Abstract
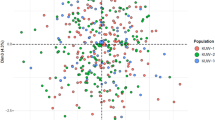
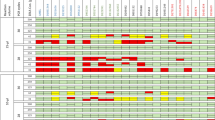
Because of their sensitivity and high level of discrimination, short tandem repeat (STR) maker systems are currently the method of choice in routine forensic casework and data banking, usually in multiplexes up to 15–17 loci. Constraints related to sample amount and quality, frequently encountered in forensic casework, will not allow to change this picture in the near future, notwithstanding the technological developments. In this study, we present a free online calculator named PopAffiliator (http://cracs.fc.up.pt/popaffiliator) for individual population affiliation in the three main population groups, Eurasian, East Asian and sub-Saharan African, based on genotype profiles for the common set of STRs used in forensics. This calculator performs affiliation based on a model constructed using machine learning techniques. The model was constructed using a data set of approximately fifteen thousand individuals collected for this work. The accuracy of individual population affiliation is approximately 86%, showing that the common set of STRs routinely used in forensics provide a considerable amount of information for population assignment, in addition to being excellent for individual identification.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves C, Amorim A, Gusmão L, Pereira L (2001) VWA STR genotyping: further inconsistencies between Perkin-Elmer and Promega kits. Int J Leg Med 115:97–99
Pamplona JP, Freitas F, Pereira L (2008) A worldwide database of autosomal markers used by the forensic community. Forensic Sci Int: Genetics Supplement Series 1:656–657
Salas A, Bandelt HJ, Macaulay V, Richards MB (2007) Phylogeographic investigations: the role of trees in forensic genetics. Forensic Sci Int 168:1–13
Jobling MA (2001) Y-chromosomal SNP haplotype diversity in forensic analysis. Forensic Sci Int 118:158–162
Phillips C, Salas A, Sánchez JJ, Fondevila M, Gómez-Tato A, Alvarez-Dios J, Calaza M, de Cal MC, Ballard D, Lareu MV, Carracedo A, SNPforID Consortium (2007) Inferring ancestral origin using a single multiplex assay of ancestry-informative marker SNPs. Forensic Sci Int Genet 1:273–280
Phillips C, Prieto L, Fondevila M, Salas A, Gómez-Tato A, Alvarez-Dios J, Alonso A, Blanco-Verea A, Brión M, Montesino M, Carracedo A, Lareu MV (2009) Ancestry analysis in the 11-M Madrid bomb attack investigation. PLoS ONE 4:e6583
Sanchez JJ, Børsting C, Balogh K, Berger B, Bogus M, Butler JM, Carracedo A, Court DS, Dixon LA, Filipović B, Fondevila M, Gill P, Harrison CD, Hohoff C, Huel R, Ludes B, Parson W, Parsons TJ, Petkovski E, Phillips C, Schmitter H, Schneider PM, Vallone PM, Morling N (2008) Forensic typing of autosomal SNPs with a 29 SNP-multiplex-results of a collaborative EDNAP exercise. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:176–183
Allocco DJ, Song Q, Gibbons GH, Ramoni MF, Kohane IS (2007) Geography and genography: prediction of continental origin using randomly selected single nucleotide polymorphisms. BMC Genomics 8:68
Amorim A, Pereira L (2005) Pros and cons in the use of SNPs in forensic kinship investigation: a comparative analysis with STRs. Forensic Sci Int 150:17–21
Rosenberg NA, Pritchard JK, Weber JL, Cann HM, Kidd KK, Zhivotovsky LA, Feldman MW (2002) Genetic structure of human populations. Science 298:2381–2385
Rosenberg NA, Mahajan S, Ramachandran S, Zhao C, Pritchard JK, Feldman MW (2005) Clines, clusters, and the effect of study design on the inference of human population structure. PLoS Genet 1:e70
Bamshad MJ, Wooding S, Watkins WS, Ostler CT, Batzer MA, Jorde LB (2003) Human population genetic structure and inference of group membership. Am J Hum Genet 72:578–589
Evett IW, Pinchin R, Buffery C (1992) An investigation of the feasibility of inferring ethnic origin from DNA profiles. JFSS 32:301–306
