Abstract
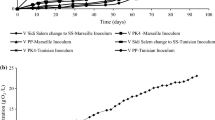
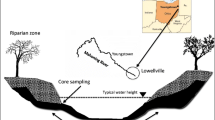
Coastal sediments contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can be candidates for remediation via an approach like land farming. Land farming converts naturally anaerobic sediments to aerobic environments, and the response of microbial communities, in terms of community structure alterations and corresponding effects on biodegradative activities, is unknown. A key goal of this study was to determine if different sediments exhibited common patterns in microbial community responses that might serve as indicators of PAH biodegradation. Sediments from three stations in the Lagos Lagoon (Nigeria) were used in microcosms, which were spiked with a mixture of four PAH, then examined for PAH biodegradation and for shifts in microbial community structure by analysis of diversity in PAH degradation genes and Illumina sequencing of 16S rRNA genes. PAH biodegradation was similar in all sediments, yet each exhibited unique microbiological responses and there were no microbial indicators of PAH bioremediation common to all sediments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bordenave S, Goni-urriza M, Vilette C, Blanchard S, Caumette P, Duran R (2008) Diversity of ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases in pristine and oil contaminated microbial mats at genomic and transcriptomic levels. Environ Microbiol 10:3201–3211. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01707.x
Bouchez-Naitali M, Blanchet D, Haeseler F, Vandecasteele JP (2008) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). In: Vandecasteele JP (ed) Petroleum microbiology: concepts, environmental implications, industrial applications, Editions Technip, vol 1. Paris, France, pp 342–411
Burgess RM, Berry WJ, Mount DR, Di Toro DM (2013) Mechanistic sediment quality guidelines based on contaminant bioavailability: equilibrium partitioning sediment benchmarks. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:102–114
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello KE, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Cebron A, Louvel B, Faure P, France-Lanord C, Chen Y, Murrell JC, Leyval C (2011) Root exudates modify bacterial diversity of phenanthrene degraders in PAH-polluted soil but not phenanthrene degradation rates. Environ Microbiol 13:722–736. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02376.x
Cebron A, Norini MP, Beguiristain T, Leyval C (2008) Real-time PCR quantification of PAH-ring hydroxylating dioxygenase (PAH-RHD alpha) genes from gram positive and gram negative bacteria in soil and sediment samples. J Microbiol Methods 73:148–159. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2008.01.009
Chen BW, Huang JY, Yuan K, Lin L, Wang XW, Yang LH, Luan TG (2016) Direct evidences on bacterial growth pattern regulating pyrene degradation pathway and genotypic dioxygenase expresssion. Marine Poll Bull 105:73–80. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.02.054
Chung WK, King GM (2001) Isolation, characterization, and polyaromatic hydrocarbon degradation potential of aerobic bacteria from marine macrofaunal burrow sediments and description of Lutibacterium anuloederans gen. Nov., sp nov., and Cycloclasticus spirillensus sp nov. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5585–5592. doi:10.1128/aem.67.12.5585-5592.2001
Clarke KR, Somerfield PJ, Gorley RN (2008) Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: similarity profiles and biota-environment linkage. J Exp Marine Biol Ecol 366:56–69. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2008.07.009
Cui ZS, Xu GS, Gao W, Li Q, Yang BJ, Yang GP, Zheng L (2014) Isolation and characterization of Cycloclasticus strains from Yellow Sea sediments and biodegradation of pyrene and fluoranthene by their syntrophic association with Marinobacter strains. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 91:45–51. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.03.005
de Gannes V, Eudoxie G, Bekele I, Hickey WJ (2015) Relations of microbiome characteristics to edaphic properties of tropical soils from Trinidad. Front Microbiol:6. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.01045
Ding GC, Heuer H, Zühlke S, Spiteller M, Pronk GJ, Heister K, Kögel-Knabner I, Smalla K (2010) Soil type-dependent responses to phenanthrene as revealed by determining the diversity and abundance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase genes by using a novel PCR detection system. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4765–4771. doi:10.1128/aem.00047-10
dos Santos HF, Cury JC, Carmo FV, dosSantos AL, Tiedje J, van Elsas JD, Rosado AS, Peixoto RS (2011) Mangrove bacterial diversity and the impact of oil contamination revealed by pyrosequencing: bacterial proxies for oil pollution. PLoS One:6. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016943
Doyle E, Muckian L, Hickey AM, Clipson N (2008) Microbial PAH degradation. In: Laskin AI, Sariaslani S, Gadd GM (eds) Advances in applied microbiology, vol 65, pp 27–66. doi:10.1016/s0065-2164(08)00602-3
