Abstract
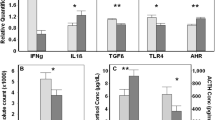
Harbor seals are exposed to increasing pressure caused by anthropogenic activities in their marine environment. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and trace elements are hazardous contaminants that accumulate in tissues of harbor seals. POPs and trace elements can negatively affect the immune-system and have been reported, e.g., to increase susceptibility to viral infections in seals. Biomarkers of the xenobiotic metabolism, cytokines, and heat-shock protein as cell mediators of the immune-system were established to evaluate the impact of environmental stressors on harbor seals. Harbor seals (n = 54) were captured on sandbanks in the North Sea during 2009–2012. Health assessments, including hematology, were performed, and RNAlater blood samples were taken and analyzed using quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Normalized transcript copy numbers were correlated to hematology and POP concentration in blood and trace metals in blood and fur. A significant correlation between xenobiotic markers and contaminant burden was found. Significant interrelationships between markers and POP compounds, as well as with season, weight, and hematology values, indicate that biomarkers reflect pollutant exposure and effects. A significant relationship between cortisol levels and heat-shock protein expression was observed indicating stress experienced during restraint of the seals. Interleukin-10 transcription showed significant correlations with trace elements in fur pointing toward immune regulatory effects of metal exposure. The molecular markers prove to be an important noninvasive tool that reflects contaminant exposure and the impact of anthropogenic stressors in seal species. The connection between interleukin-2, xenobiotic markers, and pollutants may indicate immune suppression in animals exposed to contaminants with subsequent susceptibility to inflammatory disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkahem HF (1994) The toxicity of nickel and the effects of sublethal levels on haematological parameters and behaviour of the fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 45:215–217
Aubail A, Teilmann J, Dietz R, Rigét F, Harkonen T, Karlsson O et al (2011) Investigation of mercury concentrations in fur of phocid seals using stable isotopes as tracers of trophic levels and geographical regions. Pollut Biol 34(9):1411–1420
Barouki R, Coumoul X, Fernandez-Salguero PM (2007) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor, more than a xenobiotic-interacting protein. FEBS Lett 581(19):3608–3615
Behr A, Wargel A, Siebert U, Hellwig V (2008) Analysis of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-induced modification of protein expression in primary hepatocytes from harbour seals. Organohal Comp 70:1079–1082
Beineke A, Siebert U, Muller G, Baumgartner W (2007) Increased blood Interleukin-10 mRNA levels in diseased free-ranging harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). Vet Immunol Immunopathol 115:100–106
Bodewes R, Bestebroer TM, van der Vries E, Verhagen JH, Herfst S, Koopmans MP et al (2015) Avian influenza A(H10N7) virus–associated mass deaths among harbor seals. Emerg Infect Dis 21:720
Borcard D, Gillet F, Legendre P (2011) Numerical ecology with R. Springer, New York
Bossart GD (2006) Marine mammals as sentinel species for oceans and human health. Oceanogr Mar Biol 19(2):134–137
Boyman O, Sprent J (2012) The role of interleukin-2 during homeostasis and activation of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 12:180–190
Brouwer A, Reijnders PJH, Koeman JH (1989) Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-contaminated fish induces vitamin A and thyroid hormone deficiency in the common seal (Phocavitulina). Aquat Toxicol l15(1):99–105
Burns JJ (2002) Harbor seal and spotted seal. In: Perrin WF, Würsig B, Thewissen JGM (eds) Encyclopedia of marine mammals. Academic, San Diego, pp 552–560
Byers RJ, Hoyland JA, Dixon J, Freemont AJ (2000) Subtractive hybridization–genetic takeaways and the search for meaning. Int J Exp Pathol 81(6):391–404
Caicedo MS, Pennekamp PH, McAllister K, Jacobs JJ, Hallab NJ (2010) Soluble ions more than particulate cobalt-alloy implant debris induce monocyte costimulatory molecule expression and release of proinflammatory cytokines critical to metal-induced lymphocyte reactivity. J Biomed Mater Res A 93(4):1312–1321
