Abstract
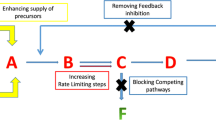
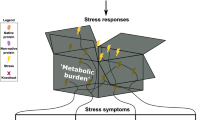
Escherichia coli is one of the most widely used strains for recombinant protein production. However, obstacles also exist in both academic researches and industrial applications, such as the metabolic burden, the carbon source waste, and the cells’ physiological deterioration. This article reviews recent approaches for improving recombinant protein production in metabolic engineering, including workhorse selection, stress factor application, and carbon flux regulation. Selecting a suitable host is the first key point for recombinant protein production. In general, it all depends on characteristics of the strains and the target proteins. It will be triggered cells physiological deterioration when the medium is significantly different from the cell’s natural environment. Coexpression of stress factors can help proteins to fold into their native conformation. Carbon flux regulation is a direct approach for redirecting more carbon flux toward the desirable pathways and products. However, some undesirable consequences are usually found in metabolic engineering, such as glucose transport inhibition, cell growth retardation, and useless metabolite accumulation. More efficient regulators and platform cell factories should be explored to meet a variety of production demands.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba H (2007) Mechanism of RNA silencing by Hfq-binding small RNAs. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:134–139
Attwood PV (1995) The structure and the mechanism of action of pyruvate carboxylase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 27:231–249
Azam TA, Iwata A, Nishimura A, Ueda S, Ishihama A (1999) Growth phase-dependent variation in protein composition of the Escherichia coli nucleoid. J Bacteriol 181:6361–6370
Baneyx F (1999) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10:411–421
Chao Y-P, Liao JC (1993) Alteration of growth yield by overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4261–4265
Chen R (2012) Bacterial expression systems for recombinant protein production: E. coli and beyond. Biotechnol Adv 30:1102–1107
Cherrington CA, Hinton M, Chopra I (1990) Effect of short-chain organic acids on macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Appl Bacteriol 68:69–74
Cho S, Shin D, Ji GE, Heu S, Ryu S (2005) High-level recombinant protein production by overexpression of Mlc in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 119:197–203
Chou CP (2007) Engineering cell physiology to enhance recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:521–532
Daegelen P, Studier FW, Lenski RE, Cure S, Kim JF (2009) Tracing ancestors and relatives of Escherichia coli B, and the derivation of B strains REL606 and BL21 (DE3). J Mol Biol 394:634–643
De Anda R, Lara AR, Hernandez V, Hernandez-Montalvo V, Gosset G, Bolivar F, Ramirez OT (2006) Replacement of the glucose phosphotransferase transport system by galactose permease reduces acetate accumulation and improves process performance of Escherichia coli for recombinant protein production without impairment of growth rate. Metab Eng 8:281–290
De Mey M, De Maeseneire S, Soetaert W, Vandamme E (2007) Minimizing acetate formation in E. coli fermentations. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:689–700
Decker K, Plumbridge J, Boos W (1998) Negative transcriptional regulation of a positive regulator: the expression of malT, encoding the transcriptional activator of the maltose regulon of Escherichia coli, is negatively controlled by Mlc. Mol Microbiol 27:381–390
Eiteman MA, Altman E (2006) Overcoming acetate in Escherichia coli recombinant protein fermentations. Trends Biotechnol 24:530–536
El-Mansi E, Holms W (1989) Control of carbon flux to acetate excretion during growth of Escherichia coli in batch and continuous cultures. J Gen Microbiol 135:2875–2883
El-Mansi M (2004) Flux to acetate and lactate excretions in industrial fermentations: physiological and biochemical implications. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:295–300
Farmer WR, Liao JC (1997) Reduction of aerobic acetate production by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3205–3210
Gao Y, Liu C, Ding Y, Sun C, Zhang R, Xian M, Zhao G (2014) Development of genetically stable Escherichia coli strains for poly (3-hydroxypropionate) production. PLoS One 9, e97845