Dubinsky EA, Conrad ME, Chakraborty R, Bill M, Borglin SE, Hollibaugh JT, Mason OU, Piceno YM, Reid FC, Stringfellow WT, Tom LM, Hazen TC, Andersen GL (2013) Succession of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria in the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Environ Sci Technol 47:10860–10867. doi:10.1021/es401676y
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh340
EPA (2005) Contaminated sediment remediation guidance for hazardous waste sites. National service center for environmental publications (NSCEP), Washington DC
Fernandez-Luqueno F, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Marsch R, Martinez-Suarez C, Vazquez-Nunez E, Dendooven L (2011) Microbial communities to mitigate contamination of PAHs in soil-possibilities and challenges: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:12–30. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0371-6
Flocco CG, Gomes NCM, Mac Cormack W, Smalla K (2009) Occurrence and diversity of naphthalene dioxygenase genes in soil microbial communities from the maritime Antarctic. Environ Microbiol 11:700–714. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01858.x
Fuentes S, Ding GC, Cardenas F, Smalla K, Seeger M (2015) Assessing environmental drivers of microbial communities in estuarine soils of the Aconcagua River in Central Chile. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91. doi:10.1093/femsec/fiv110
Geiselbrecht AD, Hedlund BP, Tichi MA, Staley JT (1998) Isolation of marine polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading Cycloclasticus strains from the Gulf of Mexico and comparison of their PAH degradation ability with that of Puget sound Cycloclasticus strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4703–4710
Gomes NCM, Borges LR, Paranhos R, Pinto FN, Krogerrecklenfort E, Mendonca-Hagler LCS, Smalla K (2007) Diversity of ndo genes in mangrove sediments exposed to different sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7392–7399. doi:10.1128/aem.01099-07
Habe H, Omori T (2003) Genetics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolism in diverse aerobic bacteria. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:225–243
Harvey RG (1997) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Wiley-VCH, New York, NY
Jain PK (2014) Microbial biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons In: Harzevili FD and Chen H (eds). CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. p 331–350 doi:10.1201/b17587-16
Jiang H, Lei R, Ding S-W, Zhu S (2014) Skewer: a fast and accurate adapter trimmer for next-generation sequencing paired-end reads. BMC Bioinformatics 15:182. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-15-182
Jiang L, Song M, Luo C, Zhang D, Zhang G (2015) Novel phenanthrene-degrading bacteria identified by DNA-stable isotope probing. PLoS One:10. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130846
Johnston CG, Johnston GP (2012) Bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In: Arora R (ed) Microbial biotechnology: energy and environment. CABI, Wallingford, Oxfordshire, England, pp 279–296
Magoˇc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Matturro B, Presta E, Rossetti S (2016) Reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethene in marine sediments: biodiversity and dehalorespiring capabilities of the indigenous microbes. Sci Total Environ 545:445–452. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.098
McKew BA, Coulon F, Osborn AM, Timmis KN, McGenity TJ (2007) Determining the identity and roles of oil-metabolizing marine bacteria from the Thames estuary, UK. Environ Microbiol 9:165–176. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01125.x
Moghadam MS, Ebrahimipour G, Abtahi B, Ghassempour A, Hashtroudi MS (2014) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a bacterial consortium enriched from mangrove sediments. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:114–125. doi:10.1186/s40201-014-0114-6
Muangchinda C, Chavanich S, Viyakarn V, Watanabe K, Imura S, Vangnai AS, Pinyakong O (2015) Abundance and diversity of functional genes involved in the degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons in Antarctic soils and sediments around Syowa Station. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4725–4735. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3721-y
Muckian L, Grant R, Doyle E, Clipson N (2007) Bacterial community structure in soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 68(8):1535–1541
Niepceron M, Portet-Koltalo F, Merlin C, Motelay-Massei A, Barray S, Bodilis J (2010) Both Cycloclasticus spp. and Pseudomonas spp. as PAH-degrading bacteria in the seine estuary (France). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 71:137–147. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00788.x
Obi CC, Adebusoye SA, Ugoji EO, Ilori MO, Amund OO, Hickey WJ (2016) Microbial communities in sediments of Lagos lagoon, Nigeria: elucidation of community structure and potential impacts of contamination by municipal and industrial wastes. Front Microbiol 7:1213. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.01213
