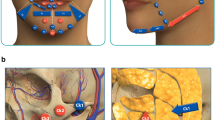
Abstract
There has been an upsurge in the technology of injectable volumetric filler materials for soft tissue augmentation of the face in the past decade. This is a dynamic field that has provided plastic surgeons and dermatologists who treat the aging face with newer tools and techniques. Injectable volumetric fillers can be applied in a variety of combinations and can be added to the various surgical options in conjunction with surgery or as maintenance following surgery. In practice, there are essentially four classes of materials that may be considered gold standard for minimally invasive rejuvenation and beautification of the face: botulinum toxin A, autologous fat, derivatives of hyaluronic acid, and, to a limited extent, hydroxyapatite. These coincide with the philosophy of applying materials and devices associated with the least amount of risk. Long lasting, or permanent–nondegradable, nonextractable, and nonabsorbable fillers remain an unresolved controversial issue, as the longer lasting the device, the greater also is the likelihood for long-term or even irreversible complications. The current trend for nonsurgical minimally invasive procedures for beautifying the face will most probably continue to surge, in light of their affordability in the growing economies around the globe, the increasing demand for a youthful look, and the need for less downtime for these procedures. There will be a rising demand for more hi-tech (bio- or genetically engineered) safe fillers with higher purity and less immunogenicity that allow a short recuperation time in order to attain a product that will serve as an ideal injectable volumetric filler for soft tissue augmentation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alster TS, West TB (2000) Human-derived and new synthetic injectable materials for soft-tissue augmentation: current status and role in cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 105(7):2515–2525 discussion 2526–2528. Review. doi:10.1097/00006534-200006000-00034
Andre P, Lowe NJ, Parc A, Clerici TH, Zimmermann U (2005) Adverse reactions to dermal fillers: a review of European experiences. J Cosmet Laser Ther 7(3–4):171–176 doi:10.1080/14764170500344393
Ashinoff R (2000) Overview: soft tissue augmentation. Clin Plast Surg 27:479–487 Review
Beljaards RC, de Roos KP, Bruins FG (2005) NewFill for skin augmentation: a new filler or a failure. Dermatol Surg 31:772–776
Bergeret-Galley C, Latouche X, Illouz YG (2001) The value of a new filler material in corrective and cosmetic surgery: DermaLive and DermaDeep. Aesthetic Plast Surg 25:249–255 doi:10.1007/s002660010131
Bigata X, Ribera M, Bielsa I, Ferrandiz C (2001) Adverse granulamatous reaction after cosmetic dermal silicone injection. Dermatol Surg 27:198–200 doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00020.x
Blitzer A, Brin MF, Keen MS, Aviv JE (1993) Botulinum toxin for the treatment of hyperfunctional lines of the face. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119:1018–1022
Butterwick KJ, Lack EA (2003) Facial volume restoration with the fat autograft muscle injection technique. Dermatol Surg 29:1019–1026 doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29294.x
Carraway JH, Mellow CG (1990) Syringe aspiration and fat concentration: a simple technique of autologous fat injection. Ann Plast Surg 24:293–296 doi:10.1097/00000637-199003000-00018
Carruthers A, Carruthers J (2001) Botulinum toxin type A: history and current cosmetic use in the upper face. Semin Cutan Med Surg 20:71–84 doi:10.1053/sder.2001.25138
Carruthers JD, Carruthers JA (1992) Treatment of glabellar frown lines with C. botulinum-A exotoxin. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 18:17–21
Carruthers J, Fagien S, Matarasso SL, Botox Consensus Group (2004) Consensus recommendations on the use of botulinum toxin type A in facial aesthetics. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(6)(Suppl):1S–22S doi:10.1097/01.PRS.0000144795.76040.D3
Christensen L, Breiting V, Janssen M, Vuust J, Hogdall E (2005) Adverse reactions to injectable soft tissue permanent fillers. Aesthetic Plast Surg 29:34–48 doi:10.1007/s00266-004-0113-6