Glick BR (1995) Metabolic load and heterologous gene expression. Biotechnol Adv 13:247–261
Gokarn R, Eiteman M, Altman E (2000) Metabolic analysis of Escherichia coli in the presence and absence of the carboxylating enzymes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1844–1850
Gottesman S (1984) Bacterial regulation: global regulatory networks. Annu Rev Genet 18:415–441
Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M (2002) Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: from nascent chain to folded protein. Science 295:1852–1858
Herrera G, Martinez A, Blanco M, O’Connor JE (2002) Assessment of Escherichia coli B with enhanced permeability to fluorochromes for flow cytometric assays of bacterial cell function. Cytometry 49:62–69
Hoffmann F, Rinas U (2001) On-line estimation of the metabolic burden resulting from the synthesis of plasmid-encoded and heat-shock proteins by monitoring respiratory energy generation. Biotechnol Bioeng 76:333–340
Hong Y, Pasternak J, Glick BR (1995) Overcoming the metabolic load associated with the presence of plasmid DNA in the plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12-2. Can J Microbiol 41:624–628
Hosono K, Kakuda H, Ichihara S (1995) Decreasing accumulation of acetate in a rich medium by Escherichia coli on introduction of genes on a multicopy plasmid. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:256–261
Jeong H, Barbe V, Lee CH, Vallenet D, Yu DS, Choi S-H, Couloux A, Lee S-W, Yoon SH, Cattolico L (2009) Genome sequences of Escherichia coli B strains REL606 and BL21 (DE3). J Mol Biol 394:644–652
Jiang X, Oohira K, Iwasaki Y, Nakano H, Ichihara S, Yamane T (2002) Reduction of protein degradation by use of protease-deficient mutants in cell-free protein synthesis system of Escherichia coli. J Biosci Bioeng 93:151–156
Jones KL, Kim S-W, Keasling J (2000) Low-copy plasmids can perform as well as or better than high-copy plasmids for metabolic engineering of bacteria. Metab Eng 2:328–338
Körner H, Sofia HJ, Zumft WG (2003) Phylogeny of the bacterial superfamily of Crp-Fnr transcription regulators: exploiting the metabolic spectrum by controlling alternative gene programs. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:559–592
Kim SY (1999) Purification of Mlc and analysis of its effects on the pts expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 274:25398–25402
Kim YS, Seo JH, Cha HJ (2003) Enhancement of heterologous protein expression in Escherichia coli by co-expression of nonspecific DNA-binding stress protein, Dps. Enzyme Microb Tech 33:460–465
Kimata K, Inada T, Tagami H, Aiba H (1998) A global repressor (Mlc) is involved in glucose induction of the ptsG gene encoding major glucose transporter in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 29:1509–1519
Koh BT, Nakashimada U, Pfeiffer M, Yap MG (1992) Comparison of acetate inhibition on growth of host and recombinant E. coli K12 strains. Biotechnol Lett 14:1115–1118
Kondo A, Kohda J, Endo Y, Shiromizu T, Kurokawa Y, Nishihara K, Yanagi H, Yura T, Fukuda H (2000) Improvement of productivity of active horseradish peroxidase in Escherichia coli by coexpression of Dsb proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 90:600–606
Kumari S, Beatty CM, Browning DF, Busby SJ, Simel EJ, Hovel-Miner G, Wolfe AJ (2000) Regulation of acetyl coenzyme a synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 182:4173–4179
Kurokawa Y, Yanagi H, Yura T (2000) Overexpression of protein disulfide isomerase DsbC stabilizes multiple-disulfide-bonded recombinant protein produced and transported to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3960–3965
Lin H, Castro NM, Bennett GN, San K-Y (2006) Acetyl-CoA synthetase overexpression in Escherichia coli demonstrates more efficient acetate assimilation and lower acetate accumulation: a potential tool in metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:870–874
Liu MY, Gui G, Wei B, Preston JF, Oakford L, Yüksel Ü, Giedroc DP, Romeo T (1997) The RNA molecule CsrB binds to the global regulatory protein CsrA and antagonizes its activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 272:17502–17510
Liu MY, Romeo T (1997) The global regulator CsrA of Escherichia coli is a specific mRNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol 179:4639–4642