Meyer E, Wiegand P, Brinkmann B (1995) Phenotype differences of STRs in 7 human populations. Int J Leg Med 107:314–322
Lowe AL, Urquhart A, Foreman LA, Evett IW (2001) Inferring ethnic origin by means of an STR profile. Forensic Sci Int 119:17–22
Fosella X, Marroni F, Manzoni S, Verzeletti A, De Ferrari F, Cerri N, Presciuttini S (2004) Assigning individuals to ethnic groups based on 13 STR loci. Int Congr Ser 1261:59–61
Graydon M, Cholette F, Ng LK (2009) Inferring ethnicity using 15 autosomal STR loci -comparisons among populations of similar and distinctly different physical traits. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:251–254
Klintschar M, Füredi S, Egyed B, Reichenpfader B, Kleiber M (2003) Estimating the ethnic origin (EEO) of individuals using short tandem repeat loci of forensic relevance. Int Congr Ser 1239:53–56
Fridman C, dos Santos PC, Kohler P, Garcia CF, Lopez LF, Massad E, Gattás GJ (2008) Brazilian population profile of 15 STR markers. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:e1–e4
Brisighelli F, Capelli C, Boschi I, Garagnani P, Lareu MV, Pascali VL, Carracedo A (2009) Allele frequencies of fifteen STRs in a representative sample of the Italian population. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e29–e30
Herrera-Paz EF, García LF, Aragon-Nieto I, Paredes M (2008) Allele frequencies distributions for 13 autosomal STR loci in 3 Black Carib (Garifuna) populations of the Honduran Caribbean coasts. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e5–e10
Jacewicz R, Jedrzejczyk M, Ludwikowska M, Berent J (2008) Population database on 15 autosomal STR loci in 1000 unrelated individuals from the Lodz region of Poland. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:e41–e43
Juárez-Cedillo T, Zuñiga J, Acuña-Alonzo V, Pérez-Hernández N, Rodríguez-Pérez JM, Barquera R, Gallardo GJ, Sánchez-Arenas R, García-Peña Mdel C, Granados J, Vargas-Alarcón G (2008) Genetic admixture and diversity estimations in the Mexican Mestizo population from Mexico City using 15 STR polymorphic markers. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:e37–e39
Kraaijenbrink T, Zuniga S, Su B, Shi H, Xiao CJ, Tang WR, de Knijff P (2008) Allele frequency distribution of 21 forensic autosomal STRs in 7 populations from Yunnan, China. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e11–e12
Omran GA, Rutty GN, Jobling MA (2009) Genetic variation of 15 autosomal STR loci in Upper (Southern) Egyptians. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e39–e44
Piatek J, Jacewicz R, Ossowski A, Parafiniuk M, Berent J (2008) Population genetics of 15 autosomal STR loci in the population of Pomorze Zachodnie (NW Poland). Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:e41–e43
Sánchez-Diz P, Menounos PG, Carracedo A, Skitsa I (2008) 16 STR data of a Greek population. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:e71–e72
Sánchez-Diz P, Acosta MA, Fonseca D, Fernández M, Gómez Y, Jay M, Alape J, Lareu MV, Carracedo A, Restrepo CM (2009) Population data on 15 autosomal STRs in a sample from Colombia. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e81–e82
Nie S, Yao J, Yan H, Yang Y, Gu T, Tang W, Li W, Wang B, Xiao C (2008) Genetic data of 15 STR loci in Chinese Yunnan Han population. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e1–e3
Soták M, Petrejcíková E, Bernasovská J, Bernasovský I, Sovicová A, Boronová I, Svicková P, Bôziková A, Gabriková D (2008) Genetic variation analysis of 15 autosomal STR loci in Eastern Slovak Caucasian and Romany (Gypsy) population. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e21–e25
Rubi-Castellanos R, Anaya-Palafox M, Mena-Rojas E, Bautista-España D, Muñoz-Valle JF, Rangel-Villalobos H (2009) Genetic data of 15 autosomal STRs (Identifiler kit) of three Mexican Mestizo population samples from the States of Jalisco (West), Puebla (Center), and Yucatan (Southeast). Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e71–e76
