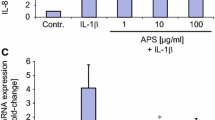
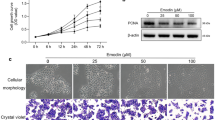
Abstract
Acne is a complex, chronic and common skin disorder of pilosebaceous units. Although it is known that exacerbation of acne results from emotional stress, the nature of the association between stress and acne remains unclear. This is due in part to the lack of substantial evidence regarding the participation of cutaneous neurogenic factors in the pathogenesis of acne. Culture of sebocytes provides a new insight into the participation of neuropeptides, notably substance P (SP), in the pathophysiology of acne. To examine the possible involvement of neurogenic factors in the pathogenesis of acne, we used immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR to compare the expression of interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), peroxisome proliferators activated receptors-γ (PPAR-γ) on the cultured sebocytes stimulated by SP. IL-1 is primarily proinflammatory cytokines to stimulate the expression of genes associated with inflammation. IL-6 is a pleiotropic cytokine with a wide range of biological activities and regulates inflammation. TNF-α is a pleiotropic pro-inflammatory cytokine that exerts multiple biologic effects. PPAR-γ is a nuclear hormone receptor and plays a unique role in stimulating sebocyte lipogenesis. More numerous immunoreactivity to IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α and PPAR-γ and increased RNA amplification for IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α and PPAR-γ were observed after addition of SP compared with the control. This study reveals that SP is involved in the pathogenesis of acne.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alestas T et al (2006) Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of leukotriene B4 and prostaglandin E2 are active in sebaceous glands. J Mol Med 84:75–87
Benfenati A, Brillanti F (1939) Sulla distribuzione delle ghiandole sebacee nella cute del corpo umino. Arch Ital Dermatol 15:33–42
Cunliffe WJ (1989) Acne. Martin Dunitz, London
Fujie T, Shikiji T, Uchida N et al (1996) Culture of cells derived from the human sebaceous glands under serum-free conditions without a biological feeder layer or specific matrices. Arch Dermatol Res 288:703–708
Katsambas A, Papakonstantinou A (2004) Acne: systemic treatment. Clin Dermatol 22:412–418
Marta Guarna M, Coulson R, Rubinchik E (2006) Anti-inflammatory activity of cationic peptides: application to the treatment of acne vulgaris. FEMS Microbiol Lett 257:1–6
Nadel JA, Borson DB (1991) Modulation of neurogenic inflammation by neutral endopeptidase. Am Rev Respir Dis 143:33–36
Olerud JE, Usui MJ, Seckin D, Chui DS, Haycox CL, Song I-S, Ansel JC, Bunnett NW. (1999) Neutral endopeptidase expression and distribution in human skin and wounds. J Invest Dermatol 112:873–881
Rohleder N, Wolf JM, Herpfer I, Fiebich BL, Kirschbaum C, Lieb K (2006) No response of plasma substance P, but delayed increase of interleukin–1 receptor antagonist to acute psychosocial stress. Life Sci 22;78(26):3082–3089
Thielitz A et al (2007) Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and aminopeptidase N target major pathogenetic steps in acne initiation. J Invest Dermatol 127:1042–1051
Toyoda M, Morohashi M (2001) Pathogenesis of acne. Med Elect Microsc 34:29–40
Toyoda M, Makino T, Kagoura M, Morohashi M (2001) Expression of neuropeptide—degrading enzymes in alopecia areata: an immunohistochemical study. Br J Dermatol 144:46–54
Toyoda M, Nakamura M, Makino T et al (2002) Sebaceous glands in acne patients express high levels of neutral endopeptidase. Exp Dermatol 11:241–247
Toyoda M, Nakamura M, Morohashi M (2002) Neuropeptides and sebaceous glands. Eur J Dermatol 12:422–427
Trivedi NR et al (2006) Peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors increase human sebum production. J Invest Dermatol 126:2002–2009
Winston MH, Shalita AR (1991) Acne vulgaris. Pathogenesis and treatment. Pediatr Clin North Am 38(4):889–903
Zouboulis CC, Xia L, Detmar M et al (1991) Culture of human sebocytes and markers of sebocytic differentiation in vitro. Skin Pharmacol 4:74–83
Zouboulis CC (2004) Acne and sebaceous gland function. Clin Dermatol 22:360–366
Zouboulis CC, Böhm M (2004) Neuroendocrine regulation of sebocytes—a pathogenetic link between stress and acne. Exp Dermatol 13:31–35
Zouboulis CC et al (2002) Corticotropin releasing hormone: an autocrine hormone that promotes lipogenesis in human sebocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7148–7153
Zouboulis CC et al (1998) The human sebocyte culture model provides new insights into development and management of seborrhea and acne. Dermatology 196:21–31
Zouboulis CC, Piquero-Martin J (2003) Update and future of systemic acne treatment. Dermatology 206:37–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, W.J., Jung, H.D., Lee, H.J. et al. Influence of substance-P on cultured sebocytes. Arch Dermatol Res 300, 311–316 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-008-0854-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-008-0854-1