Abstract
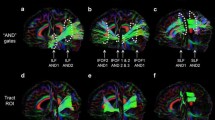
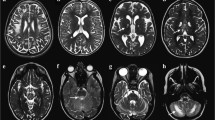
One of the morphological correlates of septo-optic dysplasia is hypoplasia of the optic nerves. As of now, it remains unknown, in how far this disorder also affects the organization of the optic radiation. Using diffusion- tensor imaging (DTI), the non-invasive evaluation of large fiber tracts including the optic radiation has become possible. We have compared DTI- data from a patient suffering from septo-optic dysplasia with those of a group of eleven healthy control subjects. The anisotropy showed statistically significant reduction in the patient with septo-optic dysplasia within the visual fiber tracts and an unordered eigenvector map. A comparison of the anisotropy in the pyramidal tract showed no significant difference. Since the patient was congenitally blind, it remains unclear whether the findings are the results of the underlying disorder or occur in all congenitally blind patients. One might presume, that, in order for the optic radiation to fully develop, an afferent input to the lateral geniculate body is necessarry.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stangel M, Vogeley KT, Jandeck C, Boeger F, Marx P, Koch HC (1998) Septooptische Dysplasie (de-Morsier-Syndrom). Nervenarzt 69:352–356
Melhem ER, Mori S, Mukundan G, Kraut MA, Pomper MG, van Zijl PC (1996) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Ching-Po Lin, Wen-Yih Isaac Tseng, Hui-Cheng Cheng Jyh-Horng Chen (2001) Validation of diffusion tensor magnetic resonances axonal fiber imaging with registered manganese-enhanced optic tracts. Neuroimage 14:1035–1047
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echos in the presence of a time dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:2808–2929
Buergel U, Schormann T, Schleicher A, Zilles K (1999) Mapping of histologically identified long fiber tracts in human cerebral hemispheres to the MRI-volume of a reference brain: Position and spatial variability of the optic radiation. Neuroimage 10:489–499
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, Di Chiro G (1996) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Beaulieu C, Allen PS (1994) Determinations of anisotropic water diffusion in nervers. Magn Reson Med 31:394–400
Hanyu H, Asano T, Ogawa K, Takasaki M, Shindo H, Kakizaki D, Abe K (1997) Age-related changes of diffusional anisotropy in the cerebral white matter in normal subjects. No To Shinkei. 49:331–336
Kinoshita Y, Ohnishi A, Kohshi K, Yokota A (1999) Apparent diffusion coefficient on rat brain and nerves intoxicated with methylmercury. Environ Res. 80:348–354
Cursiefen C, Holbach LM, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U, Naumann GO (2001) Persisting retinal ganglion cell axons in blind atrophic human eyes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 239:158–164
Chapman B (2000) Necessity for afferent activity to maintain eye-specific segregation in ferret lateral geniculate nucleus. Science 287:2479–2482
Yu-Xi F, Djupsund K, Hongfeng G, Hayden B, Kai S, Yang D (2002) Temporal specificity on the cortical plasticity of visual space representation. Science 296:1999–2003
Wahle P, Di Cristo G, Schwerdtfeger G, Engelhardt M, Berardi N, Maffei L (2003) Differential effects on cortical neurotropic factors on development of lateral geniculate nucleus and superior colliculus neurons: anterograde and retrograde actions. Development 130:611–622
Crowley JC, Katz LC (1999) Development of ocular dominance columns in absence of retinal input. Nat Neurosci. 2:1043–1045
Krings T, Coenen VA, Axer H, Moeller-Hartmann W, Mayfrank L, Weidemann J, et al (2001) Three-dimensional visualization of motor cortex and pyramidal tracts employing functional and diffusion weighted MRI. Methods, applications and limitations. Klin Neurorad 11:105–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoth, F., Krings, T. Diffusion- tensor imaging in septo-optic dysplasia. Neuroradiology 46, 759–763 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-004-1207-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-004-1207-1