Claoue BL, Rabineau P (2004) The polyalkylimide gel: experience with Bio-Alcamid™. Semin Cutan Med Surg 23:236–240 doi:10.1016/j.sder.2004.08.001
Coleman SR (2006) Facial augmentation with structural fat grafting. Clin Plast Surg 33:567–577 doi:10.1016/j.cps.2006.09.002
Coleman SR (1997) Facial recontouring with lipostructure. Clin Plast Surg 24:347–367
Coleman SR (2001) Structural fat grafts: the ideal filler? Clin Plast Surg 28:111–119
Coleman SR, Saboeiro AP (2007) Fat grafting to the breast revisited: safety and efficacy. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:775–785 doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000252001.59162.c9
de Maio M (2004) the minimal approach: an innovation in facial cosmetic procedures. Aesthetic Plast Surg 28:295–300 doi:10.1007/s00266-004-0037-1
De Ugarte DA, Ashjian PH, Elbarbary A et al (2003) Future of fat as raw material for tissue regeneration. Ann Plast Surg 50:215–219 doi:10.1097/01.SAP.0000029661.38066.15
Duffy DM (1990) Silicone: a critical review. Adv Dermatol 5:93–107
Duffy DM (2005) Liquid silicone for soft tissue augmentation. Dermatol Surg 31:1530–1541
Duranti F, Salti G, Bovani B, Calandra M, Rosati ML (1998) Injectable hyaluronic acid gel for soft tissue augmentation. A clinical and histological study. Dermatol Surg 24:1317–1325 doi:10.1016/S1076-0512(98)00151-4
Ellenbogen R (1986) Free autogenous pearl fat grafts in the face: a preliminary report of a rediscovered technique. Ann Plast Surg 16:179–194 doi:10.1097/00000637-198603000-00001
Ersek RA (1991) Transplantation of purified autologous fat: a 3-year follow up is disappointing. Plast Reconstr Surg 87:219–227
Ferreira MC, Salles AG, Giminez R, Soares MF (2004) Complications with the use of botulinum toxin type a in facial rejuvenation: report of 8 cases. Aesthetic Plast Surg 28:441–444 doi:10.1007/s00266-004-0031-7
Frankel AS, Kamer FM (1998) Chemical browlift. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124:321–323
Ghislanzoni M, Bianchi F, Barbareschi M, Alessi E (2006) Cutaneous granulomatous reaction to injectable hyaluronic acid gel. Br J Dermatol 154:755–758
Giovagnorio F, Drudi FM, Valentini C, Paonessa A (2004) Ultrasonography in follow-up of soft tissue augmentation of the face with synthetic materials: a pilot study. Acta Radiol 45:746–750 doi:10.1080/02841850410008207
Guerrerosantos J (2000) Long term outcome of sutologous fat transplantation in aesthetic facial recontouring. Clin Plast Surg 27:515–543
Guyuron B, Huddleston SW (1994) Aesthetic indications for botulinum toxin injection. Plast Reconstr Surg 93:913–918
Guyuron B, Majzoub RK (2007) Facial augmentation with core fat graft: a preliminary report. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:295–302 doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000264399.40701.71
Kanchwala SK, Holloway L, Bucky LP (2005) Reliable soft tissue augmentation: a clinical comparison of injectable soft-tissue fillers for facial-volume augmentation. Ann Plast Surg 55:30–35 doi:10.1097/01.sap.0000168292.69753.73
Karim RB, Hage JJ, van Rozelaar L, Lange CA, Raaijmakers J (2006) Complications of polyalkylimide 4% injections (Bio-Alcamid™): a report of 18 cases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:1409–1414 doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2006.01.049
Kaufman MR, Miller TA, Huang C et al (2007) Autologous fat transfer for facial recontouring: is there science behind the art. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:2287–2296 doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000260712.44089.e7
Klein AW (2001) Collagen substances. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 9:205–218, May
Klein AW (2006) Soft tissue augmentation 2006: filler fantasy. Dermatol Ther 19:129–133 doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2006.00066.x
Klein AW, Elson ML (2000) The history of substances for soft tissue augmentation. Dermatol Surg 26:1096–1105 doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2000.00512.x
Krandendonk S, Obagi S (2007) Autologous fat transfer for periorbital rejuvenation: indications, technique, and complications. Dermatol Surg 33:572–578 doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2007.33116.x
