Abstract
This study examines the effects of temporal changes on microbial parameters in a brackish aquatic ecosystem. To this aim, the abundances of prokaryotes and vibrios together with the rates of enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins by leucine aminopeptidase (LAP), polysaccharides by β-glucosidase (GLU) and organic phosphates by alkaline phosphatase (AP), heterotrophic prokaryotic production (HPP), respiration (R), were seasonally investigated, during a 2-year period in the coastal area of Cape Peloro (Messina, Italy), constituted by two brackish lakes (Faro and Ganzirri). In addition, physical and chemical parameters (temperature, salinity, nutrients) and particulate organic carbon and nitrogen (POC, PN) were measured. The influence of multiple factors on prokaryotic abundances and activities was analysed. The results showed that Cape Peloro area is characterised by high seasonal variability of the microbial parameters that is higher than the spatial one. Combined changes in particulate matter and temperature (T), could explain the variability in vibrios abundance, GLU and R activities in both lakes, indicating a direct stimulation of the warm season on the heterotrophic prokaryotic metabolism. Positive correlations between T (from 13.3 to 29.6 °C) and HPP, LAP, AP, POC, PN are also observed in Ganzirri Lake. Moreover, the trophic status index and most of the microbial parameters show significant seasonal differences. This study demonstrates that vibrios abundance and microbial activities are responsive to the spatial and seasonal changes of examined area. The combined effects of temperature and trophic conditions on the microbial parameters lead us to suggest their use as potential indicators of the prokaryotic response to climate changes in temperate brackish areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminot A, Chaussepied M (1983) Manuel des analyses chemiques au milieu marin. CNEXO, Brest 376
Azam F (1998) Microbial control of oceanic carbon flux: the plot thickens. Science 280:694–696
Azzaro M, La Ferla R, Maimone G, Monticelli LS, Zaccone R, Civitarese G (2012) Prokaryotic dynamics and heterotrophic metabolism in a deep-convection site of Eastern Mediterranean Sea (the Southern Adriatic Pit). Contin Shelf Res 44:106–118, South Adriatic Oceanogr
Bergamasco A, Azzaro M, Pulicanò G, Cortese G, Sanfilippo M (2005) Ganzirri Lake, north-eastern Sicily. In: Giordani G, Viaroli P, Swaney DP, Murray CN, Zaldívar JM, Marshall Crossland JI (eds) Nutrient fluxes in transitional zones of the Italian coast, LOICZ Reports & Studies N° 28. LOICZ, Texel, 157 pages
Blackwell KD, Oliver JD (2008) The ecology of Vibrio vulnificus, V. cholera, and V. parahaemolyticus in North Carolina Estuaries. J Microbiol 46(2):146–153
Boucher D, Debroas D (2009) Impact of environmental factors on couplings between bacterial community composition and ectoenzymatic activities in a lacustrine ecosystem. FEMS Microb Ecol 70:66–78
Carlson RE, Simpson J (1996) A coordinator’s guide to volunteer lake monitoring methods. North Am Lake Manag Soc 96
Carpenter JH (1965) The accuracy of the Winkler method for dissolved oxygen. Limnol Oceanog 10:135–140
Caruso G, Zaccone R, Crisafi E (1996) Distribution and numerical taxonomy of Vibrionaceae in the waters of the Straits of Messina. Microbiol 19:155–166
Caruso G, Monticelli L, Azzaro F, Azzaro M, Decembrini F, La Ferla R, Leonardi M, Zaccone R (2005) Dynamics of extracellular enzymatic activities in a shallow Mediterranean ecosystem (Tindari ponds, Sicily). Mar Freshw Res 56:173–188
Caruso G, Leonardi M, Monticelli LS, Decembrini F, Azzaro F, Crisafi E, Zappalà G, Bergamasco A, Vizzini S (2010) Assessment of the ecological status of Sicilian transitional waters: first characterization and classification according to a multiparametric approach. Mar Poll Bull 60(10):1682–1690
Chróst RJ (1991) Environmental control of the synthesis and activity of aquatic microbial ectoenzymes. In: Chróst RJ (ed) Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer, Germany, pp 29–59
Chróst RJ, Siuda W (2006) Microbial production, utilization, and enzymatic degradation of organic matter in the upper trophogenic layer in the pelagic zone of Lakes along a eutrophication gradient. Limnol Oceanogr 5:749–762
Chrzanowski TH, Kyle M, Elser JJ, Sterner RW (1996) Element ratios and growth dynamics of bacteria in an oligotrophic shield Lake. Aquat Microb Ecol 11:119–125
Colwell RR (1984) Vibrios in the environment. Wiley, New York
Covazzi Harriague A, Brino MD, Zampini M, Albertelli G, Pruzzo C, Misic C (2008) Vibrios in association with sedimentary crustaceans in three beaches of the northern Adriatic Sea (Italy). Mar Pollut Bull 56(3):574–579
