Abstract
Purpose
The molecular mechanisms that underlie the methotrexate (MTX)-mediated disruption of intestinal barrier function have not been fully characterized. Epithelial barrier function is determined in large part by a multiprotein complex located at the most apical part of the lateral membrane, which is referred to as a tight junction (TJ). In the present study, we examined the alteration of zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), which is a scaffolding protein that plays a pivotal role in the formation of TJs, to identify an additional molecular mechanism for epithelial barrier dysfunction.
Methods
Male Wistar rats were administered MTX (15 mg kg−1) orally once daily for 3–5 days. Intestinal mucosal permeability was determined using the in vitro everted intestinal sac technique. Mucosal inflammation was assessed by myeloperoxidase activity and production of reactive oxygen species. Altered expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and localization of ZO-1 were evaluated by RT–PCR, Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry.
Results
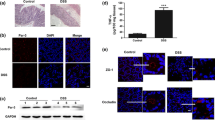
A barrier function study revealed increased intestinal permeability in rats treated with MTX for 4 days, as indicated by enhanced fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran flux. In addition, mucosal inflammation was linked to enhanced intestinal permeability. Quantitative analysis of ZO-1 expression showed the absence of significant differences in MTX-treated rats, whereas tyrosine dephosphorylation of ZO-1 was observed. Moreover, we also detected an obvious reduction of ZO-1 immunostaining along the apical membrane of intestinal villi.
Conclusions
These results indicate that, in MTX-treated rats, ZO-1 alterations may contribute to disturbance of the TJ barrier, which leads to enhanced intestinal permeability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeMeo MT, Mutlu EA, Keshavarzian A, Tobin MC (2002) Intestinal permeation and gastrointestinal disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 34:385–396
De-Souza DA, Greene LJ (2005) Intestinal permeability and systemic infections in critically ill patients: effect of glutamine. Crit Care Med 33:1125–1135
Alarcon GS (2000) Methotrexate use in rheumatoid arthritis. A clinician’s perspective. Immunopharmacology 47:259–271
Sonis ST (2004) A biological approach to mucositis. J Support Oncol 2:21–32 discussion 35–36
Gumbiner BM (1996) Cell adhesion: the molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell 84:345–357
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M (2001) Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:285–293
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141:1539–1550
Ikenouchi J, Furuse M, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (2005) Tricellulin constitutes a novel barrier at tricellular contacts of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 171:939–945
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Avila-Flores A (2000) MAGUK proteins: structure and role in the tight junction. Semin Cell Dev Biol 11:315–324
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2006) Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol 68:403–429
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K, Saitou M, Tsukita S (1999) Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins. J Cell Biol 147:1351–1363
Stevenson BR, Siliciano JD, Mooseker MS, Goodenough DA (1986) Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol 103:755–766
Gumbiner B, Lowenkopf T, Apatira D (1991) Identification of a 160-kDa polypeptide that binds to the tight junction protein ZO-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88:3460–3464
Haskins J, Gu L, Wittchen ES, Hibbard J, Stevenson BR (1998) ZO-3, a novel member of the MAGUK protein family found at the tight junction, interacts with ZO-1 and occludin. J Cell Biol 141:199–208
Adachi M, Inoko A, Hata M, Furuse K, Umeda K, Itoh M, Tsukita S (2006) Normal establishment of epithelial tight junctions in mice and cultured cells lacking expression of ZO-3, a tight-junction MAGUK protein. Mol Cell Biol 26:9003–9015
Umeda K, Ikenouchi J, Katahira-Tayama S, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Nakayama M, Matsui T, Tsukita S, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2006) ZO-1 and ZO-2 independently determine where claudins are polymerized in tight-junction strand formation. Cell 126:741–754
Katsuno T, Umeda K, Matsui T, Hata M, Tamura A, Itoh M, Takeuchi K, Fujimori T, Nabeshima Y, Noda T, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (2008) Deficiency of zonula occludens-1 causes embryonic lethal phenotype associated with defected yolk sac angiogenesis and apoptosis of embryonic cells. Mol Biol Cell 19:2465–2475
