Abstract
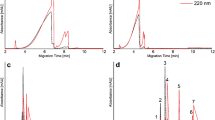
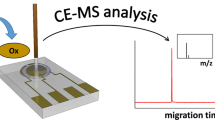
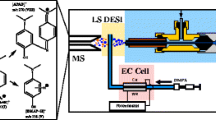
The online combination of capillary electrophoresis (CE) with mass spectrometry (MS) has long been desired for the capability of direct and simultaneous separation and detection with high efficiency, accuracy, and throughput. In this work, a novel CE-MS interface was developed, using dielectric barrier discharge ionization (DBDI). The interface employed a spray tip with a coaxial three-layer structure, into which the CE sample solution, the sheath liquid, and the nebulizing gas were introduced. The spray tip was put between the DBDI outlet and the MS inlet, thus the CE sample solution could be blended with the sheath liquid, then nebulized. The nebulized sample could be ionized by DBDI, and finally analyzed by MS. The key parameters of the interface were optimized. Then, proof-of-concept experiments separating and detecting the mixture of metronidazole and acetaminophen solutions were conducted. The results showed high separation efficiency, low time consumption, high reproducibility, and convenience in operation. In addition, the interface exhibited a high tolerance of non-volatile salts and surfactants, which would be widely used in CE analyses. All of these results demonstrated that the newly developed CE-DBDI-MS interface could be successfully used in CE-MS studies, and could be further utilized in multiple areas involving efficient separation and detection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harstad RK, Johnson AC, Weisenberger MM, Bowser MT. Capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 2016;88(1):299–319. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04125.
Olivares JA, Nguyen NT, Yonker CR, Smith RD. On-line mass spectrometric detection for capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 1987;59(8):1230–2.
Kleparnik K. Recent advances in the combination of capillary electrophoresis with mass spectrometry: from element to single-cell analysis. Electrophoresis. 2013;34(1):70–85. doi:10.1002/elps.201200488.
Lindenburg PW, Haselberg R, Rozing G, Ramautar R. Developments in interfacing designs for CE–MS: towards enabling tools for proteomics and metabolomics. Chromatographia. 2015;78(5–6):367–77. doi:10.1007/s10337-014-2795-5.
Heemskerk AA, Deelder AM, Mayboroda OA. CE-ESI-MS for bottom-up proteomics: advances in separation, interfacing and applications. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2016;35(2):259–71. doi:10.1002/mas.21432.
Hommerson P, Khan AM, de Jong GJ, Somsen GW. Ionization techniques in capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry: principles, design, and application. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2011;30(6):1096–120. doi:10.1002/mas.20313.
Kleparnik K. Recent advances in combination of capillary electrophoresis with mass spectrometry: methodology and theory. Electrophoresis. 2015;36(1):159–78. doi:10.1002/elps.201400392.
Monge ME, Harris GA, Dwivedi P, Fernandez FM. Mass spectrometry: recent advances in direct open air surface sampling/ionization. Chem Rev. 2013;113(4):2269–308. doi:10.1021/cr300309q.
Chang C, Xu G, Bai Y, Zhang C, Li X, Li M, et al. Online coupling of capillary electrophoresis with direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2013;85(1):170–6. doi:10.1021/ac303450v.
Zhang Y, Li X, Nie H, Yang L, Li Z, Bai Y, et al. Interface for online coupling of surface plasmon resonance to direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2015;87(13):6505–9. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01272.
Na N, Zhao M, Zhang S, Yang C, Zhang X. Development of a dielectric barrier discharge ion source for ambient mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2007;18(10):1859–62. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2007.07.027.
Na N, Zhang C, Zhao M, Zhang S, Yang C, Fang X, et al. Direct detection of explosives on solid surfaces by mass spectrometry with an ambient ion source based on dielectric barrier discharge. J Mass Spectrom: JMS. 2007;42(8):1079–85. doi:10.1002/jms.1243.
Gilbert-Lopez B, Geltenpoth H, Meyer C, Michels A, Hayen H, Molina-Diaz A, et al. Performance of dielectric barrier discharge ionization mass spectrometry for pesticide testing: a comparison with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and electrospray ionization. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom: RCM. 2013;27(3):419–29. doi:10.1002/rcm.6469.
Zhou Y, Wu Z, Li C, Wang N, Zhang X, Chen H, et al. Coupling neutral desorption sampling to dielectric barrier discharge ionization mass spectrometry for direct oil analysis. Anal Methods. 2014;6(5):1538. doi:10.1039/c3ay41817k.
Wolf JC, Schaer M, Siegenthaler P, Zenobi R. Direct quantification of chemical warfare agents and related compounds at low ppt levels: comparing active capillary dielectric barrier discharge plasma ionization and secondary electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2015;87(1):723–9. doi:10.1021/ac5035874.
Hayen H, Michels A, Franzke J. Dielectric barrier discharge ionization for liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009;81:10239–45. doi:10.1021/ac902176k.
Gilbert-Lopez B, Garcia-Reyes JF, Meyer C, Michels A, Franzke J, Molina-Diaz A, et al. Simultaneous testing of multiclass organic contaminants in food and environment by liquid chromatography/dielectric barrier discharge ionization-mass spectrometry. Analyst (Cambridge, U K). 2012;137(22):5403–10. doi:10.1039/c2an35705d.
Cegłowski M, Smoluch M, Babij M, Gotszalk T, Silberring J, Schroeder G. Dielectric barrier discharge ionization in characterization of organic compounds separated on thin-layer chromatography plates. PLoS One. 2014;9(8), e106088. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106088.
Zhang Y, Xu S, Wen L, Bai Y, Niu L, Song D, et al. Dielectric barrier discharge ionization based interface for online coupling surface plasmon resonance with mass spectrometry. Analyst (Cambridge, U K). 2016;141(11):3343–8. doi:10.1039/C6AN00561F.
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21275012 and 21527809). The authors thank Agilent Technologies for providing the mass spectrometer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Fundamental Aspects of Electromigrative Separation Techniques with guest editors Carolin Huhn and Pablo A. Kler.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 344 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ai, W., Bai, Y. et al. An interface for online coupling capillary electrophoresis to dielectric barrier discharge ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 8655–8661 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9822-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9822-3