Peng RH, Xiong AS, Xue Y, Fu XY, Gao F, Zhao W, Tian YS, Yao QH (2008) Microbial biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:927–955. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00127.x
Richardson RE (2013) Genomic insights into organohalide respiration. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24:498–505. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2013.02.014
Sauret C, Tedetti M, Guigue C, Dumas C, Lami R, Pujo-Pay M, Conan P, Goutx M, Ghiglione JF (2016) Influence of PAHs among other coastal environmental variables on total and PAH-degrading bacterial communities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4242–4256. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4768-0
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541. doi:10.1128/aem.01541-09
Seo J-S, Keum Y-S, Li QX (2009) Bacterial degradation of aromatic compounds. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 6:278–309. doi:10.3390/ijerph6010278
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Vacca DJ, Bleam WF, Hickey WJ (2005) Isolation of soil bacteria adapted to degrade humic acid-sorbed phenanthrene. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3797–3805. doi:10.1128/aem.71.7.3797-3805.2005
Van Hamme JD, Singh A, Ward OP (2003) Recent advances in petroleum microbiology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:503–549. doi:10.1128/mmbr.67.4.503-549.2003
Vila J, Tauler M, Grifoll M (2015) Bacterial PAH degradation in marine and terrestrial habitats. Curr Opin Biotechnol 33:95–102. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2015.01.006
Wang BJ, Lai QL, Cui ZS, Tan TF, Shao ZZ (2008) A pyrene-degrading consortium from deep-sea sediment of the West Pacific and its key member Cycloclasticus sp P1. Environ Microbiol 10:1948–1963. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01611.x
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267. doi:10.1128/aem.00062-07
Wickle W (2000) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil—A review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:229–248
Wilson MS, Herrick JB, Jeon CO, Hinman DE, Madsen EL (2003) Horizontal transfer of phnAc dioxygenase genes within one of two phenotypically and genotypically distinctive naphthalene-degrading guilds from adjacent soil environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2172–2181. doi:10.1128/aem.69.4.2172-2181.2003
Wu P, Wang YS, Sun FL, Wu ML, Peng YL (2014) Bacterial polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases in the sediments from the Pearl River estuary, China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:875–884. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-4854-5
Xia XH, Xia N, Lai Y, Dong J, Zhao P, Zhu B, Li Z, Ye W, Yuan Y, Huang J (2015) Response of PAH-degrading genes to PAH bioavailability in the overlying water, suspended sediment, and deposited sediment of the Yangtze River. Chemosphere 128:236–244. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.011
Yakimov MM, Denaro R, Genovese M, Cappello S, D'Auria G, Chernikova TN, Timmis KN, Golyshin PN, Giuliano L (2005) Natural microbial diversity in superficial sediments of Milazzo Harbor (Sicily) and community successions during microcosm enrichment with various hydrocarbons. Environ Microbiol 7:1426–1441. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00829.x
Yakimov MM, Timmis KN, Golyshin PN (2007) Obligate oil-degrading marine bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:257–266. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2007.04.006
Zhang J, Lin XG, Liu WW, Yin R (2012) Response of soil microbial community to the bioremediation of soil contaminated with PAHs. Huan Jing Ke Xue 33:2825–2831
Zhou HW, Guo CL, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2006) Genetic diversity of dioxygenase genes in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from mangrove sediments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 262:148–157. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00379.x
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by graduate fellowships from the University of Lagos (to CCO) and by an endowment from the O.N. Allen Professorship in Soil Microbiology (to WJH). Processing of Illumina data through the QIIME pipeline was done by the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Bioinformatics Resource Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by an endowment from the O.N. Allen Professorship of Soil Science, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin (to WJH).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No animals or human subjects were used in these studies.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 184 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obi, C.C., Adebusoye, S.A., Amund, O.O. et al. Structural dynamics of microbial communities in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated tropical estuarine sediments undergoing simulated aerobic biotreatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 4299–4314 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8151-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8151-6