Abstract
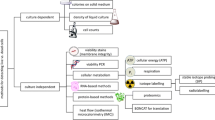
Species-specific enumeration of mixed community is invaluable as it facilitates a better understanding of the significance of the individual strains, their interactions, and the underlying mechanisms of community dynamics. Mixed microbial community has been characterized by microbiological, biochemical, or molecular biology-based methods. While microbiological and biochemical techniques do not provide adequate quantitative information of the members of the consortia and require additional techniques for a more comprehensive analysis, molecular biology-based methods analyze the microbial consortium based on specific DNA sequences and do not require isolation and culturing of bacteria for quantitative analysis. These methods outshine conventional culture-based techniques in terms of better sensitivity, reproducibility, and reliability. Quantitative molecular biology methods have been classified as PCR-based and probe hybridization methods. The PCR-based methods includes quantitative real-time PCR and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism, while fluorescent in situ hybridization and DNA microarrays fall under probe hybridization methods. The workflow, the quantification methods, and their potential applications are discussed in this review by highlighting their advantages and possible limitations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilleos C, Berthier F (2013) Quantitative PCR for the specific quantification of Lactococcus lactis and Lactobacillus paracasei and its interest for Lactococcus lactis in cheese samples. Food Microbiol 36:286–295
Åkerlund T, Nordstörm K, Bernander R (1995) Analysis of cell size and DNA content in exponentially growing and stationary-phase batch cultures of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:6791–6797
Alvarez G, González M, Isabal S, Blanc V, León R (2013) Method to quantify live and dead cells in multi-species oral biofilm by real-time PCR with propidium monoazide. AMB Express 3:1
Amann R, Fuchs B (2008) Single-cell identification in microbial communities by improved fluorescence in situ hybridization techniques
Bae J-W, Rhee S-K, Park JR, Chung W-H, Nam Y-D, Lee I, Kim H, Park Y-H (2005) Development and evaluation of genome-probing microarrays for monitoring lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8825–8835
Ballarini A, Segata N, Huttenhower C, Jousson O (2013) Simultaneous quantification of multiple bacteria by the BactoChip microarray designed to target species-specific marker genes. PLoS One 8:e55764
Barra Caracciolo A, Grenni P, Cupo C, Rosetti S (2005) In situ analysis of native microbial communities in complex samples with high particulate loads. FEMS Microbiol Lett 253:55–58
Bastein P, Procop GW, Reischl U (2008) Quantitative real-time PCR is not more sensitive than “conventional” PCR. J Clin Microbiol 46:1897–1900
Bonito RD, Marone A, Massini G, Patriarca C, Rosa S, Signorini A, Varrone C, Viola C, Izzo G (2013) Characterization by length heterogeneity (LH)-PCR of a hydrogen-producing community obtained in dark fermentation using coastal lake sediment as an inoculum. Energy Sustain Soc 3:3
Broadaway SC, Barton SA, Pyle BH (2003) Rapid staining and enumeration of small numbers of total bacteria in water by solid – phase laser cytometry. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4272–4273
Caplice E, Fitzgerald GF (1999) Food fermentations: role of microorganisms in food production and preservation. Int J Food Microbiol 50:131–149
Case RJ, Boucher Y, Dahllöf I, Holmström C, Doolittle WF, Kjelleberg S (2007) Use of 16S rRNA and rpoB genes as molecular markers for microbial ecology studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:278–288
Coats ER, Loge FJ, Smith WA, Thompson DN, Wolcott MP (2007) Functional stability of a mixed microbial consortium producing PHA from waste carbon sources. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 136–140:909–926
Coşkuner G (2002) A new molecular technique for the identification of micro-organisms in biological treatment plants: fluorescent in situ hybridization. Turk J Biol 26:57–63
Crosby LD, Criddle CS (2003) Understanding bias in microbial community analysis techniques due to rrn operon copy number heterogeneity. Biotechniques 34:790–794
Cupples AM (2008) Real-time PCR quantification of dehalococcoides populations: methods and applications. J Microbiol Methods 72:1–11
Daims H, Ramsing NB, Schleifer K-H, Wagner M (2001) Cultivation-independent, semiautomatic determination of absolute bacterial cell numbers in environmental samples by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5810–5818
Delbés C, Moletta R, Godon J-J (2000) Monitoring of activity dynamics of an anaerobic digester bacterial community using 16S rRNA polymerase chain reaction–single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Environ Microbiol 2:506–515
