Abstract
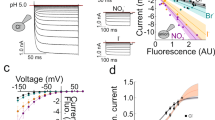
Plasma membrane γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporters (GATs) are electrogenic transport proteins that couple the cotranslocation of Na+, Cl−, and GABA across the plasma membrane of neurons and glia. A fundamental property of the transporter that determines its ability to concentrate GABA in cells and, hence, regulate synaptic and extra-synaptic GABA concentrations, is the ion/substrate coupling stoichiometry. Here, we scrutinized the currently accepted 2 Na+:1 Cl−:1 GABA stoichiometry because it is inconsistent with the measured net charge translocated per co-substrate (Na+, Cl−, and GABA). We expressed GAT1 and GAT3 in Xenopus laevis oocytes and utilized thermodynamic and uptake under voltage-clamp measurements to determine the stoichiometry of the GABA transporters. Voltage-clamped GAT1-expressing oocytes were internally loaded with GABA, and the reversal potential (V rev) of the transporter-mediated current was recorded at different external concentrations of Na+, Cl−, or GABA. The shifts in V rev for a tenfold change in the external Na+, Cl−, and GABA concentration were 84 ± 4, 30 ± 1, and 29 ± 1 mV, respectively. To determine the net charge translocated per Na+, Cl−, and GABA, we measured substrate fluxes under voltage clamp in cells expressing GAT1 or GAT3. Charge flux to substrate flux ratios were 0.7 ± 0.1 charge/Na+, 2.0 ± 0.2 charges/Cl−, and 2.1 ± 0.1 charges/GABA. Altogether, our results strongly suggest a 3 Na+:1 Cl−:1 GABA coupling stoichiometry for the GABA transporters. The revised stoichiometry has important implications for understanding the contribution of GATs to GABAergic signaling in health and disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen NJ, Káradóttir R, Attwell D (2004a) Reversal or reduction of glutamate and GABA transport in CNS pathology and therapy. Pflugers Arch 449:132–142
Allen NJ, Rossi DJ, Attwell D (2004b) Sequential release of GABA by exocytosis and reversed uptake leads to neuronal swelling in simulated ischemia of hippocampal slices. J Neurosci 24:3837–3849
Barakat L, Bordey A (2002) GAT-1 and reversible GABA transport in Bergmann glia in slices. J Neurophysiol 88:1407–1419
Belhage B, Hansen GH, Schousboe A (1993) Depolarization by K+ and glutamate activates different neurotransmitter release mechanisms in GABAergic neurons: vesicular versus non-vesicular release of GABA. Neuroscience 54:1019–1034
Bernath S, Zigmond MJ (1988) Characterization of [3H]GABA release from striatal slices: evidence for a calcium-independent process via the GABA uptake system. Neuroscience 27:563–570
Bertram S, Cherubino F, Bossi E, Castagna M, Peres A (2011) GABA reverse transport by the neuronal cotransporter GAT1: influence of internal chloride depletion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301:C1064–C1073
Bicho A, Grewer C (2005) Rapid substrate-induced charge movements of the GABA transporter GAT1. Biophys J 89:211–231
Blaustein MP, King AC (1976) Influence of membrane potential on the sodium-dependent uptake of γ-aminobutyric acid by presynaptic nerve terminals: experimental observations and theoretical considerations. J Membr Biol 30:153–173
Borden LA (1996) GABA transporter heterogeneity: pharmacology and cellular localization. Neurochem Int 29:335–356
Borden LA, Smith KE, Hartig PR, Branchek TA, Weinshank RL (1992) Molecular heterogeneity of the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transport system. Cloning of two novel high affinity GABA transporters from rat brain. J Biol Chem 267:21098–21104
Cammack JN, Schwartz EA (1996) Channel behavior in a γ-aminobutyrate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:723–727
Cammack JN, Rakhilin SV, Schwartz EA (1994) A GABA transporter operates asymmetrically and with variable stoichiometry. Neuron 13:949–960
Chen NH, Reith ME, Quick MW (2004) Synaptic uptake and beyond: the sodium- and chloride-dependent neurotransmitter transporter family SLC6. Pflugers Arch 447:519–531
Cherubino F, Bertram S, Bossi E, Peres A (2012) Pre-steady-state and reverse transport currents in the GABA transporter GAT1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302:C1096–C1108
Clark JA, Deutch AY, Gallipoli PZ, Amara SG (1992) Functional expression and CNS distribution of a β-alanine-sensitive neuronal GABA transporter. Neuron 9:337–348
