Abstract
Backgrounds and aims
There is increasing evidence that gut-derived intraepithelial lymphocytes have potent cytolytic and immunoregulatory functions, which they use to sustain epithelial integrity. The aims of this study were to investigate the roles of small intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (SI-IELs) in oral tolerance and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis.
Methods
SI-IELs or sorted γδ T cells from untreated, colitis, and colitis-extracted protein (CEP)-fed colitis mice were adoptively transferred to BALB/c mice; colitis was then induced with DSS. Cytokines were analyzed in sera from mice and culture supernatants.
Results
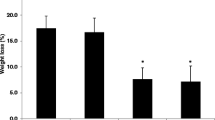
Transfer of SI-IELs or sorted γδ T cells from untreated and colitis mice all alleviated experimental colitis. Mice orally administered with five low doses of CEP showed less severe symptoms and histological injury. SI-IELs from CEP-fed colitis mice more significantly ameliorated colitis than those from control mice (weight, 94.1 ± 2.5% vs. 89.8 ± 2.6%, p < 0.05; disease activity index, 7.2 ± 1.2 vs. 8.7 ± 1.9, p < 0.05; histological scores, 22.1 ± 2.8 vs. 25.7 ± 2.1, p < 0.05, n = 8 per group); however, not did SI-γδ IELs from CEP-fed colitis mice. Alleviation of colitis was accompanied by an increase of TGF-β1 secretion and no change of IFN-γ in sera and culture supernatants. The level of serum TGF-β1 was negatively related to the severity of colitis.
Conclusions
The protective effects of SI-IELs in DSS-induced colitis were partly accomplished by γδ T cells and could be mediated by TGF-β but were not associated with IFN-γ. Oral tolerance strengthens the suppressive effects of regulatory subsets in SI-IELs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunisawa J, Takahashi I, Kiyono H (2007) Intraepithelial lymphocytes: their shared and divergent immunological behaviors in the small and large intestine. Immunol Rev 215:136–153
Cheroutre H (2005) IELs: enforcing law and order in the court of the intestinal epithelium. Immunol Rev 206:114–131
Buzoni-Gatel D, Lepage AC, Mier-Poisson IH, Bout DT, Kasper LH (1997) Adoptive transfer of gut intraepithelial lymphocytes protects against murine infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol 158:5883–5889
Muller S, Buhler-Jungo M, Mueller C (2000) Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes exert potent protective cytotoxic activity during an acute virus infection. J Immunol 164:1986–1994
Nanno M, Shiohara T, Yamamoto H, Kawakami K, Ishikawa H (2007) gammadelta T cells: firefighters or fire boosters in the front lines of inflammatory responses. Immunol Rev 215:103–113
Komano H, Fujiura Y, Kawaguchi M, Matsumoto S, Hashimoto Y, Obana S, Mombaerts P, Tonegawa S, Yamamoto H, Itohara S (1995) Homeostatic regulation of intestinal epithelia by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6147–6151
Dalton JE, Cruickshank SM, Egan CE, Mears R, Newton DJ, Andrew EM, Lawrence B, Howell G, Else KJ, Gubbels MJ, Striepen B, Smith JE, White SJ, Carding SR (2006) Intraepithelial gammadelta+ lymphocytes maintain the integrity of intestinal epithelial tight junctions in response to infection. Gastroenterology 131:818–829
Yang H, Antony PA, Wildhaber BE, Teitelbaum DH (2004) Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte gamma delta-T cell-derived keratinocyte growth factor modulates epithelial growth in the mouse. J Immunol 172:4151–4158
Mengel J, Cardillo F, Aroeira LS, Williams O, Russo M, Vaz NM (1995) Anti-gamma delta T cell antibody blocks the induction and maintenance of oral tolerance to ovalbumin in mice. Immunol Lett 48:97–102
Fujihashi K, Dohi T, Kweon MN, McGhee JR, Koga T, Cooper MD, Tonegawa S, Kiyono H (1999) gammadelta T cells regulate mucosally induced tolerance in a dose-dependent fashion. Int Immunol 11:1907–1916
Ke Y, Pearce K, Lake JP, Ziegler HK, Kapp JA (1997) Gamma delta T lymphocytes regulate the induction and maintenance of oral tolerance. J Immunol 158:3610–3618
Locke NR, Stankovic S, Funda DP, Harrison LC (2006) TCR gamma delta intraepithelial lymphocytes are required for self-tolerance. J Immunol 176:6553–6559
Kapp JA, Kapp LM, McKenna KC, Lake JP (2004) gammadelta T-cell clones from intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes inhibit development of CTL responses ex vivo. Immunology 111:155–164
Chen Y, Chou K, Fuchs E, Havran WL, Boismenu R (2002) Protection of the intestinal mucosa by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14338–14343
Inagaki-Ohara K, Chinen T, Matsuzaki G, Sasaki A, Sakamoto Y, Hiromatsu K, Nakamura-Uchiyama F, Nawa Y, Yoshimura A (2004) Mucosal T cells bearing TCRgammadelta play a protective role in intestinal inflammation. J Immunol 173:1390–1398