Delgenes JP, Escare MC, Laplace JM, Moletta R, Navarro JM (1998) Biological production of industrial chemicals, i.e. xylitol and ethanol, from lignocelluloses by controlled mixed culture systems. Ind Crop Prod 7:101–111
Díaz-Ramírez IJ, Escalante-Espinosa E, Favela-Torres E, Guítterrez-Rojas M, Ramírez-Saad H (2008) Design of defined mixed cultures for biodegradation of specific crude oil fractions, using population dynamics analysis by DGGE. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 62:21–30
Dubey SK, Tripathi AK, Upadhyay SN (2006) Exploration of soil bacterial communities for their potential as bioresource. Bioresour Technol 97:2217–2224
Erlandson K, Batt CA (1997) Strain-specific differentiation of Lactococci in mixed starter culture populations using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA—derived probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2702–2707
Everett KR, Rees-George J, Pushparajah IPS, Janssen BJ, Luo Z (2010) Advantages and disadvantages of microarrays to study microbial population dynamics—a minireview. N Z Plant Prot 63:1–6
Ezaki M, Iwami M, Yamashita M, Komori T, Umehara K, Imanaka H (1992) Biphenomycin A production by a mixed culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3879–3882
Fang C, Radosevich M, Fuhrmann JJ (2001) Characterization of rhizosphere microbial community structure in five similar grass species using FAME and BIOLOG analyses. Soil Biol Biochem 33:679–682
Fedi S, Tremaroli V, Scala D, Perez-Jimenez JR, Fava F, Young L, Zannoni D (2005) T-RFLP analysis of bacterial communities in cyclodextrin-amended bioreactors developed for biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Res Microbiol 156:201–210
Forney LJ, Zhou X, Brown CJ (2004) Molecular microbial ecology: land of the one-eyed king. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:210–220
Fox GE, Wisotzkey JD, Jurtshuk P Jr (1992) How close is close: 16S rRNA sequence identity may not be sufficient to guarantee species identity. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:166–170
Franklin RB, Taylor DB, Mill AL (1999) Characterization of microbial communities using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). J Microbiol Methods 35:225–235
Friedrich U, Lenke J (2006) Improved enumeration of lactic acid bacteria in mesophilic dairy starter cultures by using multiplex quantitative real-time PCR and flow cytometry-fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4163–4171
Gamo M, Shoji T (1999) A method of profiling microbial communities based on a most-probable-number assay that uses BIOLOG plates and multiple sole carbon sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4419–4425
Grattepanche F, Lacroix C, Audet P, Lapointe G (2005) Quantification by real-time PCR of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris in milk fermented by a mixed culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:414–421
Hagman M, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH, Jansen JI (2008) Mixed carbon sources for nitrate reduction in activated sludge-identification of bacteria and process activity studies. Water Res 42:1539–1546
Hamilton MS, Schremmer R (2002) High frequency of competitive inhibition in the Roche Cobas AMPLICOR multiplex PCR for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol 40:4393
Hatt JK, Löffler FE (2012) Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) detection chemistries affect enumeration of the Dehalococcoides 16S rRNA gene in groundwater. J Microbiol Methods 88:263–270
Herbel SR, Lauzat B, von Nickisch-Rosengk M, Kuhn M, Murugaiyan J, Weiler LH, Guenther S (2013) Species-specific quantification of probiotic lactobacilli in yoghurt by quantitative real-time PCR. J Appl Microbiol. doi:10.1111/jam.12341
Hiibel SR, Pereyra LP, Inman LY, Tischer A, Reisman D, Reardon KF, Pruden A (2008) Microbial community analysis of two field-scale sulfate-reducing bioreactors treating mine drainage. Environ Microbiol 10:2087–2097
Hjort K, Bernander R (1999) Changes in cell size and DNA content in Sulfolobus cultures during dilution and temperature shift experiments. J Bacteriol 181:5669–5675
Hristova KR, Lutenegger CM, Scow KM (2001) Detection and quantification of methyl tert-butyl ether-degrading strain PM1 by real-time TaqMan PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5154–5160
Hu H-Y, Lim B-R, Goto N, Fujie K (2001) Analytical precision and repeatability of respiratory quinones for quantitative study of microbial community structure in environmental samples. J Microbiol Methods 47:17–24
Kim D, Jhon D-Y, Park K-H, Day DF (1996) Mixed culture fermentation for the production of clinical quality dextran with starch and sucrose. Biotechnol Lett 18:1031–1034
Kim J, Lim J, Lee C (2013) Quantitative real-time PCR approaches for microbial community studies in wastewater treatment systems: applications and considerations. Biotechnol Adv. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.05.010
