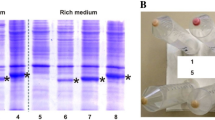
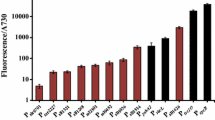
Abstract
We report here the creation of a modular, plasmid-based protein expression system utilizing elements of the native Rhodobacter puf promoter in a BioBrickTM-based vector system with DsRed encoding a red fluorescent reporter protein. A suite of truncations of the puf promoter were made to assess the influence of different portions of this promoter on expression of heterologous proteins. The 3′ end of puf was found to be particularly important for increasing expression, with transformants accumulating significant quantities of DsRed under both aerobic and anaerobic growth conditions. Expression levels of this reporter protein in Rhodobacter sphaeroides were comparable to those achieved in Escherichia coli using the strong, constitutive P lac promoter, thus demonstrating the robustness of the engineered system. Furthermore, we demonstrate the ability to tune the designed expression system by modulating cellular DsRed levels based upon the promoter segment utilized and oxygenation conditions. Last, we show that the new expression system is able to drive expression of a membrane protein, proteorhodopsin, and that membrane purifications from R. sphaeroides yielded significant quantities of proteorhodopsin. This toolset lays the groundwork for the engineering of multi-step pathways, including recalcitrant membrane proteins, in R. sphaeroides.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Hashesh M, Desaunay N, Hallenbeck PC (2013) High yield single stage conversion of glucose to hydrogen by photofermentation with continuous cultures of Rhodobacter capsulatus JP91. Bioresour Technol 128:513–517. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.091
Adams PG, Hunter CN (2012) Adaptation of intracytoplasmic membranes to altered light intensity in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1817(9):1616–1627. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.05.013
Beja O, Aravind L, Koonin EV, Suzuki MT, Hadd A, Nguyen LP, Jovanovich SB, Gates CM, Feldman RA, Spudich JL, Spudich EN, DeLong EF (2000) Bacterial rhodopsin: evidence for a new type of phototrophy in the sea. Science 289(5486):1902–1906
Canton B, Labno A, Endy D (2008) Refinement and standardization of synthetic biological parts and devices. Nat Biotechnol 26(7):787–793. doi:10.1038/nbt1413
Carrier TA, Keasling JD (1999) Library of synthetic 5′ secondary structures to manipulate mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 15(1):58–64. doi:10.1021/bp9801143
Chen DM, Han YB, Gu ZX (2006) Application of statistical methodology to the optimization of fermentative medium for carotenoids production by Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Process Biochem 41(8):1773–1778. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.03.023
Elsen S, Jaubert M, Pignol D, Giraud E (2005) PpsR: a multifaceted regulator of photosynthesis gene expression in purple bacteria. Mol Microbiol 57(1):17–26. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04655.x
Franchi E, Tosi C, Scolla G, Penna GD, Rodriguez F, Pedroni PM (2004) Metabolically engineered Rhodobacter sphaeroides RV strains for improved biohydrogen photoproduction combined with disposal of food wastes. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 6(6):552–565. doi:10.1007/s10126-004-1007-y
Gomelsky L, Moskvin OV, Stenzel RA, Jones DF, Donohue TJ, Gomelsky M (2008) Hierarchical regulation of photosynthesis gene expression by the oxygen-responsive PrrBA and AppA–PpsR systems of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol 190(24):8106–8114. doi:10.1128/JB.01094-08
Gomelsky M, Kaplan S (1997) Molecular genetic analysis suggesting interactions between AppA and PpsR in regulation of photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1. J Bacteriol 179(1):128–134
Gong L, Kaplan S (1996) Translational control of puf operon expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1. Microbiology 142(Pt 8):2057–2069
Gourdon P, Alfredsson A, Pedersen A, Malmerberg E, Nyblom M, Widell M, Berntsson R, Pinhassi J, Braiman M, Hansson O, Bonander N, Karlsson G, Neutze R (2008) Optimized in vitro and in vivo expression of proteorhodopsin: a seven-transmembrane proton pump. Protein Expr Purif 58(1):103–113. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2007.10.017
Hanson DK, Mielke DL, Laible PD (2009) Harnessing Photosynthetic Bacteria for Membrane Protein Production. In: Membrane Protein Crystallization. Curr Top Membr vol 63, pp 51–82. doi:10.1016/S1063-5823(09)63003-9
Hoff AJ, Deisenhofer J (1997) Photophysics of photosynthesis. Structure and spectroscopy of reaction centers of purple bacteria. Phys Rep 287(1–2):1–247. doi:10.1016/S0370-1573(97)00004-5
Hu Z, Zhao Z, Pan Y, Tu Y, Chen G (2010) A powerful hybrid puc operon promoter tightly regulated by both IPTG and low oxygen level. Biochemistry (Mosc) 75(4):519–2
Ind AC, Porter SL, Brown MT, Byles ED, de Beyer JA, Godfrey SA, Armitage JP (2009) Inducible-expression plasmid for Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Paracoccus denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(20):6613–6615. doi:10.1128/AEM.01587-09
Isaacs FJ, Dwyer DJ, Ding C, Pervouchine DD, Cantor CR, Collins JJ (2004) Engineered riboregulators enable post-transcriptional control of gene expression. Nat Biotechnol 22(7):841–847. doi:10.1038/nbt986
Jaschke PR, Saer RG, Noll S, Beatty JT (2011) Modification of the genome of Rhodobacter sphaeroides and construction of synthetic operons. Methods Enzymol 497:519–538. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-385075-1.00023-8
Johnson ET, Baron DB, Naranjo B, Bond DR, Schmidt-Dannert C, Gralnick JA (2010) Enhancement of survival and electricity production in an engineered bacterium by light-driven proton pumping. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(13):4123–4129. doi:10.1128/AEM.02425-09