Chen T, Cao X (2010) Stress for maintaining memory: HSP70 as a mobile messenger for innate and adaptive immunity. Eur J Immunol 40(6):1541–1544
Chopra M, Schrenk D (2011) Dioxin toxicity, aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling, and apoptosis-persistent pollutants affect programmed cell death. Crit Rev Toxicol 41(4):292–320
Common Wadden Sea Secretariat (2014) Abkommen zur Erhaltung der Seehunde im Wattenmeer. http://www.bfn.de/0302_cwss.html. Accessed 10 Aug 2014
Das K, Debacker V, Pillet S, Bouquegneau JM (2003) Heavy metals in marine mammals. In: Vos JG, Bossart GD, Fournier M, O’Shea TJ (eds) Toxicology of marine mammals. Taylor & Francis, London, pp 135–167
Das K, Siebert U, Gillet A, Dupont A, Di-Poï C, Fonfara S et al (2008) Mercury immune toxicity in harbour seals: links to in vitro toxicity. Environ Health 7(1):52
De Maio A (1995) The heat-shock response. New Horiz 3(2):198–207
De Swart RL, Ross PS, Vedder LJ, Boink FBTJ, Reijnders PJH, Mulder PGH et al (1995) Hematology and clinical chemistry values for harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) fed environmentally contaminated herring remain within normal ranges. Can J Zool 73:2035–2043
Debier C, Pomeroy PP, Dupont C, Joiris C, Comblin V, Le Boulengé E et al (2003) Quantitative dynamics of PCB transfer from mother to pup during lactation in UK grey seals Halichoerus grypus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 247:237–248
Debier C, Chalon C, Le Bœuf BJ, de Tillesse T, Larondelle Y, Thomé JP (2006) Mobilization of PCBs from blubber to blood in northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris) during the post-weaning fast. Aquat Toxicol 80(2):149–157
Dierauf LA, Gulland FMD (eds) (2001) CRC handbook of marine mammal medicine, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Dirtu AC, Jaspers VLB, Cernat R, Gheorghe A, Neels H, Covaci A (2010) Hydroxylated and neutral persistent organic pollutants in human serum from Belgium and Romania. Environ Sci Technol 44:2876–2883
Dougherty EJ, Pollenz RS (2008) Analysis of Ah receptor-ARNT and Ah receptor-ARNT2 complexes in vitro and in cell culture. Toxicol Sci 103(1):191–206
Dupont A, De Pauw-Gillet MC, Schnitzler J, Siebert U, Das K (2015) Effects of methylmercury on harbour seal peripheral blood leucocytes in vitro studied by electron microscopy. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00244-015-0207-y
Dupont A, Siebert U, Covaci A, Weijs L, Eppe G, Debier C et al (2013) Relationships between in vitro lymphoproliferative responses and levels of contaminants in blood of free-ranging adult harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) from the North Sea. Aquat Toxicol 142:210–220
Fonfara S, Kakuschke A, Rosenberger T, Siebert U, Prange A (2008) Cytokine and acute phase protein expression in blood samples of harbor seal pups. Mar Biol 155:337–345
Fossi MC, Panti C, Marsili L, Maltese S, Coppola D, Jimenez B et al (2014) Could feeding habit and migratory behaviour be the causes of different toxicological hazard to cetaceans of Gulf of California (Mexico)? Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(23):13353–13366
Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Kawajiri K (2010) Molecular mechanisms of the physiological functions of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor, a multifunctional regulator that senses and response to environmental stimuli. Prog Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 86:40–53
Griesel S, Kakuschke A, Siebert U, Prange A (2008) Trace element concentrations in blood of harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) from the Wadden Sea. Sci Total Environ 392(2):313–323
Habran S, Debier C, Crocker DE, Houser DS, Das K (2011) Blood dynamics of mercury and selenium in northern elephant seals during the lactation period. Environ Pollut 159(10):2523–2529
Habran S, Pomeroy PP, Debier C, Das K (2013) Changes in trace elements during lactation in a marine top predator, the grey seal. Aquat Toxicol 126:455–466
Hammil MO (2002) Earless seals. In: Perrin WF, Würsig B, Thewissen JGM (eds) Encyclopedia of marine mammals. Academic, San Diego, pp 352–358
Harwood J (2001) Marine mammals and their environment in the twenty-first century. J Mammal 82(3):630–640
HELCOM (2013). http://helcom.fi/Recommendations/Rec%2027-28-2.pdf#search=harbor%20seal. Accessed 10 Aug 2014