Klappenbach JA, Saxman PR, Cole JR, Schmidt TM (2001) rrndb: the ribosomal RNA operon copy number database. Nucleic Acids Res 29:181–184
Kleerebezem R, Loosdrecht MC (2007) Mixed culture biotechnology for bioenergy production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:207–212
Kösters K, Reischl U, Schmetz J, Riffelmann M, König CHWV (2002) Real-time lightcycler PCR for detection and discrimination of Bordtella pertussis and Bordtella parapertussis. J Clin Microbiol 40:1719–1722
Lee S, Fuhrman JA (1990) DNA hybridization to compare species compositions of natural bacterioplankton assemblages. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:739–746
Lee H-W, Lee S-Y, Lee J-W, Park J-B, Choi E-S, Park YK (2002) Molecular characterization of microbial community in nitrate-removing activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 41:85–94
Levy-Booth DJ, Campbell RG, Gulden RH, Hart MM, Powell JR, Klironomos JN, Pauls KP, Swanton CJ, Trevors JT, Dunfield KE (2007) Cycling of extracellular DNA in the soil environment. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2977–2991
Lisle JT, Hamilton MA, Willse AR, McFeters GA (2004) Comparison of fluorescence microscopy and solid-phase cytometry methods for counting bacteria in water. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5343–5348
Livak KJ (1999) Allelic discrimination using fluorogenic probes and the 5′ nuclease assay. Genet Anal Biomol Eng 14:143–149
Maeda H, Fujimoto C, Haruki Y, Maeda T, Kokeguchi S, Petelin M, Arai H, Tanimoto I, Nishimura F, Takashiba S (2003) Quantitative real-time PCR using TaqMan and SYBR Green for Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, tetQ gene and total bacteria. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 39:81–86
Matturo B, Heavner GL, Richardson RE, Rossetti S (2013) Quantitative estimation of Dehalococcoides mccartyi at laboratory and field scale: comparative study between CARD-FISH and Real Time PCR. J Microbiol Methods 93:127–133
McGuigan FEA, Ralston SH (2002) Single nucleotide polymorphism detection: allelic discrimination using TaqMan. Psychiatr Genet 12:133–136
Merwe TVD, Wolfaardt F, Riedel K-H (2003) Analysis of functional diversity of the microbial communities in a paper-mill water system. Water SA 29:31–34
Mohan VS (2009) Harnessing of biohydrogen from wastewater treatment using mixed fermentative consortia: process evaluation towards optimization. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:7460–7474
Müller S, Babel W (2003) Analysis of bacterial DNA patterns—an approach for controlling biotechnological processes. J Microbiol Methods 55:851–858
Nagarajan K, Loh KC, Swarup S (2013) Bioinformatics and molecular biology for quantification of closely related bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:6489–6502
Nakano Y, Takeshita T, Kamio N, Shiota S, Shibata Y, Yasui M, Yamashita Y (2008) Development and application of a T-RFLP data analysis method using correlation coefficient matrices. J Microbiol Methods 75:501–505
Nakatsu CH (2007) Soil microbial community analysis using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:562–571
Nocker A, Camper AK (2006) Selective removal of DNA from dead cells of mixed bacterial communities by use of ethidium monoazide. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1997–2004
Oslen GJ, Lane DJ, Giovannoni SJ, Pace NR (1986) Microbial ecology and evolution: ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol 40:337–365
Ovchinnikova AA, Vetrova AA, Filonov AE, Boronin AM (2009) Phenanthrene biodegradation and interaction of Pseudomonas putida BS3701 and Burkholderia sp. BS3702 in plant rhizosphere. Microbiology 78:433–439
Peplies J, Glöckner FO, Amann R (2003) Optimization strategies for DNA microarray-based detection of bacteria with 16S rRNA-targeting oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1397–1407
Phrommanich S, Suanjit S, Upatham S, Grams SV, Kruatrache M, Pokethitiyook P, Korge G, Hofmann A (2009) Quantitative detection of the oil-degrading bacterium Acinetobacter sp. Strain MUB1 by hybridization probe based real-time PCR. Microbiol Res 164:486–492
Pogačić T, Kelava N, Zamberlin Š, Dolenčić-Špehar I, Samaržija D (2010) Methods for culture-independent identification of lactic acid bacteria in dairy products. Food Technol Biotechnol 48:3–10
Raemdonck HV, Maes A, Ossieur W, Verthé K, Vercauteren T, Verstraete W, Boon N (2006) Real time PCR quantification in groundwater of the dehalrespiring Desulfitobacterium dichloroeliminans strain DCA1. J Microbiol Methods 67:294–303
Rastogi G, Sani RK (2011) Molecular techniques to assess microbial community structure, function, and dynamics in the environment. In: Iqbal A, Farah A, John P (eds) Microbes and microbial technology. Springer, New York, pp 29–57