March J, Eiteman M, Altman E (2002) Expression of an anaplerotic enzyme, pyruvate carboxylase, improves recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5620–5624
McKee AE, Rutherford BJ, Chivian DC, Baidoo EK, Juminaga D, Kuo D, Benke PI, Dietrich JA, Ma SM, Arkin AP, Petzold CJ, Adams PD, Keasling JD, Chhabra SR (2012) Manipulation of the carbon storage regulator system for metabolite remodeling and biofuel production in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-11-79
Nakano K, Rischke M, Sato S, Märkl H (1997) Influence of acetic acid on the growth of Escherichia coli K12 during high-cell-density cultivation in a dialysis reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:597–601
Nam TW, Cho SH, Shin D, Kim JH, Jeong JY, Lee JH, Roe JH, Peterkofsky A, Kang SO, Ryu S (2001) The Escherichia coli glucose transporter enzyme IICBGlc recruits the global repressor Mlc. EMBO J 20:491–498
Negrete A, Majdalani N, Phue JN, Shiloach J (2013) Reducing acetate excretion from E. coli K-12 by over-expressing the small RNA SgrS. N Biotechnol 30:269–273
Negrete A, Ng W-I, Shiloach J (2010) Glucose uptake regulation in E. coli by the small RNA SgrS: comparative analysis of E. coli K-12 (JM 109 and MG 1655) and E. coli B (BL 21). Microb Cell Fact 9:75
Nizam SA, Zhu J, Ho PY, Shimizu K (2009) Effects of arcA and arcB genes knockout on the metabolism in Escherichia coli under aerobic condition. Biochem Eng J 44:240–250
Ow DS, Lee RM, Nissom PM, Philp R, Oh SK, Yap MG (2007) Inactivating FruR global regulator in plasmid-bearing Escherichia coli alters metabolic gene expression and improves growth rate. J Biotechnol 131:261–269
Pósfai G, Plunkett G, Fehér T, Frisch D, Keil GM, Umenhoffer K, Kolisnychenko V, Stahl B, Sharma SS, De Arruda M (2006) Emergent properties of reduced-genome Escherichia coli. Science 312:1044–1046
Pavlou AK, Reichert JM (2004) Recombinant protein therapeutics-success rates, market trends and values to 2010. Nat Biotechnol 22:1513–1519
Perrenoud A, Sauer U (2005) Impact of global transcriptional regulation by ArcA, ArcB, Cra, Crp, Cya, Fnr, and Mlc on glucose catabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187:3171–3179
Phue JN, Noronha SB, Hattacharyya R, Wolfe AJ, Shiloach J (2005) Glucose metabolism at high density growth of E. coli B and E. coli K: differences in metabolic pathways are responsible for efficient glucose utilization in E. coli B as determined by microarrays and Northern blot analyses. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:805–820
Ramseier T (1996) Cra and the control of carbon flux via metabolic pathways. Res Microbiol 147:489–493
Romeo T (1998) Global regulation by the small RNA-binding protein CsrA and the non-coding RNA molecule CsrB. Mol Microbiol 29:1321–1330
Sarkar D, Shimizu K (2008) Effect of cra gene knockout together with other genes knockouts on the improvement of substrate consumption rate in Escherichia coli under microaerobic condition. Biochem Eng J 42:224–228
Sarkar D, Siddiquee KA, Arauzo-Bravo MJ, Oba T, Shimizu K (2008) Effect of cra gene knockout together with edd and iclR genes knockout on the metabolism in Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol 190:559–571
Schneider D, Duperchy E, Depeyrot J, Coursange E, Lenski RE, Blot M (2002) Genomic comparisons among Escherichia coli strains B, K-12, and O157: H7 using IS elements as molecular markers. BMC Microbiol 2:18
Shin S, Song SG, Lee DS, Pan JG, Park C (1997) Involvement of iclR and rpoS in the induction of acs, the gene for acetyl coenzyme A synthetase of Escherichia coli K-12. FEMS Microbiol Lett 146:103–108
Srivastava M, Nayak J, Mehrotra V, Kaul R, Sheela P, Gupta S, Panda A (1999) High level expression in Escherichia coli and purification of immunoreactive recombinant bonnet monkey zone pellucida glycoprotein-3. Process Biochem 35:451–457
Studier FW, Moffatt BA (1986) Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol 189:113–130
Summers DK, Sherratt DJ (1984) Multimerization of high copy number plasmids causes instability: ColE 1 encodes a determinant essential for plasmid monomerization and stability. Cell 36:1097–1103
Swartz JR (1996) Escherichia coli recombinant DNA technology. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd edn. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 1693–171