Coady MJ, Wallendorff B, Bourgeois F, Charron F, Lapointe JY (2007) Establishing a definitive stoichiometry for the Na+/monocarboxylate cotransporter SMCT1. Biophys J 93:2325–2331
Conti F, Minelli A, Melone M (2004) GABA transporters in the mammalian cerebral cortex: localization, development and pathological implications. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 45:196–212
Conti F, Melone M, Fattorini G, Bragina L, Ciappelloni S (2011) A role for GAT-1 in presynaptic GABA homeostasis? Front Cell Neurosci 5:2
Dalby NO (2003) Inhibition of γ-aminobutyric acid uptake: anatomy, physiology and effects against epileptic seizures. Eur J Pharmacol 479:127–137
Dingledine R, Korn SJ (1985) γ-Aminobutyric acid uptake and the termination of inhibitory synaptic potentials in the rat hippocampal slice. J Physiol (Lond) 366:387–409
Focke PJ, Wang X, Larsson HP (2013) Neurotransmitter transporters: structure meets function. Structure 21:694–705
Gadea A, López-Colomé AM (2001) Glial transporters for glutamate, glycine, and GABA: II. GABA transporters. J Neurosci Res 63:461–468
Gallo V, Patrizio M, Levi G (1991) GABA release triggered by the activation of neuron-like non-NMDA receptors in cultured type 2 astrocytes is carrier-mediated. Glia 4:245–255
Gaspary HL, Wang W, Richerson GB (1998) Carrier-mediated GABA release activates GABA receptors on hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 80:270–281
Gonzales AL, Lee W, Spencer SR, Oropeza RA, Chapman JV, Ku JY, Eskandari S (2007) Turnover rate of the γ-aminobutyric acid transporter GAT1. J Membr Biol 220:33–51
Gottesfeld Z, Elliott KA (1971) Factors that affect the binding and uptake of GABA by brain tissue. J Neurochem 18:683–690
Héja L, Nyitrai G, Kékesi O, Dobolyi A, Szabó P, Fiáth R, Ulbert I, Pál-Szenthe B, Palkovits M, Kardos J (2012) Astrocytes convert network excitation to tonic inhibition of neurons. BMC Biol 10:26
Isaacson JS, Solís JM, Nicoll RA (1993) Local and diffuse synaptic actions of GABA in the hippocampus. Neuron 10:165–175
Kanner BI (1978) Active transport of γ-aminobutyric acid by membrane vesicles isolated from rat brain. Biochemistry 17:1207–1211
Kanner BI, Schuldiner S (1987) Mechanism of transport and storage of neurotransmitters. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 22:1–38
Karakossian MH, Spencer SR, Gomez AQ, Padilla OR, Sacher A, Loo DD, Nelson N, Eskandari S (2005) Novel properties of a mouse γ-aminobutyric acid transporter (GAT4). J Membr Biol 203:65–82
Katayama Y, Widdicombe JH (1991) Halide transport in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 443:587–599
Kavanaugh MP, Arriza JL, North RA, Amara SG (1992) Electrogenic uptake of γ-aminobutyric acid by a cloned transporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem 267:22007–22009
Keros S, Hablitz JJ (2005) Subtype-specific GABA transporter antagonists synergistically modulate phasic and tonic GABAA conductances in rat neocortex. J Neurophysiol 94:2073–2085
Keynan S, Kanner BI (1988) γ-Aminobutyric acid transport in reconstituted preparations from rat brain: coupled sodium and chloride fluxes. Biochemistry 27:12–17
Keynan S, Suh YJ, Kanner BI, Rudnick G (1992) Expression of a cloned γ-aminobutyric acid transporter in mammalian cells. Biochemistry 31:1974–1979
Krause S, Schwarz W (2005) Identification and selective inhibition of the channel mode of the neuronal GABA transporter 1. Mol Pharmacol 68:1728–1735
Krishnamurthy H, Piscitelli CL, Gouaux E (2009) Unlocking the molecular secrets of sodium-coupled transporters. Nature 459:347–355
Kristensen AS, Andersen J, Jørgensen TN, Sørensen L, Eriksen J, Loland CJ, Strømgaard K, Gether U (2011) SLC6 neurotransmitter transporters: structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Rev 63:585–640
Kuhar MJ, Zarbin MA (1978) Synaptosomal transport: a chloride dependence for choline, GABA, glycine and several other compounds. J Neurochem 31:251–256
Liu QR, López-Corcuera B, Mandiyan S, Nelson H, Nelson N (1993) Molecular characterization of four pharmacologically distinct γ-aminobutyric acid transporters in mouse brain. J Biol Chem 268:2106–2112
Loo DD, Eskandari S, Boorer KJ, Sarkar HK, Wright EM (2000) Role of Cl- in electrogenic Na+-coupled cotransporters GAT1 and SGLT1. J Biol Chem 275:37414–37422