Reardon KF, Mosteller DC, Rogers JB, DuTeau NM, Kim K-H (2002) Biodegradation kinetics of aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures by pure and mixed bacterial cultures. Environ Health Perspect 110:1005–1011
Rhee SK, Liu X, Wu L-Y, Chong SC, Wan X, Zhou J (2004) Detection of genes involved in biodegradation and biotransformation of in microbial communities by using 50-mer oligonucleotide microarrays. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4303–4317
Ririe KM, Rasmussen RP, Wittwer CT (1997) Product differentiation by analysis of DNA melting curves during the polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem 245:154–160
Ritchie NJ, Schutter ME, Dick RP, Myrold DD (2000) Use of length heterogeneity PCR and fatty acid methyl ester profiles to characterize microbial communities in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1668–1675
Rogers JB, DuTeau NM, Reardon KF (2000) Use of 16S-rRNA to investigate microbial population dynamics during biodegradation of toluene and phenol by a binary culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 70:436–445
Rudi K, Moen B, Drømtorp SM, Holck AL (2005) Use of ethidium monoazide and PCR in combination for quantification of viable and dead cells in complex samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1018–1024
Sanz JL, Kochling T (2007) Molecular biology techniques used in wastewater treatment: an overview. Process Biochem 42:119–133
Saravanan P, Pakshirajan K, Saha P (2008) Kinetics of phenol and m-cresol biodegradation by an indigenous mixed microbial culture isolated from sewage treatment plant. J Environ Sci 20:1508–1513
Schadt CW, Zhou J (2006) Advances in microarray-based technologies for soil microbial community analyses. In: Nannipieri P, Smalla K (eds) Nucleic acids and proteins in soil. Springer, New York, pp 189–203
Schmidt JK, Konig B, Reichl U (2007) Characterization of a three bacteria mixed culture in a chemostat: evaluation and application of a quantitative terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis for absolute and species specific cell enumeration. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:738–756
Schönhuber H, Fuchs B, Juretschko S, Amann R (1997) Improved sensitivity of whole-cell hybridization by the combination of horseradish peroxidase-labeled oligonucleotides and tyramide signal amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3268–3273
Schweiger F, Tebbe CC (1998) A new approach to utilize PCR-single-strand-conformation polymorphism for 16S rRNA gene-based microbial community analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4870–4876
Singh BK, Nozaries L, Munro S, Anderson IC, Campbell C (2006) Use of multiplex terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism for rapid and simultaneous analysis of different components of the soil microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7278–7285
Smalla K, Wachtendorf U, Heuer H, Liu W-T, Forney L (1998) Analysis of BIOLOG GN substrate utilization patterns by microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1220–1225
Smits THM, Devenoges C, Szynalski K, Maillard J, Holliger C (2004) Development of a real-time PCR method for quantification of the three genera Dehalobacter, Dehalococcoides and Desulfitobacterium in microbial communities. J Microbiol Methods 57:369–378
Soto K, Collantes G, Zahar M, Kuznar J (2005) Simultaneous enumeration of Phaedactylum tricornutum (MLB 292) and bacteria growing in mixed communities. Lat Am J Aquat Res 33:143–149
Spiegelman D, Whissell G, Greer CW (2005) A survey of the methods for the characterization of microbial consortia and communities. Can J Microbiol 51:355–386
Stoecker K, Dorninger C, Daims H, Wagner M (2010) Double labeling of oligonucleotide probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization (DOPE-FISH) improves signal intensity and increases rRNA accessibility. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:922–926
Suzuki MT, Taylor LT, DeLong EF (2000) Quantitative analysis of small-subunit rRNA genes in mixed microbial populations via 50-nuclease assays. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4605–4614
Talbot G, Topp E, Palin MF, Massé DI (2008) Evaluation of molecular methods used for establishing the interactions and functions of microorganisms in anaerobic bioreactors. Water Res 42:513–537
Thies JE (2007) Soil microbial community analysis using terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:579–591
Tischer K, Zeder M, Klug R, Pernthaler J, Schattenhofer M, Harms H, Wendeberg A (2012) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (CARD-FISH) of microorganisms in hydrocarbon contaminated aquifer sediment samples. Syst Appl Microbiol 35:526–532
Tolvanen KES, Karp MT (2011) Molecular methods for characterizing mixed microbial communities in hydrogen-fermenting systems. J Hydrogen Energy 36:5280–5288
Tourva TP (2003) Copy number of ribosomal operons in prokaryotes and its effect on phylogenetic analysis. Microbiology 72:437–452
