003) Role of TASK2 potassium channels regarding volume regulation in primary cultures of mouse proximal tubules. J Gen Physiol 122:177–190
Ben-Abu Y, Zhou Y, Zilberberg N, Yifrach O (2009) Inverse coupling in leak and voltage-activated K+ channel gates underlies distinct roles in electrical signaling. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:71–79
Blumer JB, Smrcka AV, Lanier SM (2007) Mechanistic pathways and biological roles for receptor-independent activators of G-protein signaling. Pharmacol Ther 113:488–506
Breitwieser GE (1991) G protein-mediated ion channel activation. Hypertension 17:684–692
Chen X, Talley EM, Patel N, Gomis A, McIntire WE, Dong B, Viana F, Garrison JC, Bayliss DA (2006) Inhibition of a background potassium channel by Gq protein a-subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:3422–3427
Cid LP, Niemeyer MI, Ramírez A, Sepúlveda FV (2000) Splice variants of a ClC-2 chloride channel with differing functional characteristics. Am J Physiol 279:C1198–C1210
Cid LP, Roa-Rojas HA, Niemeyer MI, González W, Araki M, Araki K, Sepúlveda FV (2013) TASK-2: a K2P K+ channel with complex regulation and diverse physiological functions. Front Physiol (submitted):
Clapham DE, Neer EJ (1997) G protein βγ subunits. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:167–203
Cohen A, Ben-Abu Y, Hen S, Zilberberg N (2008) A novel mechanism for human K2P2.1 channel gating. Facilitation of C-type gating by protonation of extracellular histidine residues. J Biol Chem 283:19448–19455
Dascal N (2001) Ion-channel regulation by G proteins. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:391–398
Davis BA, Hogan EM, Boron WF (1992) Role of G proteins in stimulation of Na-H exchange by cell shrinkage. Am J Physiol 262:C533–C536
Decher N, Maier M, Dittrich W, Gassenhuber J, Bruggemann A, Busch AE, Steinmeyer K (2001) Characterization of TASK-4, a novel member of the pH-sensitive, two- pore domain potassium channel family. FEBS Lett 492:84–89
Díaz M, Sepúlveda FV (1995) Characterisation of Ca2+-dependent inwardly rectifying K+ currents in HeLa cells. Pflügers Arch 430:168–180
Doroshenko P (1991) Second messengers mediating activation of chloride current by intracellular GTP gamma S in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol (London) 436:725–738
Doyle DA, Morais Cabral J, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 280:69–77
Enyedi P, Czirják G (2010) Molecular background of leak K+ currents: two-pore domain potassium channels. Physiol Rev 90:559–605
Estévez AY, Bond T, Strange K (2001) Regulation of ICl, swell in neuroblastoma cells by G protein signaling pathway. Am J Physiol 281:C89–C98
Flores CA, Cid LP, Niemeyer MI, Sepúlveda FV (2011) B lymphocytes taken to task: a role for a background conductance K2P K+ channel in B cells. Focus on "Expression of TASK-2 and its upregulation by B cell receptor stimulation in WEHI-231 mouse immature B cells". Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 300:C976–C978
Gestreau C, Heitzmann D, Thomas J, Dubreuil V, Bandulik S, Reichold M, Bendahhou S, Pierson P, Sterner C, Peyronnet-Roux J, Benfriha C, Tegtmeier I, Ehnes H, Georgieff M, Lesage F, Brunet JF, Goridis C, Warth R, Barhanin J (2010) Task2 potassium channels set central respiratory CO2 and O2 sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:2325–2330
Girard C, Duprat F, Terrenoire C, Tinel N, Fosset M, Romey G, Lazdunski M, Lesage F (2001) Genomic and functional characteristics of novel human pancreatic 2P domain K+ channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 282:249–256
Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS (2006) Aquaporin-1 facilitates epithelial cell migration in kidney proximal tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:39–45
Herlitze S, García DE, Mackie K, Hille B, Scheuer T, Catterall WA (1996) Modulation of Ca2+ channels by G-protein βγ subunits. Nature 380:258–262
Hoffmann EK, Pedersen SF (2011) Cell volume homeostatic mechanisms: effectors and signalling pathways. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 202:465–485
Hoshi T, Zagotta WN, Aldrich RW (1990) Biophysical and molecular mechanism of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science 250:533–538
Hougaard C, Jørgensen F, Hoffmann EK (2001) Modulation of the volume-sensitive K+ current in Ehrlich ascites tumour cells by pH. Pflügers Arch 442:622–633
Hougaard C, Niemeyer MI, Hoffmann EK, Sepúlveda FV (2000) K+ current activated by leukotriene D4 or osmotic swelling of Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Pflügers Arch 440:283–294
