Abstract
It is well known that gene expression is regulated at the level of individual cells, and more evidence is now emerging that heterogeneity of cell regulation is orders of magnitude greater than previously thought. In order to detect meaningful variations in transcription levels, it is necessary to measure gene expression at single cell levels rather than in bulk cells, where individual differences or heterogeneity could be lost. In this work, we report an improved reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) protocol which allows the direct measurement of gene expression in one tube (5–25 μl of total PCR mixture) at the single mammalian cell level. The protocol employs a new cell lysis buffer, and involves no RNA isolation or nested PCR steps, significantly reducing the possibility of contamination and errors. We successfully applied this protocol in qRT-PCR and linear-after-the-exponential (LATE)-PCR to analyze selected genes of various expression levels from three cell lines. Although further characterization of RNA stability is important, the preliminary results showed that gene expression heterogeneity could be common among members of genetically identical cell populations. The protocol illustrated can be utilized for a wide array of applications without much modification, such as cancer cell analysis and preimplantation genetic diagnostics. In addition, the protocol is based on intercalator-based (SYBR Green PCR) chemistry, which is less expensive and suitable for high-throughput platforms.

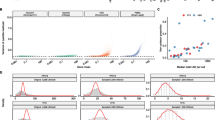
Gene expression heterogeneity in genetically identical cell population. qRT-PCR analysis of p53 transcript in HeLa cells with two negative controls in red. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of p53 transcript with 10 cells in each PCR. 10 PCR were analyzed; (B) qRT-PCR analysis of p53 transcript with 5 cells in each reaction. 8 PCR were analyzed; (C) qRT-PCR analysis of p53 transcript with single cell in each reaction tube. 9 reactions were analyzed; and (D) Statistical analysis on Ct values from panel A, B, and C above. The final total volume is 25 μl for all PCR analysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eddinger TG, Meer DP (1997) Comp Biochem Physiol 117B:29–38
Lidstrom ME, Meldrum DR (2003) Nat Rev Microbiol 1:158–164
Jensen KB, Watt FM (2006) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11958–11963
Ross IL, Browne CM, Hume DA (1994) Immunol Cell Biol 72:177–185
Elowitz MB, Levine AJ, Siggia ED, Swain PS (2002) Science 297:1183–1186
Blake WJ, Kaern M, Cantor CR, Collins JJ (2003) Nature 422:633–637
Cai L, Friedman N, Xie XS (2006) Nature 440:358–362
Maheshri N, O’Shea EK (2007) Ann Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 36:413–434
Raj A, Peskin CS, Tranchina D, Vargas DY, Tyagi S (2006) PLoS Biol 4:e309
Esumi S, Kaneko R, Kawamura Y, Yagi T (2006) Nat Protoc 1:2143–2151
Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M, Forootan A, Jonak J, Lind K, Sindelka R, Sjöback R, Sjögreen B, Strömbom L, Ståhlberg A, Zoric N (2006) Mol Aspects Med 27:95–125
Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA (2006) Nat Protoc 1:1559–1582
Hartshorn C, Eckert J, Hartung O, Wangh L (2007) BMC Biotechnol 7:87
Lindqvist N, Vidal-Sanz M, Hallbook F (2002) Brain Res Protoc 10:75–83
Wacker MJ, Tehel MM, Gallagher PM (2008) J Appl Physiol 105:308–315
Eberwine J, Yeh H, Miyashiro K, Cao Y, Nair S, Finnell R, Zettel M, Coleman P (1992) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3010–3014
Christensen KV, Lambert DWM, JDC EJ (2000) NeuroReport 11:3577–3582
Esumi S, Wu SX, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Sugimoto Y, Tamamaki N (2008) Neurosci Res 60:439–451
Faumont N, Saati TA, Brousset P, Offer C, Delson G, Meggetto F (2001) J Gen Virol 82:1169–1174
Miragi T, Murakami K, Sawada T, Taguchi H, Miyoshi I (1998) Leukemia 12:1645–1650
Liss B (2002) Nucleic Acids Res 30:e89
Yan L, Kaczorowski G, Kohler M (2002) Anal Biochem 304:267–270
Vrettou C, Traeger-Synodinos J, Tzetis M, Palmer G, Sofocleous C, Kanavakis E (2004) Hum Mutat 23:513–521
Peixoto A, Monteiro M, Rocha B, Veiga-Fernandes H (2004) Genome Res 14:1938–1947
Taniguchi K, Kajiyama T, Kambara H (2009) Nat Meth 6:503–506
Szöllős E, Hellgren O, Hasselquis D (2008) J Parasitol 94:562–564
Polanca-Wessels MC, Barrett MT, Galipeau PC, Rohrer KL, Reid BJ, Rabinovitch PS (1998) Gastroenterology 114:295–304
Palanca-Wessels MCA, Klingelhutz A, Reid BJ, Norwood TH, Opheim KF (2003) Carcinogenesis 24:1183–1190
Anis YH, Holl MR, Meldrum DR (2008) Automated vision-based selection and placement of single cells in microwell array formats. In: Proc 4th IEEE Conf Automation Science and Engineering, Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 Aug 2008, p 315
Sanchez JA, Pierce KE, Rice JE, Wangh LJ (2004) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1933–1938
Pierce KE, Sanchez JA, Rice JE, Wangh LJ (2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8609–8614
Hartshorn C, Anshelevich A, Wangh LJ (2005) BMC Biotechnol 5:2
Salk JJ, Sanchez JA, Peirce KE, Rice JE, Soares KC, Wangh LJ (2006) Anal Biochem 353:124–132
Phillips JK, Lipski J (2000) Auton Neurosci 86:1–12
McGuire S, Fisher C, Holl MR, Meldrum DR (2008) Rev Sci Instrum 79:086111
Nandakumar V, Holl MR, Meldrum DR (2008) A flexible framework for automation of single cell and cell-to-cell interaction analyses. In: Proc 4th IEEE Conf Automation Science and Engineering, Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 Aug 2008, p 424
Chao SH, Meldrum DR (2009) Lab Chip 9:867–869
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Drs. L. Wangh and A. Sanchez from Brandies University for their help with LATE-PCR technology. We would also like to thank Dr. B. Reid for kindly supplying the CP-C cells. Dr. Y. Anis is acknowledged for his help with single-cell loading. This work was supported by a CEGS Microscale Life Science Center (MLSC) project (Grant #: p50-HG002360) from NIH, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Thompson, H., Hemphill, C. et al. An improved one-tube RT-PCR protocol for analyzing single-cell gene expression in individual mammalian cells. Anal Bioanal Chem 397, 1853–1859 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3754-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3754-0