Simms TM, Garcia C, Mirabal S, McCartney Q, Herrera RJ (2008) The genetic legacy of the transatlantic slave trade in the island of New Providence. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2:310–317
Budowle B, Moretti TR (1999) Genotype profiles for six population groups at the 13 CODIS Short Tandem Repeat core loci and other PCRB Based loci. Forensic Sci Commun 1
Zhivotovsky LA, Veremeichyk VM, Kuzub NN, Atramentova LA, Udina IG, Kartel NA, Tsybovsky IS (2009) A reference data base on STR allele frequencies in the Belarus population developed from paternity cases. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e107–e109
Zhivotovsky LA, Malyarchuk BA, Derenko MV, Wozniak M, Grzybowski T (2009) Developing STR databases on structured populations: the native South Siberian population versus the Russian population. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e111–e116
Zhivotovsky LA, Akhmetova VL, Fedorova SA, Zhirkova VV, Khusnutdinova EK (2009) An STR database on the Volga-Ural population. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e133–e136
Li C, Li L, Zhao Z, Lin Y, Que T, Liu Y, Xue J (2009) Genetic polymorphism of 17 STR loci for forensic use in Chinese population from Shanghai in East China. Forensic Sci Int Genet 3:e117–e118
Andreassen R, Pereira L, Dupuy BM, Mevaag B (2009) Icelandic population data for the STR loci in the AMPFlSTR®SGM Plus™ system and the PowerPlex® Y-system. Forensic Sci Int Genet (in press)
Tillmar AO, Bäckström G, Montelius K (2009) Genetic variation of 15 autosomal STR loci in a Somali population. Forensic Sci Int Genet 4:e19–e20
Lopes V, Serra A, Gamero J, Sampaio L, Balsa F, Oliveira C, Batista L, Corte-Real F, Vieira DN, Vide MC, Anjos MJ, Carvalho M (2009) Allelic frequency distribution of 17 STRs from Identifiler and PowerPlex-16 in Central Portugal area and the Azores archipelago. Forensic Sci Int Genet 4:e1–e7
Witten IH, Frank E (2005) Data Mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques, 2nd Edition, Morgan Kaufmann
Fonseca NA, Camacho R, Pereira L (submitted) On the prediction of an individual affiliation to a major population group based on information from a small set of autosomal STRs—a machine learning approach
Muro T, Fujihara J, Imamura S, Nakamura H, Yasuda T, Takeshita H (2008) Allele frequencies for 15 STR loci in Ovambo population using AmpFlSTR Identifiler Kit. Leg Med (Tokyo) 10:157–159
Acknowledgments
IPATIMUP is an Associate Laboratory of the Portuguese Ministry of Science, Technology and Higher Education and is partially supported by FCT, the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology. CRACS-INESC Porto is supported by Programa Operacional Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação (POCTI) e Quadro Comunitário de Apoio III. NJ and DH were supported by grant 196-1962766-2751. LZh received grants from the Russian Academy of Science for Mol & Cell Biol and FSM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
LP delineated the project and collected the database. RC and NAF performed the machine learning analyses, interpreted results and constructed the online calculator. The remaining authors contributed genotype profiles for the database and collaborated in the improvement of the manuscript and of the online tool’s output.
Luísa Pereira and Nuno A. Fonseca contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, L., Alshamali, F., Andreassen, R. et al. PopAffiliator: online calculator for individual affiliation to a major population group based on 17 autosomal short tandem repeat genotype profile. Int J Legal Med 125, 629–636 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-010-0472-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-010-0472-2