Abstract
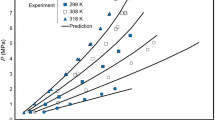
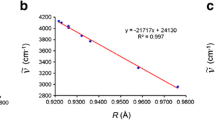
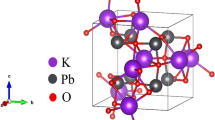
General equations to correlate and predict the thermodynamic properties of hydrated borates were developed based on the experimental results according to their structural types. The thermodynamic properties (ΔH f 0 and ΔG f 0) of a hydrated borate phase are the sum of the contributions of the cations in aqueous solution, the borate polyanions, and the structural water to the corresponding thermodynamic properties. This method is called the group contribution method, and it is extensively used to calculate the thermodynamic properties of many kinds of inorganic compounds, such as silicates and clay minerals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 November 1998 / Accepted: 11 October 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, B. & Gao, S. Calculation of thermodynamic properties of hydrated borates by group contribution method. Phys Chem Min 27, 342–346 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050263
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050263