Eiler M, Johansson, Bertilsson S (2006) Environmental influences on vibrio populations in Northern temperate and boreal coastal waters (Baltic and Skagerrak Seas). Appl Environ Microbiol 72(9):6004–6011
Ferrarin C, Bergamasco A, Umgiesser G, Cucco A (2013) Spatial zonation of transitional waters derived from modelled water renewal times. J Mar Syst 117–118:96–107
Heidelberg JF, Heidelberg KB, Colwell RR (2002) Seasonality of Chesapeake Bay bacterioplankton species. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5488–5497
Hoppe HG, Arnosti C, Herndl GJ (2002) Ecological significance of bacterial enzymes in the marine environment. In: Burns RG, Dick RP (eds) Enzyme in the environment: activity ecology and application. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 73–108
Huq A, Sack RB, Nizam A, Longini IM, Nair GB, Ali A, Morris JG Jr, Khan MN, Siddique AK, Yunus M, Albert MJ, Sack DA, Colwell RR (2005) Critical factors influencing the occurrence of Vibrio cholerae in the environment of Bangladesh. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(8):4645–4654
Huston AL, Deming JW (2002) Relationships between microbial extracellular enzymatic activity and suspended and sinking particulate organic matter: seasonal transformations in the North Water. Deep-Sea Res 49:5211–5225, II
Jones MK, Oliver JD (2009) Vibrio vulnificus: disease and pathogenesis. Infect Immun 77(5):1723–1733
Kaneko T, Colwell RR (1978) Annual cycle of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Chesapeake Bay. Microb Ecol 4:135–155
Kiersztyn B, Siuda W, Chróst RJ (2012) Persistence of bacterial proteolytic enzymes in Lake ecosystems. FEMS Microb Ecol 80:124–134
Kirchman DL (1993) Leucine incorporation as a measure of biomass production by heterotrophic bacteria. In: Kemp PF, Sherr BF, Sherr EB (eds.) Handbook of methods in Aquat Microb Ecol Lewis, Boca Raton, FL, 509-512
Kimes NE, Grim CJ, Johson WR, Hasan NA, Tall BD, Kothary MH, Kiss H, Munk AC, Tapia R, Green L, Detter C, Bruce D, Brettin TS, Colwell RR, Morris PJ (2012) Temperature regulation of virulence factors in the pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. ISME J 6:835–846
La Ferla R, Zaccone R, Caruso G, Azzaro M (2001) Enzymatic activities and carbon flux through the microbial compartment in the Adriatic Sea. In: Faranda FM Guglielmo L, Spezie G (eds) The Mediterranean ecosystems: structure and processes. Springer 61:468-493
La Ferla R, Azzaro M, Maimone G (2006) Microbial respiration and trophic regimes in the Northern Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 69(1–2):196–204
La Ferla R, Maimone G, Azzaro M, Conversano F, Brunet C, Cabral AS, Paranhos R (2012) Vertical distribution of the prokaryotic cell size in the Mediterranean Sea. Helg Mar Res 66(4):635–650
Lara RJ, Neogi SB, Islam S, Mahmud ZH, Yamasaki S, Nair GB (2009) Influence of estuarine dynamic and catastrophic climatic event on Vibrio distribution in the Karnaphuli Estuary, Bangladesh. Eco Health 6:279–286
Lee S, Fuhrman JA (1987) Relationships between biovolume and biomass of naturally derived marine bacterioplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(6):1298–1303
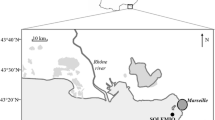
Leonardi M, Azzaro F, Azzaro M, Caruso G, Mancuso M, Monticelli LS, Maimone G, La Ferla R, Raffa F, Zaccone R (2009) A multidisciplinary study of the Cape Peloro brackish area (Messina, Italy): characterization of trophic conditions, microbial abundances and activities. Mar Ecol 30(s1):33–42
Mancuso M, Costanzo MT, Maricchiolo G, Gristina M, Zaccone R, Cuccu D, Genovese L (2010) Characterization of chitinolytic bacteria and histological aspects of Shell Disease Syndrome in European Spiny Lobster (Palinurus elephas) (Fabricius 1787). J Inv Path 104:242–244
Mancuso M, Zaccone R, Carella F, Maiolino P, De Vico G First episode of a shell disease syndrome in Carcinus aestuarii (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunidae) at Volturno River. J Aquac Res Develop in press
Maugeri TL, Crisafi E, Zaccone R (1987) Halophilic vibrios in cultivated molluscs. Microb Alimen Nutrit 5:135–139
Maugeri TL, Caccamo D, Gugliandolo C (2000) Potentially pathogenic vibrios in brackish waters and mussels. J Appl Microbiol 89:261–266
Neogi SB, Koch BP, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Pohl C, Kattner G, Yamasaki G, Lara RJ (2011) Biogeochemical controls on the bacterial population in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Biogeosciences 8:3747–3759
Noquerela I, Blanch AR (2008) Identification of Vibrio spp. with a set of dichotomous keys. J Appl Microb 105:175–185