Traversi D, Villa S, Acri M, Pietrangeli B, Degan R, Gilli G (2011) The role of different methnogen groups evaluated by real-time qPCR as high-efficiency bioindicators of wet anaerobic co-digestion of organic waste. AMB Express 2011:1–28
Trotha R, Reichl U, Thies FL, Sperling D, König B (2002) Adaption of a fragment analysis technique to an automated high-throughput multicapillary electrophoresis device for the precise qualitative and quantitative characterization of microbial communities. Electrophoresis 23:1070–1079
Uhlik O, Leewis M-C, Strejcek M, Musilova L, Mackova M, Leigh MB, Macek T (2013) Stable isotope probing in the metagenomics era: a bridge towards improved bioremediation. Biotechnol Adv 31:154–165
Valasek MA, Repa JY (2005) The power of real-time PCR. Adv Physiol Educ 29:151–159
Valera MJ, Torija MJ, Mas A, Mateo E (2013) Acetobacter malorum and Acetobacter cerevisiae identification and quantification by real-time PCR with TaqMan MGB probes. Food Microbiol 36:30–39
Van Ert MN, Easterday WR, Simonson TS, U’Ren JM, Pearson T, Kenefic LJ, Busch JD, Huynh LY, Dukerich M, Trim CB, Beaudry J, Welty-Bernard A, Read T, Fraser CM, Ravel J, Keim P (2007) Strain-specific single-nucleotide polymorphism assays for the Bacillus anthracis Ames strain. J Clin Microbiol 45:47–53
van Frankenhuyzen JK, Trevors JT, Flemming CA, Lee H, Habash MB (2013) Optimization, validation, and application of a real-time PCR protocol for quantification of viable bacterial cells in municipal sewage sludge and biosolids using reporter genes and Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:1251–1261
Wagner M, Haider S (2012) New trend in fluorescent in situ hybridization for identification and functional analyses of microbes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:96–102
Wang GCY, Wang Y (1997) Frequency of formation of chimeric molecules as a consequence of PCR coamplification of 16S rRNA genes from mixed bacterial genomes. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4645–4650
Watanabe K, Yamamoto S, Hino S, Harayama S (1998) Population dynamics of phenol-degrading bacteria in activated sludge determined by gyrB-targeted quantitative PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1203–1209
Werker AG, Becker J, Huitema C (2003) Assessment of activated sludge microbial community analysis in full-scale biological wastewater treatment plants using patterns of fatty acid isopropyl esters (FAPEs). Water Res 37:2162–2172
Wilen B-M, Onuki M, Hermannson M, Lumley D, Mino T (2008) Microbial community structure in activated sludge floc analysed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and its relation to floc stability. Water Res 42:2300–2308
Wilson JW, Ramamurthy R, Porwollik S, McClelland M, Hammond T, Allen P, Ott CM, Pierson DL, Nickerson CA (2002) Microarray analysis identifies Salmonella genes belonging to the low-shear modeled microgravity regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:13807–13812
Winderl C, Anneser B, Griebler C, Meckenstock RU, Lueders T (2008) Depth-Resolved quantification of anaerobic toluene degraders and aquifer microbial community patterns in distinct redox zones of a tar oil contaminant plume. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:792–801
Wittwer CT, Herrmann MG, Moss AA, Rasmussen RP (1997) Continuous fluorescence monitoring of rapid cycle DNA amplification. Biotechniques 22:130–138
Wu L, Thompson DK, Liu X, Fields MW, Bagwell CE, Tiedje JM, Zhou J (2004) Development and evaluation of micro-array based whole-genome hybridization for detection of micro-organisms within the context of environmental applications. Environ Sci Technol 38:6775–6782
Yilmaz LS, Parnerkar S, Noguera DR (2011) mathFISH, a web tool that uses thermodynamics-based mathematical models for in silico evaluation of oligonucleotide probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1118–1122
Yu CP, Chu KH (2005) A quantitative assay for linking microbial community function and structure of a naphthalene-degrading microbial consortium. Environ Sci Technol 39:9611–9619
Yu C-P, Ahuja R, Sayler G, Chu K-H (2005) Quantitative molecular assay for finger printing microbial communities of wastewater and estrogen—degrading consortia. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1433–1444
Zhang T, Fang HHP (2006) Applications of real-time polymerase chain reaction for quantification of microorganisms in environmental samples. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:281–289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagarajan, K., Loh, KC. Molecular biology-based methods for quantification of bacteria in mixed culture: perspectives and limitations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 6907–6919 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5870-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5870-9