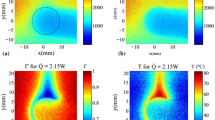
Abstract
Planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging is carried out in a hypersonic gun tunnel at a freestream Mach number of 8.9 and Reynolds number of \(47.4 \times 10^6\,\hbox {m}^{-1}\) (\(N_2\) is the test gas). The fluorescence of toluene \((C_7H_8)\) is correlated with the red shift of the emission spectra with increasing temperature. A two-colour approach is used where, following an excitation at 266 nm, emission spectra at two different bands are captured in separate runs using two different filters. Two different flow fields are investigated using this method: (i) hypersonic flow past a blunt nose, which is characterised by a bow shock with strong entropy effects, and (ii) an attached shock-wave/boundary-layer interaction induced by a flare located further downstream on the same blunt cylinder body. Measurements from as low as the freestream temperature of \(68.3\) K all the way up to \(380\) K \((T_{\infty }-5.6T_{\infty })\) are obtained. The uncertainty at the higher temperature level is approximately \(\pm 15\) %, while at the low end of the temperature, an additional \(\pm 15\) % uncertainty is expected. Application of the technique is further challenged at high temperatures due to the exponentially reduced fluorescence quantum yields and the occurrence of toluene pyrolysis near the stagnation region (\(T_\mathrm{o}=1150\) K). Overall, results are found to be within \(10\) % agreement with the expected distributions, thus demonstrating suitability of the technique for hypersonic flow thermometry applications in low-enthalpy facilities.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson J Jr (2000) Hypersonic and high-temperature gas dynamics, 2nd edn. AIAA Education Series. ISBN-13: 978–1563477805
Burton CS, Noyes JWA (1968) Electronic energy relaxation in toluene vapor. J Chem Phys 49:1705–1714
Cessou A, Meier U, Stepowski D (2000) Applications of planar laser induced fluorescence in turbulent reacting flows. Meas Sci Technol 11(7):887–901
Cheung BH (2011) Tracer-based planar laser-induced fluorescence diagnostics: quantitative photophysics and time-resolved imaging. PhD Thesis, Stanford University
D’Alessio J, Lazzaro M, Massoli P, Moccia V (2002) Absorption spectroscopy of toluene pyrolysis. Opt Las Eng 37:495–508
Devillers R, Bruneaux G, Schulz C (2009) Investigation of toluene LIF at high pressure and high temperature in an optical engine. Appl Phys B 96:735–739
Einecke S, Schulz C, Sick V (2000) Measurement of temperature, fuel concentration and equivalence ratio fields using tracer LIF in IC engine combustion. Appl Phys B 71(5):717–723
Estruch-Samper D, Lawson N, Garry K (2009) Application of optical measurement techniques to supersonic and hypersonic aerospace flows. J Aerosp Eng 22(4):383–395
Estruch-Samper D, Vanstone L, Ganapathisubramani B, Hillier R (2012) Effect of roughness-induced disturbances on axisymmetric hypersonic laminar boundary layer. AIAA paper 2012–675
Faust S, Dreier T, Schulz C (2011) Temperature and bath gas composition dependence of effective uorescence lifetimes of toluene excited at 266 nm. Chem Phys 383(13):611
Fiala A, Hillier R, Mallinson SG, Wijensinghe HS (2006) Heat transfer measurement of turbulent spots in a hypersonic blunt-body boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 555:81–111
Hatanaka K, Saito T, Hirota M, Nakamura Y, Suzuki Y, Koyaguchi T (2012) Flow visualization of supersonic free jet utilizing acetone PLIF. Vis Mech Proc 2(1)
Inman JA, Bathel BF, Johansen CT, Danehy PM, Jones SB, Gragg JG, Splinter SC (2011) Nitric oxide PLIF measurements in the hypersonic materials environmental test system (HYMETS). At the 49th AIAA aerospace sciences meeting, AIAA paper 2011–1090
