Abstract
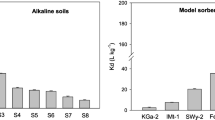
Phenolic acids have been implicated in the process of allelopathy and are, therefore, of interest in plant management as a basis for new herbicide structures. The potential bioavailability of phenolic acids is controlled by sorption–desorption processes in soil. Sorption–desorption of p-coumaric acid (4-hydroxycinnamic acid), ferulic acid (3-methoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid), veratric acid (3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid), vanillic acid (3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid), and p-hydroxybenzoic acid (4-hydroxybenzoic acid) was characterized on soils with varying physicochemical properties. The phenolic acids sorbed quickly (<8 h) and in high proportions to the amount applied (average 84% of applied was sorbed). Sorption was irreversible with the batch desorption method used (0.01 N CaCl2 extraction). Pretreatment of soils to remove organic matter and free metal oxides from the soils decreased sorption, particularly in soils with free oxides removed. Statistical analysis suggested that sorption of p-coumaric and ferulic acids was correlated with soil clay content and veratric acid sorption was correlated with several soil factors. In contrast, no consistent relationship between soil characteristics and vanillic and p-hydroxybenzoic acid sorption was found. Based on the results of these experiments, i.e. the high reactivity of the phenolic acids, it is unlikely that these chemicals would be transported far from their point of origin, limiting their range of influence. It appears that, for phenolic acids to have allelopathic effects on plants, they would have to persist in the soil for long periods, resulting in a buildup of the chemical to high enough levels so that sufficient chemical would be in solution to cause the allelopathic effects, even though they may be strongly sorbed at lower concentrations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmark CL, Jackson WA, Volk RJ, Blum U (1992) Differential inhibition by ferulic acid of nitrate and ammonium uptake in Zea mays L. Plant Physiol 98:639–645
Blum U, Worsham AD, King LD, Gerig TM (1994) Use of water and EDTA extractions to estimate available (free and reversibly bound) phenolic acids in Cecil soil. J Chem Ecol 20:341–359
Blum U, Shafer SR, Lehman ME (1999) Evidence for inhibitory allelopathic interactions involving phenolic acids in field soils: concepts vs an experimental model. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18:673–693
Bollag J-M, Liu S-Y, Minard RD (1982) Enzymatic oligomerization of vanillic acid. Soil Biol Biochem 14:157–163
Booker FL, Blum U, Fiscus EL (1992) Short-term effects of ferulic acid on ion uptake and water relations in cucumber seedlings. J Exp Bot 43:649–655
Celis R, Koskinen WC (1999) An isotopic exchange method for the characterization of the irreversibility of pesticide sorption–desorption in soil. J Agric Food Chem 47:782–790
Clay SA, Koskinen WC (1990) Characterization of alachlor and atrazine desorption from soils. Weed Sci 38:74–80
Dalton BR, Blum U, Weed SB (1983) Allelopathic substances in ecosystems: effectiveness of sterile soil components in altering recovery of ferulic acids. J Chem Ecol 9:1185–1201
Dalton BR, Blum U, Weed SB (1989a) Differential sorption of exogenously applied ferulic, p-coumaric, p-hydroxybenzoic, and vanillic acids in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:757–762
Dalton BR, Blum U, Weed SB (1989b) Plant phenolic acids in soils: sorption of ferulic acid by soil and soil components sterilized by different techniques. Soil Biol Biochem 21:1011–1018
Di Toro DM, Horzempa LM (1982) Reversible and resistant components of PCB adsorption–desorption: isotherms. Environ Sci Technol 16:594–602
Haider K, Martin JP (1975) Decomposition of specifically C-14 labeled benzoic and cinnamic acid derivatives in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 39:657–662
Haider K, Martin JP, Rietz E (1977) Decomposition in soil of 14C-labeled coumaryl alcohols; free and linked into dehydropolymer and plant lignins and model humic acids. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41:556–562
Huang PM, Wang TSC, Wang MK, Wu MH, Hsu NW (1977) Retention of phenolic acids by noncrystalline hydroxy-aluminum and -iron compounds and clay minerals of soils. Soil Sci 123:213–219
Jackson ML, Lim CH, Zelazny LW (1986) Oxides, hydroxides, and aluminosilicates. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods, 2nd edn. ASA, Madison, Wis., pp 101–150
Klein K, Blum U (1990) Inhibition of cucumber leaf expansion by ferulic acid in split-root experiments. J Chem Ecol 16:455–463
Koskinen WC, O’Connor GA, Cheng HH (1979) Characterization of hysteresis in the desorption of 2,4,5-T from soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:871–874
Kunze GW, Dixon JB (1986) Pretreatment for mineralogical analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods, 2nd edn. ASA, Madison, Wis., pp 91–100
Lehmann RG, Cheng HH (1988) Reactivity of phenolic acids in soil and formation of oxidation products. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:1304–1309
Lehmann RG, Cheng HH, Harsh JB (1987) Oxidation of phenolic acids by soil iron and manganese oxides. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:352–356
Lyu SW, Blum U (1990) Effects of ferulic acid, an allelopathic compound, on net P, K, and water uptake by cucumber seedlings in a split-root system. J Chem Ecol 16:2429–2439
Lyu SW, Blum U, Gerig TM, O’Brien TE (1990) Effects of mixtures of phenolic acids on phosphorus uptake by cucumber seedlings. J Chem Ecol 6:2559–2567
Makino T, Takahashi Y, Sakurai Y, Nanzyo M (1996) Influence of soil chemical properties on adsorption and oxidation of phenolic acids in soil suspension. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 42:867–879
Martin JP, Haider K (1976) Decomposition of specifically C-14-labeled ferulic acid: free and linked into model humic acid-type polymers. Soil Sci Soc Am J 40:377–380
McBride MB (1987) Adsorption and oxidation of phenolic compounds by iron and manganese oxides. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1466–1472
Rice EL (1984) Allelopathy. Academic Press, Orlando, Fla.
Sheskin DJ (1997) Handbook of parametric and nonparametric statistical procedures. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla.
Theng BKG (1974) Organic reactions catalysed by clay minerals. In:. Theng BKG (ed) The chemistry of clay—organic reactions. Halsted Press, New York, pp 269–281
Wang TSC, Li SW, Ferng YL (1978) Catalytic polymerization of phenolic compounds by clay minerals. Soil Sci 126:15–21
Acknowledgement
We thank Greg Pillar for his assistance in completing the batch equilibration procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cecchi, A.M., Koskinen, W.C., Cheng, H.H. et al. Sorption–desorption of phenolic acids as affected by soil properties. Biol Fertil Soils 39, 235–242 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0710-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0710-6