Abstract
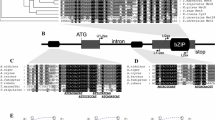
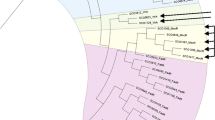
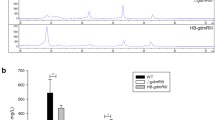
Myo-inositol is important for Streptomyces growth and morphological differentiation. Genomic sequence analysis revealed a myo-inositol catabolic gene cluster in Streptomyces coelicolor. Disruption of the corresponding genes in this cluster abolished the bacterial growth on myo-inositol as a single carbon source. The transcriptions of these genes were remarkably enhanced by addition of myo-inositol in minimal medium. A putative regulatory gene SCO6974, encoding a GntR family protein, is situated in the cluster. Disruption of SCO6974 significantly enhanced the transcription of myo-inositol catabolic genes. SCO6974 was shown to interact with the promoter regions of myo-inositol catabolic genes using electrophoretic mobility shift assays. DNase I footprinting assays demonstrated that SCO6974 recognized a conserved palindromic sequence (A/T)TGT(A/C)N(G/T)(G/T)ACA(A/T). Base substitution of the conserved sequence completely abolished the binding of SCO6974 to the targets demonstrating that SCO6974 directly represses the transcriptions of myo-inositol catabolic genes. Furthermore, the disruption of SCO6974 was correlated with a reduced sporulation of S. coelicolor in mannitol soya flour medium and with the overproduction of actinorhodin and calcium-dependent antibiotic. The addition of myo-inositol suppressed the sporulation deficiency of the mutant, indicating that the effect could be related to a shortage in myo-inositol due to its enhanced catabolism in this strain. This enhanced myo-inositol catabolism likely yields dihydroxyacetone phosphate and acetyl-CoA that are indirect or direct precursors of the overproduced antibiotics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. doi:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Anderson TB, Brian P, Champness WC (2001) Genetic and transcriptional analysis of absA, an antibiotic gene cluster-linked two-component system that regulates multiple antibiotics in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 39:553–566. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02240.x
Borodina I, Siebring J, Zhang J, Smith CP, van Keulen G, Dijkhuizen L, Nielsen J (2008) Antibiotic overproduction in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) mediated by phosphofructokinase deletion. J Biol Chem 283:25186–25199. doi:10.1074/ jbc. M 803105200
Boutte CC, Srinivasan BS, Flannick JA, Novak AF, Martens AT, Batzoglou S, Viollier PH, Crosson S (2008) Genetic and computational identification of a conserved bacterial metabolic module. PLoS Genet 4:e1000310. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000310
Bzymek KP, Newton GL, Ta P, Fahey RC (2007) Mycothiol import by Mycobacterium smegmatis and function as a resource for metabolic precursors and energy production. J Bacteriol 189:6796–6805. doi:10.1128/JB.00644-07
Cerdeño AM, Bibb MJ, Challis GL (2001) Analysis of the prodiginine biosynthesis gene cluster of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): new mechanisms for chain initiation and termination in modular multienzymes. Chem Biol 8:817–829. doi:10.1016/S1074 -5521(01)00054-0
Chater KF (2011) Differentiation in Streptomyces: the properties and programming of diverse cell-types. In: Dyson P (ed) In Streptomyces. Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Norfolk, pp 43–86
Chouayekh H, Nothaft H, Delaunay S, Linder M, Payrastre B, Seghezzi N, Titgemeyer F, Virolle MJ (2007) Phosphoinositides are involved in control of the glucose-dependent growth resumption that follows the transition phase in Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol 189:741–749. doi:10.1128/JB.00891-06
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645. doi:10.1073/pnas.120163297
Flärdh K, Buttner MJ (2009) Streptomyces morphogenetics: dissecting differentiation in a filamentous bacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:36–49. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1968
Gottelt M, Kol S, Gomez-Escribano JP, Bibb M, Takano E (2010) Deletion of a regulatory gene within the cpk gene cluster reveals novel antibacterial activity in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiol SGM 156:2343–2353. doi:10.1099/ mic. 0.038281-0
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1541–1546. doi:10.1073/pnas.0337542100
Gust B, Chandra G, Jakimowicz D, Yuqing T, Bruton CJ, Chater KF (2004) Lambda red-mediated genetic manipulation of antibiotic-producing Streptomyces. Adv Appl Microbiol 54:107–128. doi:10.1016/S0065-2164(04)54004-2
Hesketh A, Fink D, Gust B, Rexer HU, Scheel B, Chater K, Wohlleben W, Engels A (2002) The GlnD and GlnK homologues of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) are functionally dissimilar to their nitrogen regulatory system counterparts from enteric bacteria. Mol Microbiol 46:319–330. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03149.x
Hoischen C, Gura K, Luge C, Gumpert J (1997) Lipid and fatty acid composition of cytoplasmic membranes from Streptomyces hygroscopicus and its stable protoplast-type L form. J Bacteriol 179:3430–3436, pmid: 9171384
Hojati Z, Milne C, Harvey B, Gordon L, Borg M, Flett F, Wilkinson B, Sidebottom PJ, Rudd BA, Hayes MA, Smith CP, Micklefield J (2002) Structure, biosynthetic origin, and engineered biosynthesis of calcium-dependent antibiotics from Streptomyces coelicolor. Chem Biol 9:1175–1187. doi:10.1016/S1074-5521(02)00252-1
Hoskisson PA, Rigali S (2009) Variation in form and function the helix-turn-helix regulators of the GntR superfamily. Adv Appl Microbiol 69:1–22. doi:10.1016/S0065-2164(09)69001-8
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Centre, Norwich Research Park
Kohler PR, Choong EL, Rossbach S (2011) The RpiR-like repressor IolR regulates inositol catabolism in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 193:5155–5163. doi:10.1128/JB.05371-11