Oberbeckmann S, Fuchs BM, Meiners M, Wichels A, Wiltshire KH, Gerdts G (2012) Seasonal dynamics and modelling of a Vibrio community in coastal waters of the North Sea. Microb Ecol 63(3):543–551
Oliver JD, Wear JE, Thomas MB, Warner M, Linder K (1986) Production of extracellular enzymes and cytotoxicity by Vibrio vulnificus. Diagnostic Microb. Infect Dis 5:99–111
Packard TT, Williams PJ, Le B (1981) Rates of respiratory oxygen consumption and electron transport in surface seawater from the northwest Atlantic Ocean. Oceanol Acta 4:351–358
Pollard PC, Moriarty DJW (1984) Validity of the tritiated thymidine methods for estimating bacteria growth rates: measurement of isotope dilution during DNA synthesis. Appl Envir Microbiol 4:1076–1083
Porter KG, Feig YS (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol Oceanogr 25:943–948
Pruzzo C, Vezzulli L, Colwell RR (2008) Global impact of Vibrio cholerae interactions with chitin. Envir Microbiol 10(6):1400–1410
Pugnetti A, Del Negro P, Giani M, Acri F, Bernardi Aubry B, Bianchi F, Berto D, Valeri A (2010) Phytoplankton–bacterioplankton interaction and carbon fluxes trough microbial communities in the microtidial lagoon (Lagoon of Venice, Northern Italy) FEMS Microb Ecol:1-12
Smith DC, Azam F (1992) A simple, economical method for measuring bacterial protein synthesis rates in seawater using 3H-leucine. Mar Microb Food Webs 6:107–114
Staley C, Reckhow KH, Lukasik J, Harwood VJ (2012) Assessment of source of human pathogens and fecal contamination in a Florida freshwater lake. Wat Res 46:5799–5812
Strickland JD, Parsons TR (1972) A manual of seawater analysis. Canada Fish Res Board Bull 167:310
Thomson FL, Iida T, Swings J (2004) Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:403–431
Turner JW, Good B, Cole D, Lipp EK (2009) Plankton composition and environmental factors contribute to Vibrio seasonality. ISME J 3(9):1082–1092
Vezzulli L, Brettar I, Pezzati E, Reid PC, Colwell RR, Hofle MG, Pruzzo C (2011) Long-term effects of ocean warming on the prokaryotic community: evidence from the vibrios. ISME J 1-10
Zaccone R, Crisafi E, Genovese L (1992) Ecology of vibrios in the Oliveri Tindari lagoon (Messina) two-year study. PSZN: Mar Ecol 13(2):149–161
Zaccone R, Caruso G (2002) Microbial hydrolysis of polysaccharides and organic phosphates in the northern Adriatic Sea. Chem Ecol 18(1, 2):85–94
Zaccone R, Caruso G, Calì C (2002) Heterotrophic bacteria in the Northern Adriatic Sea: seasonal changes and enzyme profile. Mar Env Res 54(1):1–19
Zaccone R, Monticelli LS, Seritti A, Santinelli C, Azzaro M, Boldrin A, La Ferla R, Ribera d’Alcalà M (2003) Bacterial processes in the intermediate and deep layers of the Ionian Sea in winter 1999: vertical profiles and their relationship to the different water masses. J Geophys Res 108(C9):8117
Zaccone R, Azzaro M, Caroppo C, La Ferla R, Zampino D, Caruso G, Leonardi M, Maimone G, Sitran R (2004) Deep-chlorophyll maximum time series in the Augusta Gulf (Ionian Sea): microbial community structures and functions. Chem Ecol 20(s1):S276–S284
Zaccone R, Caruso G, Azzaro M, Azzaro F, Crisafi E, Decembrini F, De Domenico E, De Domenico M, La Ferla R, Leonardi M, Lo Giudice A, Maimone G, Mancuso M, Michaud L, Monticelli LS, Raffa F, Ruggeri G, Bruni V (2010) Prokaryotic activities and abundance in pelagic areas of the Ionian Sea. Chem Ecol 26(S1):169–197
Zaccone R, Boldrin A, Caruso G, La Ferla R, Maimone G, Santinelli C, Turchetto M (2012) Enzymatic activities and prokaryotic abundance in relation to organic matter along a West–East Mediterranean transect (TRANSMED cruise). Microb Ecol 64(1):54–66
Acknowledgments
This study is a contribution to the international IMBER project. The work was supported by funds from the MIUR VECTOR (2006–2009) project: Vulnerability of the marine Ecosystems to Climate changes and Their role in the Mediterranean Carbon cycles. Line 4: DIVCOST, Activity 5.2, 5.4: Study of the effects of climate variations in the ecology of pathogenic species and mussel culture in brackish coastal environments of the Cape Peloro lagoon area. The authors are grateful to the technical staff of IAMC-CNR Messina: Mr. Francesco Soraci and Mr. Alessandro Cosenza for their assistance during sampling and data elaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaccone, R., Azzaro, M., Azzaro, F. et al. Seasonal Dynamics of Prokaryotic Abundance and Activities in Relation to Environmental Parameters in a Transitional Aquatic Ecosystem (Cape Peloro, Italy). Microb Ecol 67, 45–56 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0307-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0307-z