Lu CC, Hilgemann DW (1999a) GAT1 (GABA:Na+:Cl-) cotransport function. Steady state studies in giant Xenopus oocyte membrane patches. J Gen Physiol 114:429–444
Lu CC, Hilgemann DW (1999b) GAT1 (GABA:Na+:Cl-) cotransport function. Kinetic studies in giant Xenopus oocyte membrane patches. J Gen Physiol 114:445–457
Mager S, Naeve J, Quick M, Labarca C, Davidson N, Lester HA (1993) Steady states, charge movements, and rates for a cloned GABA transporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron 10:177–188
Mager S, Kleinberger-Doron N, Keshet GI, Davidson N, Kanner BI, Lester HA (1996) Ion binding and permeation at the GABA transporter GAT1. J Neurosci 16:5405–5414
Martin DL (1973) Kinetics of the sodium-dependent transport of gamma-aminobutyric acid by synaptosomes. J Neurochem 21:345–356
Martin DL, Smith AA 3rd (1972) Ions and the transport of gamma-aminobutyric acid by synaptosomes. J Neurochem 19:841–855
Matskevitch I, Wagner CA, Stegen C, Bröer S, Noll B, Risler T, Kwon HM, Handler JS, Waldegger S, Busch AE, Lang F (1999) Functional characterization of the betaine/γ-aminobutyric acid transporter BGT-1 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem 274:16709–16716
Matthews E Jr, Rahnama-Vaghef A, Eskandari S (2009) Inhibitors of the γ-aminobutyric acid transporter 1 (GAT1) do not reveal a channel mode of conduction. Neurochem Int 55:732–740
Meinild AK, Forster IC (2012) Using lithium to probe sequential cation interactions with GAT1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302:C1661–C1675
Milanese M, Romei C, Usai C, Oliveri M, Raiteri L (2014) A new function for glycine GlyT2 transporters: stimulation of γ-aminobutyric acid release from cerebellar nerve terminals through GAT1 transporter reversal and Ca2+-dependent anion channels. J Neurosci Res 92:398–408
Moscowitz JA, Cutler RW (1980) Bidirectional movement of γ-aminobutyric acid in rat spinal cord slices. J Neurochem 35:1394–1399
Nelson N (1998) The family of Na+/Cl− neurotransmitter transporters. J Neurochem 71:1785–1803
Nelson H, Mandiyan S, Nelson N (1990) Cloning of the human brain GABA transporter. FEBS Lett 269:181–184
O’Malley DM, Sandell JH, Masland RH (1992) Co-release of acetylcholine and GABA by the starburst amacrine cells. J Neurosci 12:1394–1408
Omoto JJ, Maestas MJ, Rahnama-Vaghef A, Choi YE, Salto G Jr, Sanchez RV, Anderson CM, Eskandari S (2012) Functional consequences of sulfhydryl modification of the γ-aminobutyric acid transporter 1 at a single solvent-exposed cysteine residue. J Membr Biol 245:841–857
Overstreet LS, Westbrook GL (2003) Synapse density regulates independence at unitary inhibitory synapses. J Neurosci 23:2618–2626
Overstreet LS, Jones MV, Westbrook GL (2000) Slow desensitization regulates the availability of synaptic GABAA receptors. J Neurosci 20:7914–7921
Owe SG, Marcaggi P, Attwell D (2006) The ionic stoichiometry of the GLAST glutamate transporter in salamander retinal glia. J Physiol (Lond) 577:591–599
Penmatsa A, Gouaux E (2014) How LeuT shapes our understanding of the mechanisms of sodium-coupled neurotransmitter transporters. J Physiol (Lond) 592:863–869
Pin JP, Bockaert J (1989) Two distinct mechanisms, differentially affected by excitatory amino acids, trigger GABA release from fetal mouse striatal neurons in primary culture. J Neurosci 9:648–656
Radian R, Kanner BI (1983) Stoichiometry of sodium- and chloride-coupled γ-aminobutyric acid transport by synaptic plasma membrane vesicles isolated from rat brain. Biochemistry 22:1236–1241
Ransom CB, Tao W, Wu Y, Spain WJ, Richerson GB (2013) Rapid regulation of tonic GABA currents in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 109:803–812
Rasola A, Galietta LJ, Barone V, Romeo G, Bagnasco S (1995) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a GABA/betaine transporter from human kidney. FEBS Lett 373:229–233
Richerson GB, Wu Y (2003) Dynamic equilibrium of neurotransmitter transporters: not just for reuptake anymore. J Neurophysiol 90:1363–1374
Risso S, DeFelice LJ, Blakely RD (1996) Sodium-dependent GABA-induced currents in GAT1-transfected HeLa cells. J Physiol (Lond) 490(Pt 3):691–702
Romei C, Sabolla C, Raiteri L (2014) GABA release provoked by disturbed Na+, K+ and Ca2+ homeostasis in cerebellar nerve endings: roles of Ca2+ channels, Na+/Ca2+ exchangers and GAT1 transporter reversal. Neurochem Int 72:1–9