Hellwig V (2011) Effects of persistent pollutants on marine mammals. In: Quante M, Ebinghaus R, Flöser G (eds) Persistent pollution—past, present and future. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 337–362
Hyvärinen H, Sipilä T (1984) Heavy metals and high pup mortality in the Saimaa ringed seal population in eastern Finland. Mar Pollut Bull 15(9):335–337
Jensen T, van de Bildt M, Dietz HH, Andersen TH, Hammer AS, Kuiken T et al (2002) Another phocine distemper outbreak in Europe. Science 297(5579):209
Kakuschke A, Prange A (2007) The influence of metal pollution on the immune system a potential stressor for marine mammals in the North Sea. Int J Comp Psychol 20:179–193
Kakuschke A, Valentine-Thon E, Fonfara S, Griesel S, Siebert U, Prange A (2006) Metal sensitivity of marine mammals: a case study of a gray seal (Halichoerus grypus). Mar Mamm Sci 22(4):985–996
Kakuschke A, Valentine-Thon E, Fonfara S, Griesel S, Rosenberger T, Siebert U et al (2008) Metal-induced impairment of the cellular immunity of newborn harbor seals (Phoca vitulina). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55(1):129–136
Kiremidjian-Schumacher L, Roy M, Wishe HI, Cohen MW, Stotzky G (1990) Selenium and immune cell functions. I. Effect on lymphocyte proliferation and production of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Exp Biol Med 193(2):136–142
Kok JB, Roelofs RW, Giesendorf BA, Pennings JL, Waas ET, Feuth T et al (2005) Normalization of gene expression measurements in tumor tissues: comparison of 13 endogenous control genes. Lab Invest 85(1):154–159
Korff V, Wargel A, Lehnert K, Siebert U, Hellwig V (unpublished data) Studies of cellular toxicity of PCBs and PFOS on primary hepatocytes from harbor seals (Phoca vitulina)
Lehnert K, Müller S, Weirup L, Ronnenberg K, Pawliczka I, Rosenberger T et al (2014) Molecular biomarkers in grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) to evaluate pollutant exposure, health and immune status. Mar Pollut Bull 88(1):311–318
Lyche JL, Nourizadeh-Lillabadi R, Almaas C, Stavik B, Berg V, Skåre JU et al (2010) Natural mixtures of persistent organic pollutants (POP) increase weight gain, advance puberty, and induce changes in gene expression associated with steroid hormones and obesity in female zebrafish. J Toxicol Environ Health A 73(15):1032–1057
Müller G, Wohlsein P, Beineke A, Haas L, Greiser-Wilke I, Siebert U et al (2004) PhocineDistemper in German Seals, 2002. Emerg Infect Dis 10(4):723–725
Müller S, Lehnert K, Seibel H, Driver J, Ronnenberg K, Teilmann J et al (2013) Evaluation of immune and stress status in harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena): can hormones and mRNA expression levels serve as indicators to assess stress? BMC Vet Res 9(1):145
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre PR, O’Hara RB et al. (2013) Vegan: Community Ecology Package. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Reddy ML, Dierauf LA, Gulland FMD (2001) Marine mammals as sentinels of ocean health. CRC handbook of marine mammal medicine, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 3–13
Ronald K, Tessaro SV, Uthe JF, Freeman HC, Frank R (1977) Methylmercury poisoning in the harp seal (Pagophilus groenlandicus). Sci Total Environ 8(1):1–11
Ross P, De Swart R, Addison R, van Loveren H, Vos J, Osterhaus A (1996) Contaminant-induced immunotoxicity in harbor seals: WILDLIFE at risk? Toxicology 112(2):157–169
Siebert U, Joiris C, Holsbeek L, Benke H, Failing K, Frese K et al (1999) Potential relation between mercury concentrations and necropsy findings in cetaceans from German waters of the North and Baltic seas. Mar Pollut Bull 38(4):285–295
Siebert U, Müller S, Gilles A, Sundermeyer J, Narberhaus I (2012) Species profiles marine mammals. In: Narberhaus I, Krause J, Bernitt U (eds) Threatened biodiversity in the German North and Baltic Seas—sensitivities towards human activities and the effects of climate change. Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, Bonn, pp 447–509
Sormo EG, Skaare JU, Jussi I, Jussi M, Jenssen BM (2003) Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in Baltic and Atlantic gray seal (Halichoerus grypus) pups. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2789–2799
Tabuchi M, Veldhoen N, Dangerfield N, Jeffries S, Helbing CC, Ross PS (2006) PCB-related alteration of thyroid hormones and thyroid hormone receptor gene expression in free-ranging harbor seals (Phoca vitulina). Environ Health Perspect 114(7):1024–1031