Tsuchiya T, Fukuda S, Hamada H, Nakamura A, Kohama Y, Ishikawa H, Tsujikawa K, Yamamoto H (2003) Role of gamma delta T cells in the inflammatory response of experimental colitis mice. J Immunol 171:5507–5513
Kuhl AA, Pawlowski NN, Grollich K, Loddenkemper C, Zeitz M, Hoffmann JC (2007) Aggravation of intestinal inflammation by depletion/deficiency of gammadelta T cells in different types of IBD animal models. J Leukoc Biol 81:168–175
Faria AM, Weiner HL (2005) Oral tolerance. Immunol Rev 206:232–259
Hyun JG, Barrett TA (2006) Oral tolerance therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 101:569–571
Trentham DE (1998) Oral tolerization as a treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 24:525–536
von Herrath MG, Dyrberg T, Oldstone MB (1996) Oral insulin treatment suppresses virus-induced antigen-specific destruction of beta cells and prevents autoimmune diabetes in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest 98:1324–1331
Ilan Y, Gotsman I, Pines M, Beinart R, Zeira M, Ohana M, Rabbani E, Engelhardt D, Nagler A (2000) Induction of oral tolerance in splenocyte recipients toward pretransplant antigens ameliorates chronic graft versus host disease in a murine model. Blood 95:3613–3619
Whitacre CC, Gienapp IE, Meyer A, Cox KL, Javed N (1996) Oral tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 778:217–227
Ilan Y, Weksler-Zangen S, Ben-Horin S, Diment J, Sauter B, Rabbani E, Engelhardt D, Chowdhury NR, Chowdhury JR, Goldin E (2000) Treatment of experimental colitis by oral tolerance induction: a central role for suppressor lymphocytes. Am J Gastroenterol 95:966–973
Gotsman I, Shlomai A, Alper R, Rabbani E, Engelhardt D, Ilan Y (2001) Amelioration of immune-mediated experimental colitis: tolerance induction in the presence of preexisting immunity and surrogate antigen bystander effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:926–932
Dasgupta A, Kesari KV, Ramaswamy KK, Amenta PS, Das KM (2001) Oral administration of unmodified colonic but not small intestinal antigens protects rats from hapten-induced colitis. Clin Exp Immunol 125:41–47
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R (1990) A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694–702
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ (1993) Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest 69:238–249
Dieleman LA, Palmen MJ, Akol H, Bloemena E, Pena AS, Meuwissen SG, Van Rees EP (1998) Chronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) is characterized by Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol 114:385–391
Resendiz-Albor AA, Esquivel R, Lopez-Revilla R, Verdin L, Moreno-Fierros L (2005) Striking phenotypic and functional differences in lamina propria lymphocytes from the large and small intestine of mice. Life Sci 76:2783–2803
Ye Y, Jin X, Yue M, Chen SH, Yu CH, Li YM (2010) The protective effect of oral colitis-derived proteins in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease is associated with an increase in γδ T cells in large intestinal mucosa. Int J Colorectal Dis 25:1055–1062
Buzoni-Gatel D, Debbabi H, Moretto M, Dimier-Poisson IH, Lepage AC, Bout DT, Kasper LH (1999) Intraepithelial lymphocytes traffic to the intestine and enhance resistance to Toxoplasma gondii oral infection. J Immunol 162:5846–5852
Hoffmann JC, Pawlowski NN, Grollich K, Loddenkemper C, Zeitz M, Kuhl AA (2008) Gammadelta T lymphocytes: a new type of regulatory T cells suppressing murine 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis. Int J Colorectal Dis 23:909–920
Pomie C, Menager-Marcq I, van Meerwijk JP (2008) Murine CD8+ regulatory T lymphocytes: the new era. Hum Immunol 69:708–714
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H, Hori S, Fehervari Z, Shimizu J, Takahashi T, Nomura T (2006) Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev 212:8–27
Sydora BC, Mixter PF, Holcombe HR, Eghtesady P, Williams K, Amaral MC, Nel A, Kronenberg M (1993) Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes are activated and cytolytic but do not proliferate as well as other T cells in response to mitogenic signals. J Immunol 150:2179–2191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Grant Y2110864 from Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Y., Yue, M., Jin, X. et al. The effect of oral tolerance on the roles of small intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in murine colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate. Int J Colorectal Dis 27, 583–593 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1354-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1354-x