Roux MJ, Supplisson S (2000) Neuronal and glial glycine transporters have different stoichiometries. Neuron 25:373–383
Rudnick G (1998) Ion-coupled neurotransmitter transport: thermodynamic vs. kinetic determinations of stoichiometry. Meth Enzymol 296:233–247
Rudnick G, Krämer R, Blakely RD, Murphy DL, Verrey F (2014) The SLC6 transporters: perspectives on structure, functions, regulation, and models for transporter dysfunction. Pflugers Arch 466:25–42
Sacher A, Nelson N, Ogi JT, Wright EM, Loo DD, Eskandari S (2002) Presteady-state and steady-state kinetics and turnover rate of the mouse γ-aminobutyric acid transporter (mGAT3). J Membr Biol 190:57–73
Schwartz EA (1987) Depolarization without calcium can release γ-aminobutyric acid from a retinal neuron. Science 238:350–355
Skovstrup S, Taboureau O, Bräuner-Osborne H, Jørgensen FS (2010) Homology modelling of the GABA transporter and analysis of tiagabine binding. ChemMedChem 5:986–1000
Skovstrup S, David L, Taboureau O, Jørgensen FS (2012) A steered molecular dynamics study of binding and translocation processes in the GABA transporter. PLoS One 7:e39360
Solís JM, Nicoll RA (1992) Postsynaptic action of endogenous GABA released by nipecotic acid in the hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 147:16–20
Strasberg P, Elliott KA (1967) Further studies on the binding of γ-aminobutyric acid by brain. Can J Biochem 45:1795–1807
Taylor J, Gordon-Weeks PR (1991) Calcium-independent γ-aminobutyric acid release from growth cones: role of gamma-aminobutyric acid transport. J Neurochem 56:273–280
Thompson SM, Gähwiler BH (1992) Effects of the GABA uptake inhibitor tiagabine on inhibitory synaptic potentials in rat hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurophysiol 67:1698–1701
Wang D, Deken SL, Whitworth TL, Quick MW (2003) Syntaxin 1A inhibits GABA flux, efflux, and exchange mediated by the rat brain GABA transporter GAT1. Mol Pharmacol 64:905–913
Weinstein H, Varon S, Muhleman DR, Roberts E (1965) A carrier-mediated transfer model for the accumulation of 14C-γ-aminobutyric acid by subcellular brain particles. Biochem Pharmacol 14:273–288
Weiss JN (1997) The Hill equation revisited: uses and misuses. FASEB J 11:835–841
Whitlow RD, Sacher A, Loo DD, Nelson N, Eskandari S (2003) The anticonvulsant valproate increases the turnover rate of γ-aminobutyric acid transporters. J Biol Chem 278:17716–17726
Wu Y, Wang W, Richerson GB (2001) GABA transaminase inhibition induces spontaneous and enhances depolarization-evoked GABA efflux via reversal of the GABA transporter. J Neurosci 21:2630–2639
Wu Y, Wang W, Richerson GB (2003) Vigabatrin induces tonic inhibition via GABA transporter reversal without increasing vesicular GABA release. J Neurophysiol 89:2021–2034
Wu Y, Wang W, Richerson GB (2006) The transmembrane sodium gradient influences ambient GABA concentration by altering the equilibrium of GABA transporters. J Neurophysiol 96:2425–2436
Wu Y, Wang W, Díez-Sampedro A, Richerson GB (2007) Nonvesicular inhibitory neurotransmission via reversal of the GABA transporter GAT-1. Neuron 56:851–865
Yamashita A, Singh SK, Kawate T, Jin Y, Gouaux E (2005) Crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of Na+/Cl–dependent neurotransmitter transporters. Nature 437:215–223
Yazulla S, Kleinschmidt J (1983) Carrier-mediated release of GABA from retinal horizontal cells. Brain Res 263:63–75
Zomot E, Bendahan A, Quick M, Zhao Y, Javitch JA, Kanner BI (2007) Mechanism of chloride interaction with neurotransmitter:sodium symporters. Nature 449:726–730
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Donald Loo and Ms. Rachel Sanchez for carefully reading the manuscript, and Ms. Renee J. Estephan and Ms. Elizabeth Michaela Lizhar for technical assistance. This work was supported in part by a U.S. National Institute of General Medical Sciences Grant awarded to S.E. (SC1GM086344).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willford, S.L., Anderson, C.M., Spencer, S.R. et al. Evidence for a Revised Ion/Substrate Coupling Stoichiometry of GABA Transporters. J Membrane Biol 248, 795–810 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9797-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9797-6