Kuran I, Tumerdem B (2005) A new simple method used to prepare fat for injection. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27:18–22 doi:10.1007/s00266-004-0059-8
Lahiri A, Waters R (2007) Experience with Bio-Alcamid, a new soft tissue endoprosthesis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60:663–667 doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2006.07.010
Lai et al (2003) Surgical treatment of facial siliconoma involving the temporal area. Plast Reconstr Surg 155:553–558
Lemperle G, Morhenn V, Charrier U (2003) Human histology and persistence of various injectable filler substances for soft tissue augmentation. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27:354–366 doi:10.1007/s00266-003-3022-1
Locke MB, de Chalain T (2008) Current practice in autologous fat transplantation. Suggested clinical guidelines based on a review of recent literature. Ann Plast Surg 60:98–102
Lohuis PJ, Watts SJ, Vuyk HD (2001) Augmentation of the nasal dorsum using Gore-Tex: intermediate results of a retrospective analysis of experience in 66 patients. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 26:214–217 doi:10.1046/j.1365-2273.2001.00453.x
Lombardi et al (2004) Orofacial granulomas after injection of cosmetic fillers. Histopathologic and clinical study of 11 cases. J Oral Pathol Med 33:115–120 doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.2004.00194.x
Lowe NJ, Maxwell CA, Patnaik R (2005) Adverse reactions to dermal fillers. Dermatol Surg 31(11 Pt 2):1616–1625. review
Manna F, Dentini M, Desideri P et al (1999) Comparative chemical evaluation of two commercially available derivatives of hyaluronic acid (hylaform from rooster combs and restylane from streptococcus) used for soft tissue augmentation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 13:183–192
Marmur ES, Phelps R, Goldberg DJ (2004) Clinical, histologic and electron microscopic findings after injection of a calcium hydroxylapatite filler. J Cosmet Laser Ther 6:223–226 doi:10.1080/147641704100003048
Matarasso SL (2007) Injectable collagens: lost but not forgotten-A review of products, indications, and injection techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(6)(Supplement):17S–26S doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000248802.65041.ff
Matarasso SL, Carruthers JD, Jewell ML, the Restylane Consensus Group (2006) Consensus recommendations for soft-tissue augmentation with nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid (Restylane). Plast Reconstr Surg 117(3)(Supplement):3S–34S doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000204759.76865.39
Missana MC, Laurent I, Barreau L, Balleyguier C (2007) Autologous fat transfer in reconstructive breast surgery: indications, technique and results. Eur J Surg Oncol 33:685–690 doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2006.12.002
Mizuno H, Zuk PA, Zhu M et al (2002) Myogenic differentiation by human processed lipoaspirate cells. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:199–209 doi:10.1097/00006534-200201000-00030
Murillo WL (2004) Buttock augmentation: case study of fat injection monitored by magnetic resonance imaging. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:1606–1614 doi:10.1097/01.PRS.0000138760.29273.5D
Narins RS, Beer K (2006) Liquid injectable silicone: a review of its history, immunology, technical considerations, complications, and potential. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(Suppl.):77S doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000234919.25096.67
Nelson L, Stewart KJ (2008) Plastic surgical options for HIV-associated lipodystrophy. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:359–365 doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2007.11.014
Nelson L, Stewart KJ (2008) Experience in the treatment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:366–371 doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2007.10.031
Neuber F (1893) Fett transplantation. Chir Kong Verhandl Deutsch Ges Chir 22:66–68
Niechajev I, Sevcuk O (1994) Long term results of fat transplantation: clinical and histological studies. Plast Reconstr Surg 94:496–506 doi:10.1097/00006534-199409000-00012