Johansen CT, McRae CD, Daney PM, Gallo ECA, Cantu LML, Magnotti G, Cutler AD, Rockwell RD Jr, Goyne CP, McDaniel JC (2014) OH PLIF visualization of the UVa supersonic combustion experiment: configuration A. J Vis 17(2):131–141
Koban W, Koch JD, Hanson RK, Schulz C (2004) Absorption and fluorescence of toluene vapor at elevated temperatures. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6(11):2940–2945
Koban W, Koch JD, Hanson RK, Schulz C (2005) Toluene LIF at elevated temperatures: implications for fuel-air ratio measurements. Appl Phys B 80(2):147–150
Luong M, Koban W, Schulz C (2006) Novel strategies for imaging temperature distribution using toluene LIF. J Phys Conf Ser 45:133–139
Mallinson SG, Hillier R, Jackson AP, Kirk DC, Soltani S, Zanchetta M (2000) Gun tunnel flow calibration: defining input conditions for hypersonic flow computations. Shock Waves 10:313–322
Miller VA, Gamba M, Mungal MG, Hanson RK (2013) Single- and dual-band collection toluene PLIF thermometry in supersonic flows. Exp Fluids 54:1539, 13 pp
Narayanaswamy V, Burns R, Clemens NT (2011) Kr-PLIF for scalar imaging in supersonic flows. Opt Lett 36(21):4185–4187
Needham DA, Stollery JL, Elfstrom GM (1970) Design and operation of the Imperial College Number 2 Hypersonic Gun Tunnel. Imperial College London, Aero Report 70–04
O’Byrne S, Danehy PM, Houwing AFP (2006) Investigation of hypersonic nozzle flow uniformity using NO fluorescence. Shock Waves 5:1–7
Oehlschlaeger MA, Davidson DF, Hanson RK (2007) Thermal decomposition of toluene: overall rate and branching ratio. Proc Combust Inst 31:2119
Rossmann T, Mungal MG, Hanson RK (2003) Nitric-oxide planar laser-induced fluorescence applied to low-pressure hypersonic flow fields for the imaging of mixture fraction. Appl Opt 42(33):6682–6695
Schultz DL, Jones TV (1973) Heat-transfer measurements in short-duration hypersonic facilities. AGARDograph, 165
Settles GS (2012) Schlieren and shadowgraph techniques: visualizing phenomena in transparent media (Experimental Fluid Mechanics). Springer, New York. ISBN-13: 978–3642630347
Sjoholm J, Rosell J, Li B, Richter M, Li Z, Bai X, Alden M (2012) Simultaneous visualization of \(OH, CH, CH_2O\) and toluene PLIF in a methane jet flame with varying degrees of turbulence. Proc Comb Inst 34(1):1475–1482
Strozzi C, Sotton J, Mura A, Bellenoue M (2009) Characterization of a two-dimensional temperature field within a rapid compression machine using a toluene planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging technique. Meas Sci Technol 20:125403, 13 pp
Yoo J, Mitchell D, Davidson DF, Hanson RK (2010) Planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging in shock tube flows. Exp Fluids 49:751–759
Yoo J, Mitchell D, Davidson DF, Hanson RK (2011) Near-wall imaging using toluene-based planar laser-induced fluorescence in shock tube flow. Shock Waves 21(6):523–532
Zimmermann F, Koban W, Schulz C (2006) Temperature diagnostics using laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) of toluene. OSA/LACSEA, Incline Village, Nevada, Combustion II (TuB)
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out under the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research council (EPSRC) grant EP/H020853/1 and made use of the EPSRC Engineering instrument Pool to borrow the iCCD spectrometer and iCCD imaging camera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Estruch-Samper, D., Vanstone, L., Hillier, R. et al. Toluene-based planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging of temperature in hypersonic flows. Exp Fluids 56, 115 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-1987-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-1987-6