Kohler PR, Zheng JY, Schoffers E, Rossbach S (2010) Inositol catabolism, a key pathway in Sinorhizobium meliloti for competitive host nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7972–7980. doi:10.1128/AEM. 01972-10
Liu G, Chater KF, Chandra G, Niu G, Tan H (2013) Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:112–143. doi:10.1128/MMBR. 00054-12
Liu G, Tian Y, Yang H, Tan H (2005) A pathway-specific transcriptional regulatory gene for nikkomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ansochromogenes that also influences colony development. Mol Microbiol 55:1855–1866. doi:10.1111/j.1365 -2958. 2005. 04512.x
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Malpartida F, Hopwood DA (1984) Molecular-cloning of the whole biosynthetic-pathway of a Streptomyces antibiotic and its expression in a heterologous host. Nature 309:462–462. doi:10.1038/309462a0
Martín JF (2004) Phosphate control of the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites is mediated by the PhoR-PhoP system: an unfinished story. J Bacteriol 186:5197–5201. doi:10.1128/JB.186.16.5197-5201.2004
McCormick JR, Flärdh K (2012) Signals and regulators that govern Streptomyces development. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36:206–231. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011. 00317.x
Michell RH (2008) Inositol derivatives: evolution and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:151–161. doi:10.1038/nrm2334
Miroux B, Walker JE (1996) Over-production of proteins in Escherichia coli: mutant hosts that allow synthesis of some membrane proteins and globular proteins at high levels. J Mol Biol 260:289–298. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0399
Morinaga T, Ashida H, Yoshida KI (2010) Identification of two scyllo-inositol dehydrogenases in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 156:1538–1546. doi:10.1099/mic. 0.037499-0
Pan Y, Liu G, Yang H, Tian Y, Tan H (2009) The pleiotropic regulator AdpA-L directly controls the pathway-specific activator of nikkomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Mol Microbiol 72:710–723. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009. 06681.x
Pan Y, Lu C, Dong H, Yu L, Liu G, Tan H (2013) Disruption of rimP-SC, encoding a ribosome assembly cofactor, markedly enhances the production of several antibiotics in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microb Cell Factories 12:65. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-12-65
Rigali S, Nothaft H, Noens EE, Schlicht M, Colson S, Müller M, Joris B, Koerten HK, Hopwood DA, Titgemeyer F, Wezel GP (2006) The sugar phosphotransferase system of Streptomyces coelicolor is regulated by the GntR-family regulator DasR and links N-acetylglucosamine metabolism to the control of development. Mol Microbiol 61:1237–1251. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05319.x
Ryu YG, Butler MJ, Chater KF, Lee KJ (2006) Engineering of primary carbohydrate metabolism for increased production of actinorhodin in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7132–7139. doi:10.1128/AEM. 01308-06
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sola-Landa A, Moura RS, Martín JF (2003) The two-component PhoR-PhoP system controls both primary metabolism and secondary metabolite biosynthesis in Streptomyces lividans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:6133–6138. doi:10.1073/pnas.0931429100
Tiffert Y, Supra P, Wurm R, Wohlleben W, Wagner R, Reuther J (2008) The Streptomyces coelicolor GlnR regulon: identification of new GlnR targets and evidence for a central role of GlnR in nitrogen metabolism in actinomycetes. Mol Microbiol 67:861–880. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06092.x
Turner BL, Papházy MJ, Haygarth PM, McKelvie ID (2002) Inositol phosphates in the environment. Phil Trans R Soc London B 357:449–469. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.0837
Yebra MJ, Zúñiga M, Beaufils S, Pérez-Martínez G, Deutscher J, Monedero V (2007) Identification of a gene cluster enabling Lactobacillus casei BL23 to utilize myo-inositol. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3850–3858. doi:10.1128/AEM. 00243-07
Yoshida KI, Aoyama D, Ishio I, Shibayama T, Fujita Y (1997) Organization and transcription of the myo-inositol operon, iol, of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 179:4591–4598, pmid: 9226270
Yoshida KI, Shibayama T, Aoyama D, Fujita Y (1999) Interaction of a repressor and its binding sites for regulation of the Bacillus subtilis iol divergon. J Mol Biol 285:917–929. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2398
Yoshida KI, Yamaguchi M, Morinaga T, Kinehara M, Ikeuchi M, Ashida H, Fujita Y (2008) myo-Inositol catabolism in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 283:10415–10424. doi:10.1074/jbc.M708043200
Zhang G, Tian Y, Hu K, Zhu Y, Chater KF, Feng C, Liu L, Tan H (2012) Importance and regulation of inositol biosynthesis during growth and differentiation of Streptomyces. Mol Microbiol 83:1178–1194. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08000.x
Zianni M, Tessanne K, Merighi M, Laguna R, Tabita FR (2006) Identification of the DNA bases of a DNase I footprint by the use of dye primer sequencing on an automated capillary DNA analysis instrument. J Biomol Tech 17:103–113, pmid: 16741237
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31170088 and 31200929). We are grateful to Prof. Keith Chater (John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK) for providing E. coli ET12567/pUZ8002 and plasmid pSET152. We would like to thank Dr. Ying Wen (China Agriculture University, Beijing, China) for her kind help in EMSAs.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L.Y. and S.L. contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 653 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Li, S., Gao, W. et al. Regulation of myo-inositol catabolism by a GntR-type repressor SCO6974 in Streptomyces coelicolor . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 3141–3153 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6368-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6368-1