Abstract
Tamoxifen is a mainstay in the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer and is metabolized to more than 30 different compounds. Little is known about in vivo concentrations of estrogenic metabolites E-metabolite E, Z-metabolite E, and bisphenol and their relevance for tamoxifen efficacy. Therefore, we developed a highly sensitive HPLC-ESI-MS/MS quantification method for tamoxifen metabolites bisphenol, E-metabolite E, and Z-metabolite E as well as for the sex steroid hormones estradiol, estrone, testosterone, androstenedione, and progesterone. Plasma samples were subjected to protein precipitation followed by solid phase extraction. Upon derivatization with 3-[(N-succinimide-1-yl)oxycarbonyl]-1-methylpyridinium iodide, all analytes were separated on a sub-2-μm column with a gradient of acetonitrile in water with 0.1 % of formic acid. Analytes were detected on a triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer with positive electrospray ionization in the multiple reaction monitoring mode. Our method demonstrated high sensitivity, accuracy, and precision. The lower limits of quantification were 12, 8, and 25 pM for bisphenol, E-metabolite E, and Z-metabolite E, respectively, and 4 pM for estradiol and estrogen, 50 pM for testosterone and androstenedione, and 25 pM for progesterone. The method was applied to plasma samples of postmenopausal patients taken at baseline and under tamoxifen therapy.

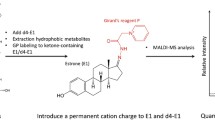
Sample preparation and derivatization for highly sensitive quantification of estrogenic tamoxifen metabolites and steroid hormones by HPLC-MS/MS



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mürdter TE, Schroth W, Bacchus-Gerybadze L, Winter S, Heinkele G, Simon W, Fasching PA, Fehm T, Eichelbaum M, Schwab M, Brauch H (2011) Activity levels of tamoxifen metabolites at the estrogen receptor and the impact of genetic polymorphisms of phase I and II enzymes on their concentration levels in plasma. Clin Pharmacol Ther 89:708–717. doi:10.1038/clpt.2011.27
Murphy CS, Langan-Fahey SM, McCague R, Jordan VC (1990) Structure-function relationships of hydroxylated metabolites of tamoxifen that control the proliferation of estrogen-responsive T47D breast cancer cells in vitro. Mol Pharmacol 38:737–743
Wiebe VJ, Osborne CK, McGuire WL, DeGregorio MW (1992) Identification of estrogenic tamoxifen metabolite(s) in tamoxifen-resistant human breast tumors. J Clin Oncol 10:990–994
Jordan VC, Fritz NF, Langan-Fahey S, Thompson M, Tormey DC (1991) Alteration of endocrine parameters in premenopausal women with breast cancer during long-term adjuvant therapy with tamoxifen as the single agent. J Natl Cancer Inst 83:1488–1491
Furr BJA, Jordan VC (1984) The pharmacology and clinical use of tamoxifen. Pharmacol Ther 25:127–205
Pasqualini JR, Chetrite G, Blacker C, Feinstein MC, Delalonde L, Talbi M, Maloche C (1996) Concentrations of estrone, estradiol, and estrone sulfate and evaluation of sulfatase and aromatase activities in pre- and postmenopausal breast cancer patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:1460–1464
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, Speizer FE (1998) Plasma sex steroid hormone levels and risk of breast cancer in post-menopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1292–1299. doi:10.1093/jnci/90.17.1292
Missmer SA, Eliassen AH, Barbieri RL, Hankinson SE (2004) Endogenous estrogen, androgen, and progesterone concentrations and breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:1856–1865. doi:10.1093/jnci/djh336
Becker KL, Bilezikian JP, Bremner WJ, Hung W (2001) Principles and practice of endocrinology and metabolism. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
Lu WJ, Xu C, Pei Z, Mayhoub AS, Cushman M, Flockhart DA (2012) The tamoxifen metabolite norendoxifen is a potent and selective inhibitor of aromatase (CYP19) and a potential lead compound for novel therapeutic agents. Breast Cancer Res Treat 133:99–109. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1699-4
Santa T (2013) Derivatization in liquid chromatography for mass spectrometric detection. Drug Discov Ther 7:9–17. doi:10.5582/ddt.2013.v7.1.9
Ke Y, Bertin J, Gonthier R, Simard J-N, Labrie F (2014) A sensitive, simple and robust LC–MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of seven androgen- and estrogen-related steroids in postmenopausal serum. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 144:523–534. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.08.015
Wang Q, Rangiah K, Mesaros C, Snyder NW, Vachani A, Song H, Blair IA (2015) Ultrasensitive quantification of serum estrogens in postmenopausal women and older men by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids 96:140–152. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2015.01.014
Yang W-C, Regnier FE, Sliva D, Adamec J (2008) Stable isotope-coded quaternization for comparative quantification of estrogen metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 870:233–240. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.06.026
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Margit Geisler and Markus König for their excellent logistic and technical support. This work has been supported by the German Research Foundation, Bonn (Grants MU 1727/2-1 and SCHR 1323/2-1), the Hans L. Merkle Foundation, Essen, and the Robert Bosch Foundation, Stuttgart, Germany.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johänning, J., Heinkele, G., Precht, J.C. et al. Highly sensitive simultaneous quantification of estrogenic tamoxifen metabolites and steroid hormones by LC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 7497–7502 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8907-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8907-8