Inanobe A, Morishige KI, Takahashi N, Ito H, Yamada M, Takumi T, Nishina H, Takahashi K, Kanaho Y, Katada T (1995) Gβγ directly binds to the carboxyl terminus of the G protein-gated muscarinic K+ channel, GIRK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 212:1022–1028
Ishii T, Hashimoto T, Ohmori H (1996) Hypotonic stimulation induced Ca2+ release from IP3-sensitive internal stores in a green monkey kidney cell line. J Physiol 493(Pt 2):371–384
Ivanina T, Rishal I, Varon D, Mullner C, Frohnwieser-Steinecke B, Schreibmayer W, Dessauer CW, Dascal N (2003) Mapping the Gβγ-binding sites in GIRK1 and GIRK2 subunits of the G protein-activated K+ channel. J Biol Chem 278:29174–29183
Jelacic TM, Sims SM, Clapham DE (1999) Functional expression and characterization of G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels containing GIRK3. J Membr Biol 169:123–129
Jiang Y, Lee A, Chen J, Cadene M, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (2002) The open pore conformation of potassium channels. Nature 417:523–526
Jones MB, Siderovski DP, Hooks SB (2004) The Gβγ dimer as a novel source of selectivity in G-protein signaling: GGL-ing at convention. Mol Interv 4:200–214
Kirkegaard SS, Lambert IH, Gammeltoft S, Hoffmann EK (2010) Activation of the TASK-2 channel after cell swelling is dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C844–C853
L'Hoste S, Poet M, Duranton C, Belfodil R, Barriere H, Rubera I, Tauc M, Poujeol C, Barhanin J, Poujeol P (2007) Role of TASK2 in the control of apoptotic volume decrease in proximal kidney cells. J Biol Chem 282:36692–36703
Lambert IH (1987) Effect of arachidonic acid, fatty acids, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes on volume regulation in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Membr Biol 98:207–221
Luscher C, Slesinger PA (2010) Emerging roles for G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium (GIRK) channels in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:301–315
Magidovich E, Yifrach O (2004) Conserved gating hinge in ligand- and voltage-dependent K+ channels. Biochemistry 43:13242–13247
Margalit A, Livne AA, Funder J, Granot Y (1993) Initiation of RVD response in human platelets: mechanical–biochemical transduction involves pertussis-toxin-sensitive G protein and phospholipase A2. J Membr Biol 136:303–311
Mathie A (2007) Neuronal two-pore-domain potassium channels and their regulation by G protein-coupled receptors. J Physiol (London) 578:377–385
Nam JH, Shin DH, Zheng H, Lee DS, Park SJ, Park KS, Kim SJ (2011) Expression of TASK-2 and its upregulation by B cell receptor stimulation in WEHI-231 mouse immature B cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 300:C1013–C1022
Niemeyer MI, Cid LP, Barros LF, Sepúlveda FV (2001) Modulation of the two-pore domain acid-sensitive K+ channel TASK-2 (KCNK5) by changes in cell volume. J Biol Chem 276:43166–43174
Niemeyer MI, Cid LP, Peña-Münzenmayer G, Sepúlveda FV (2010) Separate gating mechanisms mediate the regulation of K2P potassium channel TASK-2 by intra- and extracellular pH. J Biol Chem 285:16467–16475
Niemeyer MI, González-Nilo FD, Zúñiga L, González W, Cid LP, Sepúlveda FV (2006) Gating of two-pore domain K+ channels by extracellular pH. Biochem Soc Trans 34:903–906
Niemeyer MI, González-Nilo FD, Zúñiga L, González W, Cid LP, Sepúlveda FV (2007) Neutralization of a single arginine residue gates open a two-pore domain, alkali-activated K+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:666–671
Niemeyer MI, Hougaard C, Hoffmann EK, Jørgensen F, Stutzin A, Sepúlveda FV (2000) Characterisation of a cell swelling-activated K+-selective conductance of Ehrlich mouse ascites tumour cells. J Physiol (London) 524:757–767
Niemeyer MI, Stutzin A, Sepúlveda FV (2002) A voltage-independent K+ conductance activated by cell swelling in Ehrlich cells is modulated by a G-protein-mediated process. Biochim Biophys Acta 1562:1–5
Piechotta PL, Rapedius M, Stansfeld PJ, Bollepalli MK, Erhlich G, Andres-Enguix I, Fritzenschaft H, Decher N, Sansom MS, Tucker SJ, Baukrowitz T (2011) The pore structure and gating mechanism of K2P channels. EMBO J 30:3607–3619
Reyes R, Duprat F, Lesage F, Fink M, Salinas M, Farman N, Lazdunski M (1998) Cloning and expression of a novel pH-sensitive two pore domain K+ channel from human kidney. J Biol Chem 273:30863–30869