Nordstrom RE, Wang J, Fan J (1997) “Spaghetti” fat grafting: a new technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 99:917–918
Pacini S, Ruggiero M, Morucci G et al (2002) Bio-alcamid: a novelty for reconstructive and cosmetic surgery. Ital J Anat Embryol 107:209–214
Pinsolle V, Chichery A, Grolleau JL, Chavoin JP (2008) Autologous fat injection in Poland’s syndrome. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:784–791
Pitaru S, Noff M, Blok L, Nir E, Pitaru S, Goldlust A, Savion N (2007) Long-term efficacy of a novel ribose—cross-linked collagen dermal filler: a histologic and histomorphometric study in an animal model. Dermatol Surg 33:1045–1054 doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2007.33218.x
Ramon Y, Fodor L, Ullmann Y (2007) Preliminary experiences with Bio-Alcamid in HIV facial lipoatrophy. Dermatology 214:151–154
Raszewski R, Guyuron B, Lash RH, McMahon JT, Tuthill RJ (1990) A severe fibrotic reaction after cosmetic liquid silicone injection. A case report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 18:225–228 doi:10.1016/S1010-5182(05)80417-2
Rotunda AM, Narins RS (2006) Poly-L-lactic acid: a new dimension in soft tissue augmentation. Dermatol Ther 19:151–158 doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2006.00069.x
Sclafani AP, Romo T 3rd, Jacono AA, McCormick S, Cocker R, Parker A (2000) Evaluation of acellular dermal graft in sheet (AlloDerm) and injectable (micronized AlloDerm) forms for soft tissue augmentation. Clinical observations and histological analysis. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2:130–136 doi:10.1001/archfaci.2.2.130
Sclafani AP, McCornick SA, Cocker R (2002) Biophysical and microscopic analysis of homologous dermal and fascial materials for facial aesthetic and reconstructive uses. Arch Facial Plast Surg 4:164–171 doi:10.1001/archfaci.4.3.164
Shafir R, Amir A, Gur E (2000) Long-term complications of facial injections with Restylane (injectable hyaluronic acid). Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1215–1216 doi:10.1097/00006534-200010000-00048
Sidwell RU, Dhillon AP, Butlert PEM, Rustin MHA (2004) Localized granulamatous reaction to a semi-permanent hyaluronic acid and acrylic hydrogel cosmetic filler. Clin Exp Dermatol 29:630–632 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2004.01625.x
Sklar JA, White SM (2004) Radiance FN: a new soft tissue filler. Dermatol Surg 30:764–768 doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2004.30214.x
Spear SL, Wilson HB, Lockwood MD (2005) Fat injection to correct contour deformities in the reconstructed breast. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:1300–1305 doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000181509.67319.cf
Terino EO (2001) Alloderm acellular dermal graft: applications in aesthetic soft-tissue augmentation. Clin Plast Surg 28:83–99. Review
Tirakunwichcha S, Tulvatana W, Kulvichit K (2003) An unusual complication from esthetic injection of liquid silicone into the forehead. Am J Ophthalmol 136:944–945 doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(03)00465-3
Tzikas TL (2004) Lipografting: autologous fat grafting for total facial rejuvenation. Facial Plast Surg 20:135–143 doi:10.1055/s-2004-861754
Valdatta L, Thione A, Buoro M, Tuinder S (2001) A case of life-threatening sepsis after breast augmentation by fat injection. Aesthetic Plast Surg 25:347–349 doi:10.1007/s002660010147
Position VII Statement of IQUAM, the International Committee for Quality Assurance, Medical Technologies and Devices in Plastic Surgery, 15 July 2006, Regensburg, Germany. www.IQUAM.org
Zheng DN, Li QF, Lei H, Zheng SW (2008) Autologous fat grafting to the breast for cosmetic enhancement: experience in 66 patients with long-term follow up. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:792–798
Zocchi ML, Zuliani F (2008) Bicompartmental breast lipostructuring. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32:313–328 doi:10.1007/s00266-007-9089-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topaz, M. Injectable volumetric fillers and botulinum toxin in facial rejuvenation. Eur J Plast Surg 31, 281–291 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-008-0296-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-008-0296-1