Gao F, Nakamaru M, Masubuchi Y, Horie T (2001) Protective effect of a synthetic analog of prostaglandin E(1) on the small intestinal damage induced by the administration of methotrexate to rats. J Pharm Sci 90:1040–1048
Miyazono Y, Gao F, Horie T (2004) Oxidative stress contributes to methotrexate-induced small intestinal toxicity in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 39:1119–1127
Maeda T, Miyazono Y, Ito K, Hamada K, Sekine S, Horie T (2009) Oxidative stress and enhanced paracellular permeability in the small intestine of methotrexate treated rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol (in press)
Basuroy S, Seth A, Elias B, Naren AP, Rao R (2006) MAPK interacts with occludin and mediates EGF-induced prevention of tight junction disruption by hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J 393:69–77
Mazzon E, Cuzzocrea S (2008) Role of TNF-alpha in ileum tight junction alteration in mouse model of restraint stress. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G1268–G1280
Scharl M, Paul G, Barrett KE, McCole DF (2009) AMP-activated protein kinase mediates the interferon-gamma-induced decrease in intestinal epithelial barrier function. J Biol Chem 284:27952–27963
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G (1982) Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol 78:206–209
Tomita M, Menconi MJ, Delude RL, Fink MP (2000) Polarized transport of hydrophilic compounds across rat colonic mucosa from serosa to mucosa is temperature dependent. Gastroenterology 118:535–543
Podolsky DK (1993) Regulation of intestinal epithelial proliferation: a few answers, many questions. Am J Physiol 264:G179–G186
Riaz AA, Schramm R, Sato T, Menger MD, Jeppsson B, Thorlacius H (2003) Oxygen radical-dependent expression of CXC chemokines regulate ischemia/reperfusion-induced leukocyte adhesion in the mouse colon. Free Radic Biol Med 35:782–789
de Koning BA, van Dieren JM, Lindenbergh-Kortleve DJ, van der Sluis M, Matsumoto T, Yamaguchi K, Einerhand AW, Samsom JN, Pieters R, Nieuwenhuis EE (2006) Contributions of mucosal immune cells to methotrexate-induced mucositis. Int Immunol 18:941–949
Logan RM, Stringer AM, Bowen JM, Gibson RJ, Sonis ST, Keefe DM (2009) Is the pathobiology of chemotherapy-induced alimentary tract mucositis influenced by the type of mucotoxic drug administered? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63:239–251
Chen Y, Lu Q, Schneeberger EE, Goodenough DA (2000) Restoration of tight junction structure and barrier function by down-regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in ras-transformed Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Mol Biol Cell 11:849–862
Van Itallie CM, Balda MS, Anderson JM (1995) Epidermal growth factor induces tyrosine phosphorylation and reorganization of the tight junction protein ZO-1 in A431 cells. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 4):1735–1742
Resta-Lenert S, Smitham J, Barrett KE (2005) Epithelial dysfunction associated with the development of colitis in conventionally housed mdr1a–/–mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289:G153–G162
Ciccocioppo R, Finamore A, Ara C, Di Sabatino A, Mengheri E, Corazza GR (2006) Altered expression, localization, and phosphorylation of epithelial junctional proteins in celiac disease. Am J Clin Pathol 125:502–511
Suzuki T, Elias BC, Seth A, Shen L, Turner JR, Giorgianni F, Desiderio D, Guntaka R, Rao R (2009) PKC eta regulates occludin phosphorylation and epithelial tight junction integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:61–66
Tamura A, Kitano Y, Hata M, Katsuno T, Moriwaki K, Sasaki H, Hayashi H, Suzuki Y, Noda T, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (2008) Megaintestine in claudin-15-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 134:523–534
Furuse M, Sasaki H, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) A single gene product, claudin-1 or -2, reconstitutes tight junction strands and recruits occludin in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 143:391–401
Miele L, Valenza V, La Torre G, Montalto M, Cammarota G, Ricci R, Masciana R, Forgione A, Gabrieli ML, Perotti G, Vecchio FM, Rapaccini G, Gasbarrini G, Day CP, Grieco A (2009) Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 49:1877–1887
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Global COE Program (Global Center for Education and Research in Immune System Regulation and Treatment), MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamada, K., Shitara, Y., Sekine, S. et al. Zonula Occludens-1 alterations and enhanced intestinal permeability in methotrexate-treated rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66, 1031–1038 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1253-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1253-9