Riquelme G, Sepúlveda FV, Jørgensen F, Pedersen S, Hoffmann EK (1998) Swelling-activated potassium currents of Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1371:101–106
Sandoz G, Douguet D, Chatelain F, Lazdunski M, Lesage F (2009) Extracellular acidification exerts opposite actions on TREK1 and TREK2 potassium channels via a single conserved histidine residue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14628–14633
Smrcka AV (2008) G protein βγ subunits: central mediators of G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2191–2214
Stansfeld PJ, Grottesi A, Sands ZA, Sansom MS, Gedeck P, Gosling M, Cox B, Stanfield PR, Mitcheson JS, Sutcliffe MJ (2008) Insight into the mechanism of inactivation and pH sensitivity in potassium channels from molecular dynamics simulations. Biochemistry 47:7414–7422
Van der WT, Tomassen SF, de Jonge HR, Tilly BC (2000) Signalling mechanisms involved in volume regulation of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 10:289–296
Vázquez-Juárez E, Ramos-Mandujano G, Hernández-Benítez R, Pasantes-Morales H (2008) On the role of G-protein coupled receptors in cell volume regulation. Cell Physiol Biochem 21:1–14
Veale EL, Kennard LE, Sutton GL, MacKenzie G, Sandu C, Mathie A (2007) Gaq-mediated regulation of TASK3 two-pore domain potassium channels: the role of protein kinase C. Mol Pharmacol 71:1666–1675
Voets T, Droogmans G, Raskin G, Eggermont J, Nilius B (1999) Reduced intracellular ionic strength as the initial trigger for activation of endothelial volume-regulated anion channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:5298–5303
Voets T, Manolopoulos V, Eggermont J, Ellory C, Droogmans G, Nilius B (1998) Regulation of a swelling-activated chloride current in bovine endothelium by protein tyrosine phosphorylation and G proteins. J Physiol (London) 506:341–352
Warth R, Barrière H, Meneton P, Bloch M, Thomas J, Tauc M, Heitzmann D, Romeo E, Verrey F, Mengual R, Guy N, Bendahhou S, Lesage F, Poujeol P, Barhanin J (2004) Proximal renal tubular acidosis in TASK2 K+ channel-deficient mice reveals a mechanism for stabilizing bicarbonate transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:8215–8220
Wettschureck N, Offermanns S (2005) Mammalian G proteins and their cell type specific functions. Physiol Rev 85:1159–1204
Woo DH, Han KS, Shim JW, Yoon BE, Kim E, Bae JY, Oh SJ, Hwang EM, Marmorstein AD, Bae YC, Park JY, Lee CJ (2012) TREK-1 and Best1 channels mediate fast and slow glutamate release in astrocytes upon GPCR activation. Cell 151:25–40
Yellen G (2002) The voltage-gated potassium channels and their relatives. Nature 419:35–42
Yévenes GE, Moraga-Cid G, Guzman L, Haeger S, Oliveira L, Olate J, Schmalzing G, Aguayo LG (2006) Molecular determinants for G protein βγ modulation of ionotropic glycine receptors. J Biol Chem 281:39300–39307
Yévenes GE, Peoples RW, Tapia JC, Parodi J, Soto X, Olate J, Aguayo LG (2003) Modulation of glycine-activated ion channel function by G-protein βγ subunits. Nat Neurosci 6:819–824
Zhou Y, Morais-Cabral JH, Kaufman A, MacKinnon R (2001) Chemistry of ion coordination and hydration revealed by a K+ channel-Fab complex at 2.0 A resolution. Nature 414:43–48
Zilberberg N, Ilan N, Goldstein SA (2001) KCNKO: opening and closing the 2-P-domain potassium leak channel entails "C-type" gating of the outer pore. Neuron 32:635–648
Zúñiga L, Márquez V, González-Nilo FD, Chipot C, Cid LP, Sepúlveda FV, Niemeyer MI (2011) Gating of a pH-sensitive K2P potassium channel by an electrostatic effect of basic sensor residues on the selectivity filter. PLoS One 6:e16141
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs. Jürgen Daut (Marburg), Stéphane A. Laporte (Montréal) and Carlos B. González (Valdivia) for cDNAs for TASK-3, and AT1 and V1a receptors. Mauricio Bórquez is acknowledged for his help with some of the experiments. Financial support was obtained from Fondecyt grants 1090478 and 3085021. The Centro de Estudios Científicos (CECS) is funded by the Chilean Government through the Centres of Excellence Base Financing Program of Conicyt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
C. Añazco and G. Peña-Münzenmayer should be considered joint first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Añazco, C., Peña-Münzenmayer, G., Araya, C. et al. G protein modulation of K2P potassium channel TASK-2. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 1715–1726 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1314-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1314-0