Abstract
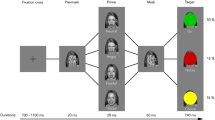
Studies indicate that explicit and implicit processing of affectively charged stimuli may be reflected in specific behavioral markers and physiological signatures. This study investigated whether the pleasantness ratings of a neutral target were affected by subliminal perception of pleasant and painful facial expressions. Participants were presented images depicting face of non-famous models being slapped (painful condition), caressed (pleasant condition) or touched (neutral condition) by the right hand of another individual. In particular, we combined the continuous flash suppression technique with the affective misattribution procedure (AMP) to explore subliminal empathic processing. Measures of pupil reactivity along with empathy traits were also collected. Results showed that participants rated the neutral target as less or more likeable congruently with the painful or pleasant facial expression presented, respectively. Pupil dilation was associated both with the implicit attitudes (AMP score) and with empathic concern. Thus, the results provide behavioral and physiological evidence that state-related empathic reactivity can occur at an entirely subliminal level and that it is linked to autonomic responses and empathic traits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida J, Pajtas PE, Mahon BZ, Nakayama K, Caramazza A (2013) Affect of the unconscious: visually suppressed angry faces modulate our decisions. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 13(1):94–101
Avenanti A, Bueti D, Galati G, Aglioti SM (2005) Transcranial magnetic stimulation highlights the sensorimotor side of empathy for pain. Nat Neurosci 8(7):955–960
Avenanti A, Minio-Paluello I, Bufalari I, Aglioti SM (2006) Stimulus-driven modulation of motor-evoked potentials during observation of others’ pain. Neuroimage 32(1):316–324
Avenanti A, Minio-Paluello I, Bufalari I, Aglioti SM (2009) The pain of a model in the personality of an onlooker: influence of state-reactivity and personality traits on embodied empathy for pain. Neuroimage 44(1):275–283
Avenanti A, Sirigu A, Aglioti SM (2010) Racial bias reduces empathic sensorimotor resonance with other-race pain. Curr Biol 20(11):1018–1022
Azevedo RT, Macaluso E, Avenanti A, Santangelo V, Cazzato V, Aglioti SM (2012) Their pain is not our pain: brain and autonomic correlates of empathic resonance with the pain of same and different race individuals. Hum Brain Mapp 34(12):3168–3181
Bernhardt BC, Singer T (2012) The neural basis of empathy. Annu Rev Neurosci 35:1–23
Bird G, Silani G, Brindley R, White S, Frith U, Singer T (2010) Empathic brain responses in insula are modulated by levels of alexithymia but not autism. Brain 133(Pt 5):1515–1525
Botvinick M, Jha AP, Bylsma LM, Fabian SA, Solomon PE, Prkachin KM (2005) Viewing facial expressions of pain engages cortical areas involved in the direct experience of pain. Neuroimage 25(1):312–319
Bradley MM, Miccoli L, Escrig MA, Lang PJ (2008) The pupil as a measure of emotional arousal and autonomic activation. Psychophysiology 45(4):602–607
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112(1):155–159
Davis MH (1980) A multidimensional approach to individual differences in empathy
Decety J, Jackson PL (2004) The functional architecture of human empathy. Behav Cogn Neurosci Rev 3(2):71–100
Dimberg U, Thunberg M, Elmehed K (2000) Unconscious facial reactions to emotional facial expressions. Psychol Sci 11(1):86–89
Duan X, Dai Q, Gong Q, Chen H (2010) Neural mechanism of unconscious perception of surprised facial expression. Neuroimage 52(1):401–407
Ekman P (1999) Facial expressions. Handb Cogn Emot 16:301–320
Flexas A, Rossello J, Christensen JF, Nadal M, Olivera La Rosa A, Munar E (2013) Affective priming using facial expressions modulates liking for abstract art. PLoS One 8(11):e80154
Garrido MI, Barnes GR, Sahani M, Dolan RJ (2012) Functional evidence for a dual route to amygdala. Curr Biol 22(2):129–134
Garvert MM, Friston KJ, Dolan RJ, Garrido MI (2014) Subcortical amygdala pathways enable rapid face processing. Neuroimage 102(P2):309–316
Glascher J, Adolphs R (2003) Processing of the arousal of subliminal and supraliminal emotional stimuli by the human amygdala. J Neurosci 23(32):10274–10282