Kien NB, Kong IS, Lee MG, Kim JK (2010) Coenzyme Q10 production in a 150-l reactor by a mutant strain of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37(5):521–529. doi:10.1007/s10295-010-0699-4
Kim MS, Baek JS, Lee JK (2006) Comparison of H-2 accumulation by Rhodobacter sphaeroides KD131 and its uptake hydrogenase and PHB synthase deficient mutant. Int J Hydrogen Energ 31(1):121–127. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2004.10.023
Kobayashi J, Yoshimune K, Komoriya T, Kohno H (2011) Efficient hydrogen production from acetate through isolated Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Biosci Bioeng 112(6):602–605. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.08.008
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM 2nd, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166(1):175–176
Lee SK, Chou H, Ham TS, Lee TS, Keasling JD (2008) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for biofuels production: from bugs to synthetic biology to fuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19(6):556–563. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.10.014
Mank NN, Berghoff BA, Hermanns YN, Klug G (2012) Regulation of bacterial photosynthesis genes by the small noncoding RNA PcrZ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(40):16306–16311. doi:10.1073/pnas.1207067109
McKinlay JB, Harwood CS (2010) Carbon dioxide fixation as a central redox cofactor recycling mechanism in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(26):11669–11675. doi:10.1073/pnas.1006175107
Naylor GW, Addlesee HA, Gibson LCD, Hunter CN (1999) The photosynthesis gene cluster of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Photosynth Res 62(2–3):121–139. doi:10.1023/A:1006350405674
Niederman RA (2013) Membrane development in purple photosynthetic bacteria in response to alterations in light intensity and oxygen tension. Photosynth Res 116(2-3):333–348. doi:10.1007/s11120-013-9851-0
Pfleger BF, Pitera DJ, Smolke CD, Keasling JD (2006) Combinatorial engineering of intergenic regions in operons tunes expression of multiple genes. Nat Biotechnol 24(8):1027–1032. doi:10.1038/nbt1226
Rajasekhar N, Sasikala C, Ramana CV (1998) Photobiotransformation of indole to its value-added derivatives by Rhodobacter sphaeroides OU5. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 20(3–4):177–179. doi:10.1038/sj.jim.2900501
Roy A, Shukla AK, Haase W, Michel H (2008) Employing Rhodobacter sphaeroides to functionally express and purify human G protein-coupled receptors. Biol Chem 389(1):69–78. doi:10.1515/BC.2008.001
Salis HM, Mirsky EA, Voigt CA (2009) Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression. Nat Biotechnol 27(10):946–950. doi:10.1038/nbt.1568
Saltikov CW, Newman DK (2003) Genetic identification of a respiratory arsenate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(19):10983–10988. doi:10.1073/pnas.1834303100
Shetty RP, Endy D, Knight TF Jr (2008) Engineering BioBrick vectors from BioBrick parts. J Biol Eng 2:5. doi:10.1186/1754-1611-2-5
Sistrom WR (1960) A requirement for sodium in the growth of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol 22:778–785
Stone KM, Voska J, Kinnebrew M, Pavlova A, Junk MJ, Han S (2013) Structural insight into proteorhodopsin oligomers. Biophys J 104(2):472–481. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2012.11.3831
Strack RL, Strongin DE, Bhattacharyya D, Tao W, Berman A, Broxmeyer HE, Keenan RJ, Glick BS (2008) A noncytotoxic DsRed variant for whole-cell labeling. Nat Methods 5(11):955–957. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1264
Tabita FR (2004) Research on carbon dioxide fixation in photosynthetic microorganisms (1971-present). Photosynth Res 80(1–3):315–332
Tehrani A, Beatty JT (2004) Effects of precise deletions in Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction center genes on steady-state levels of reaction center proteins: a revised model for reaction center assembly. Photosynth Res 79(1):101–108. doi:10.1023/B:Pres.0000011927.51349.E8
Vasilyeva L, Miyake M, Nakamura C, Nakada E, Tsygankov A, Asada Y, Miyake J (1999) Expression of luciferase gene under control of the puf promoter from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 77(9):337–345. doi:10.1385/Abab:77:1–3:337
Vick JE, Johnson ET, Choudhary S, Bloch SE, Lopez-Gallego F, Srivastava P, Tikh IB, Wawrzyn GT, Schmidt-Dannert C (2011) Optimized compatible set of BioBrick vectors for metabolic pathway engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92(6):1275–1286. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3633-4
Yeliseev AA, Kaplan S (1999) A novel mechanism for the regulation of photosynthesis gene expression by the TspO outer membrane protein of Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1. J Biol Chem 274(30):21234–21243. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.30.21234
Zhao HP, Ontiveros-Valencia A, Tang Y, Kim BO, Ilhan ZE, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Rittmann B (2013) Using a two-stage hydrogen-based membrane biofilm reactor (MBfR) to achieve complete perchlorate reduction in the presence of nitrate and sulfate. Environ Sci Technol 47(3):1565–1572. doi:10.1021/es303823n
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Anthony Dean for the use of the flow cytometer. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Grant CBET-0756296. I.B.T. was supported by a predoctoral National Institute of Health traineeship (GM008347).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 542 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tikh, I.B., Held, M. & Schmidt-Dannert, C. BioBrickTM compatible vector system for protein expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 3111–3119 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5527-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5527-8