Terpe K (2006) Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:211–222
Timmermans J, Van Melderen L (2010) Post-transcriptional global regulation by CsrA in bacteria. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:2897–2908
Valgepea K, Adamberg K, Nahku R, Lahtvee P-J, Arike L, Vilu R (2010) Systems biology approach reveals that overflow metabolism of acetate in Escherichia coli is triggered by carbon catabolite repression of acetyl-CoA synthetase. BMC Syst Biol 4:166
Vanderpool CK, Gottesman S (2004) Involvement of a novel transcriptional activator and small RNA in post-transcriptional regulation of the glucose phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system. Mol Microbiol 54:1076–1089
Vemuri G, Altman E, Sangurdekar D, Khodursky A, Eiteman M (2006a) Overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli during steady-state growth: transcriptional regulation and effect of the redox ratio. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3653–3661
Vemuri GN, Eiteman MA, Altman E (2006b) Increased recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli strains with overexpressed water-forming NADH oxidase and a deleted ArcA regulatory protein. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:538–542
Vidal L, Pinsach J, Striedner G, Caminal G, Ferrer P (2008) Development of an antibiotic-free plasmid selection system based on glycine auxotrophy for recombinant protein overproduction in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 134:127–136
Waegeman H, Beauprez J, Moens H, Maertens J, De Mey M, Foulquie-Moreno MR, Heijnen JJ, Charlier D, Soetaert W (2011) Effect of iclR and arcA knockouts on biomass formation and metabolic fluxes in Escherichia coli K12 and its implications on understanding the metabolism of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). BMC Microbiol 11:70. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-11-70
Waegeman H, De Lausnay S, Beauprez J, Maertens J, De Mey M, Soetaert W (2013) Increasing recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli K12 through metabolic engineering. N Biotechnol 30:255–261
Walter S, Buchner J (2002) Molecular chaperones-cellular machines for protein folding. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 41:1098–1113
Wang ZW, Chen Y, Chao Y-P (2006) Enhancement of recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli by coproduction of aspartase. J Biotechnol 124:403–411
Waters LS, Storz G (2009) Regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Cell 136:615–628
Xu J, Li W, Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Liu J, Hu Z (2006) Stability of plasmid and expression of a recombinant gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) vaccine in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:780–788
Yamamoto K, Ishihama A (2003) Two different modes of transcription repression of the Escherichia coli acetate operon by IclR. Mol Microbiol 47:183–194
Yoon SH, Han M-J, Jeong H, Lee CH, Xia X-X, Lee D-H, Shim JH, Lee SY, Oh TK, Kim JF (2012) Comparative multi-omics systems analysis of Escherichia coli strains B and K-12. Genome Biol 13:R37
Yoon SH, Jeong H, Kwon S-K, Kim JF (2009) Genomics, biological features, and biotechnological applications of Escherichia coli B:“Is B for better?!” Systems biology and biotechnology of Escherichia coli. Springer, pp 1–17. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9394-4
Zhao G, Ceci P, Ilari A, Giangiacomo L, Laue TM, Chiancone E, Chasteen ND (2002) Iron and hydrogen peroxide detoxification properties of DNA-binding protein from starved cells A ferritin-like DNA-binding protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 277:27689–27696
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the100-Talent Project of CAS (to GZ), National 863 Program of China (SS2013AA050703-2), Taishan Scholars Climbing Program of Shandong (No. tspd20150210) and Key Program of CAS (KGZD-EW-606-1-3).
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Feng, X., Ding, Y. et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to improve recombinant protein production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 10367–10377 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6955-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6955-9