Gobbini MI, Gors JD, Halchenko YO, Hughes HC, Cipolli C (2013) Processing of invisible social cues. Conscious Cogn 22(3):765–770
Green DM, Swets JA (1966) Signal detection theory and psychophysics, vol 1. Wiley, New York
Greenwald AG, Klinger MR, Schuh ES (1995) Activation by marginally perceptible (“subliminal”) stimuli: dissociation of unconscious from conscious cognition. J Exp Psychol Gen 124(1):22–42
Han S, Fan Y, Xu X, Qin J, Wu B, Wang X et al (2009) Empathic neural responses to others’ pain are modulated by emotional contexts. Hum Brain Mapp 30(10):3227–3237
Jiang Y, He S (2006) Cortical responses to invisible faces: dissociating subsystems for facial-information processing. Curr Biol 16(20):2023–2029
Killgore WD, Yurgelun-Todd DA (2004) Activation of the amygdala and anterior cingulate during nonconscious processing of sad versus happy faces. Neuroimage 21(4):1215–1223
LeDoux J (2003) The emotional brain, fear, and the amygdala. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23(4–5):727–738
Minio-Paluello I, Avenanti A, Aglioti SM (2006) Left hemisphere dominance in reading the sensory qualities of others’ pain? Soc Neurosci 1(3–4):320–333
Morris SB, DeShon RP (2002) Combining effect size estimates in meta-analysis with repeated measures and independent-groups designs. Psychol Methods 7(1):105–125
Murphy ST, Zajonc RB (1993) Affect, cognition, and awareness: affective priming with optimal and suboptimal stimulus exposures. J Pers Soc Psychol 64(5):723–739
Nosek BA, Hawkins CB, Frazier RS (2011) Implicit social cognition: from measures to mechanisms. Trends Cogn Sci 15(4):152–159
Partala T, Surakka V (2003) Pupil size variation as an indication of affective processing. Int J Hum Comput Stud 59(1):185–198
Pasley BN, Mayes LC, Schultz RT (2004) Subcortical discrimination of unperceived objects during binocular rivalry. Neuron 42(1):163–172
Payne BK, Cheng CM, Govorun O, Stewart BD (2005) An inkblot for attitudes: affect misattribution as implicit measurement. J Pers Soc Psychol 89(3):277–293
Payne BK, Hall DL, Cameron CD, Bishara AJ (2010) A process model of affect misattribution. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 36(10):1397–1408
Preston SD, de Waal FB (2002) Empathy: Its ultimate and proximate bases. Behav Brain Sci 25(1):1–20 discussion 20–71
Schachter S, Singer JE (1962) Cognitive, social, and physiological determinants of emotional state. Psychol Rev 69:379–399
Stein T, Senju A, Peelen MV, Sterzer P (2011) Eye contact facilitates awareness of faces during interocular suppression. Cognition 119(2):307–311
Tamietto M, de Gelder B (2009) Neural bases of the non-conscious perception of emotional signals. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(10):697–709
Tamietto M, Pullens P, de Gelder B, Weiskrantz L, Goebel R (2012) Subcortical connections to human amygdala and changes following destruction of the visual cortex. Curr Biol 22(15):1449–1455
Tsuchiya N, Koch C (2005) Continuous flash suppression reduces negative afterimages. Nat Neurosci 8(8):1096–1101
Tsuchiya N, Koch C, Gilroy LA, Blake R (2006) Depth of interocular suppression associated with continuous flash suppression, flash suppression, and binocular rivalry. J Vis 6(10):1068–1078
Vuilleumier P, Armony JL, Driver J, Dolan RJ (2001) Effects of attention and emotion on face processing in the human brain: an event-related fMRI study. Neuron 30(3):829–841
Whalen PJ, Kagan J, Cook RG, Davis FC, Kim H, Polis S et al (2004) Human amygdala responsivity to masked fearful eye whites. Science 306(5704):2061
Yang E, Zald DH, Blake R (2007) Fearful expressions gain preferential access to awareness during continuous flash suppression. Emotion 7(4):882–886
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the EU Information and Communication Technologies Grant (VERE Project, FP7-ICT-2009-5, Prot. Num. 257695) and the Italian Ministry of Health (Grant RF-2010-2312912).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiesa, P.A., Liuzza, M.T., Acciarino, A. et al. Subliminal perception of others’ physical pain and pleasure. Exp Brain Res 233, 2373–2382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4307-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4307-8