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/
Teigen SW, Andersen RA, Daae HL, Skaare JU (1999) Heavy metal content in liver and kidneys of grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) in various life stages correlated with metallothionein levels: some metal-binding characteristics of this protein. Environ Toxicol Chem 18(10):364–2369
van Raalte DH, Li M, Pritchard PH, Wasan KM (2004) Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR)-alpha: a pharmacological target with a promising future. Pharm Res 21(9):1531–1538
Vinther M, Larse F (2004) Updated estimates of harbor porpoise (Phocoenaphocoena) bycatch in the Danish North Sea bottom-set gillnet fishery. J Cetacean Res Manag 6:19–24
Waterman B, Siebert U, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Oehlmann J (2003) Endokrine Effekte durch Tributylzinn (TBT). In: Lozan JL, Rachor E, Reise K, Sündermann JV, Westernhagen H (eds) Warnsignale aus Nordsee und Wattenmeer. Eine Aktuelle Umweltbilanz, Hamburg, pp 239–247
Weijs L, Das K, Siebert U, van Elk N, Jauniaux T, Neels H et al (2009a) PCBs, PBDEs and their hydroxylated metabolites in serum of free-ranging harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) and harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena): levels and profiles. Environ Int 35:842–850
Weijs L, Dirtu AC, Das K, Gheorghe A, Reijnders PJ, Neels H et al (2009b) Inter-species differences for polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in marine top predators from the Southern North Sea: part 1. accumulation patterns in harbor seals and harbor porpoises. Environ Pollut 157(2):437–444
Weirup L, Müller S, Ronnenberg K, Rosenberger T, Siebert U, Lehnert K (2013) Immune-relevant and new xenobiotic molecular biomarkers to assess anthropogenic stress in seals. Mar Environ Res 92:43–51
Wenzel C, Adelung D, Kruse H, Wassermann O (1993) Trace-metal accumulation in hair and skin of the harbor seal, Phoca vitulina. Mar Pollut Bull 26:152–155
Willett KL, Ulrich EM, Hites RA (1998) Differential toxicity and environmental fates of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers. Environ Sci Technol 32(15):2197–2207
Wolkers H, Lydersen C, Kovacs KM (2004) Accumulation and lactational transfer of PCBs and pesticides in harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) from Svalbard, Norway. Sci Total Environ 319(1):137–146
Yee TW (2014) VGAM: Vector Generalized Linear and Additive Models. R packageversion 0.9-4. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=VGAM
Zhou H, Qu Y, Wu H, Liao C, Zheng J, Diao X et al (2010) Molecular phylogenies and evolutionary behavior of AhR (aryl hydrocarbon receptor) pathway genes in aquatic animals: implications for the toxicology mechanism of some persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Chemosphere 78(2):193–205
Zohari S, Neimanis A, Härkönen T, Moraeus C, Valarcher JF, Dabrera G et al. (2014) Avian influenza A (H10N7) virus involvement in mass mortality of harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) in Sweden, March through October 2014. Eurosurveillance 19(46):1–6. http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20967
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all volunteers, in particular, seal hunters in Schleswig–Holstein, for conducting seal catches. The authors thank all individuals who helped with the blood-sampling protocol on the sandbank and in the laboratory. The authors are grateful to Sven Würtz for his advice on qPCR methodology. K. Das is a F.R.S.-FNRS Research Associate. This article is a MARE publication 301. The authors are grateful to C. Brochoire and M. Chambosse (Ulg) for their help in trace element analyses. The seal capture was performed under the funding of the Ministry of Renewable Energies, Agriculture, Environment and Rural Areas of Schleswig–Holstein and Schleswig–Holstein’s Government-Owned Company for Coastal Protection, National Parks and Ocean Protection, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehnert, K., Ronnenberg, K., Weijs, L. et al. Xenobiotic and Immune-Relevant Molecular Biomarkers in Harbor Seals as Proxies for Pollutant Burden and Effects. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 70, 106–120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0202-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0202-3