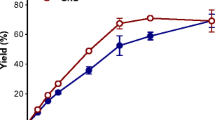
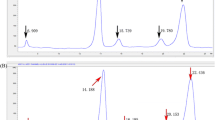
Abstract
The gene for cellobiose 2-epimerase (CE) from Ruminococcus albus NE1 was overexpressed in Escherichia coli cells. The recombinant CE was purified to homogeneity by a simple purification procedure with a high yield of 88%, and the molecular mass was 43.1 kDa on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and 44.0 kDa on gel chromatography. It exhibited optimal activity around at 30°C and pH 7.5, and the enzyme activity was inhibited by Al3+, Fe3+, Co2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Ag+, N-bromosuccinimide, iodoacetate, and 4-chloromercuribenzoate. In addition to cello-oligosaccharides, the enzyme was found to effectively 2-epimerize lactose to yield 4-O-β-d-galactopyranosyl-d-mannose (epilactose), which occurs in cow milk as a rare oligosaccharide. The K m and k cat/K m values toward lactose were 33 mM and 1.6 s−1 mM−1, and those toward cellobiose were 13.8 mM and 4.6 s−1 mM−1, respectively. N-Acetyl-d-glucosamine, uridine 5′-diphosphate-glucose, d-glucose 6-phosphate, maltose, sophorose, laminaribiose, and gentiobiose were inert as substrates for the recombinant CE. We demonstrated that epilactose was resistant to rat intestinal enzymes, utilized by human adult bifidobacteria, and stimulated the tight junction permeability in Caco-2 cells. These results strongly suggest that this rare disaccharide is promising for use as a prebiotic.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bryant MP, Burkey LA (1953) Cultural methods and some characteristics of some of the more numerous groups of bacteria in the bovine rumen. J Dairy Sci 36:205–217
Cataldi TRI, Angelotti M, Bufo SA (1999) Method development for the quantitative determination of lactulose in heat-treated milks by HPAEC with pulsed amperometric detection. Anal Chem 71:4919–4925
Dinoto A, Marques M, Sakamoto K, Fukiya S, Watanabe J, Ito S, Yokota A (2006) Population dynamics of Bifidobacterium species in human feces during raffinose administration monitored by fluorescence in situ hybridization-flow cytometry. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7739–7747
Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB (1995) Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J Nutr 125:1401–1412
Goldberg R, Gillou L, Prat R, Penhoat CH, Michon V (1991) Structural features of the cell-wall polysaccharides of Asparagus officinalis seeds. Carbohydr Res 210:263–276
Hara H, Li ST, Sasaki M, Maruyama T, Terada A, Ogata Y, Fujita K, Ishigami H, Hara K, Fujimori I, Mitsuoka T (1994) Effective dose of lactosucrose on fecal flora and fecal metabolites of humans. Bifidobact Microflora 13:51–63
Hungate RE (1957) Microorganisms in the rumen of cattle fed a constant ration. Can J Microbiol 3:289–311
Hungate RE (1969) A roll tube method for the cultivation of strict anaerobes. Methods Microbiol 3B:117–132
Igarashi K, Hatada Y, Hagihara H, Saeki K, Takaiwa M, Uemura T, Ara K, Ozaki K, Kawai S, Kobayashi T, Ito S (1998) Enzymatic properties of a novel liquefying α-amylase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus isolate and entire nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3282–3289
Ito S, Hamada S, Yamaguchi K, Umene S, Ito H, Matsui H, Ozawa T, Taguchi H, Watanabe J, Wasaki J, Ito S (2007) Cloning and sequencing of the cellobiose 2-epimerase gene from an obligatory anaerobe, Ruminococcus albus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:640–645
Kitahara M, Takamine F, Imanaka T, Benno Y (2001) Clostridium hiranonis sp. nov., a human intestinal bacterium with bile acid 7 α-dehydroxylating activity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:39–44
Kobayashi Y, Taguchi H, Goto TN, Koike S, Ohmiya K (2003) Expression and export of a Ruminococcus albus cellulase in Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens through the use of an alternative gene promoter and signal sequence. Can J Microbiol 49:375–382
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (Lond) 227:680–685
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Matsuki T, Watanabe K, Fujimoto J, Kado Y, Takada T, Matsumoto K, Tanaka R (2004) Quantitative PCR with 16SrRNA-gene-targeted species-specific primers for analysis of human intestinal bifidobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:167–173
Mishima T, Tanaka K, Tsuge H, Sugita J, Nakahara M, Hayakawa T (2005) Studies on absorption and hydrolysis of ethyl alpha-d-glucoside in rat intestine. J Agric Food Chem 53:7257–5261
Miyamoto M, Ajisaka K (2004) Regioselectivity in β-galactosidase-catalyzed transglycosylation for the enzymatic assembly of d-galactosyl-d-mannose. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:2086–2090
Moreno FJ, Villamiel M, Olano A (2003) Effect of high pressure on isomerization and degradation of lactose in alkaline media. J Agric Food Chem 51:1894–1896
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high-molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Ohara H, Karita S, Kimura T, Sakka K, Ohmiya K (2000) Characterization of the cellulolytic complex (cellulosome) from Ruminococcus albus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:254–260
Ohmiya K, Shimizu M, Taya M, Shimizu S (1982) Purification and properties of cellobiosidase from Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol 150:407–409
Ohmiya K, Shirai M, Kurachi Y, Shimizu S (1985) Isolation and properties of β-glucosidase from Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol 161:432–434
Ohmiya K, Maeda K, Shimizu S (1987) Purification and properties of endo-(1→4)-β-d-glucanase from Ruminococcus albus. Carbohydr Res 166:145–155
Poonperm W, Takata G, Okada H, Morimoto K, Granström TB, Izumori K (2007) Cloning, sequencing, overexpression and characterization of l-rhamnose isomerase from Bacillus pallidus Y25 for rare sugar production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1297–1307
Roberfroid M (2007) Prebiotics: the concept revisited. J Nutr 137:830S–837S
Suzuki T, Hara H (2004) Various nondigestible saccharides open a paracellular calcium transport pathway with the induction of intracellular calcium signaling in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 134:1935–1941
Suzuki T, Hara H (2006) Difructose anhydride III and sodium caprate activate paracellular transport via different intracellular events in Caco-2 cells. Life Sci 79:401–410
Tyler TR, Leatherwood JM (1967) Epimerization of disaccharides by enzyme preparations from Ruminococcus albus. Arch Biochem Biophys 119:363–367
Xiao M, Tanaka K, Oian XM, Yamamoto K, Kumagai H (2000) High-yield production and characterization of α-galactosidase from Bifidobacterium breve grown on raffinose. Biotechnol Lett 22:747–751
Ziemer C, Gibson G (1998) An overview of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in the functional food concept: perspectives and future strategies. Int Dairy J 8:473–479
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. H. Hara and Dr. A. Yokota of Hokkaido University (Sapporo, Japan) for invaluable discussions about present results and Dr. E. Fukushi of Hokkaido University for NMR measurements. This work was supported in part by research grants from the National Projects on Protein Structural and Functional Analysis and the Knowledge Cluster Initiative (2nd stage, “Sapporo Biocluster Bio-S”), MEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, S., Taguchi, H., Hamada, S. et al. Enzymatic properties of cellobiose 2-epimerase from Ruminococcus albus and the synthesis of rare oligosaccharides by the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79, 433–441 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1449-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1449-7